Introduction
Radiation oncology has seen significant advancements in recent decades, driven by the introduction of several innovative technologies. These include intensity-modulated radiation therapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, stereotactic body radiation therapy, image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), and respiratory beam control. These technologies have increased the precision of treatments [1], reduced side effects [2,3], and improved patient outcomes [4–6]. Furthermore, the advent of various imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, and PET scans, coupled with significant developments in computational resources, has greatly expanded the capabilities of radiation oncology. These imaging modalities provide complementary information: CT scans deliver detailed anatomical information, MRI offers exceptional soft tissue contrast, and PET scans provide metabolic insights into tumors. By integrating these modalities, radiation oncologists can achieve more accurate tumor localization, more precise treatment planning, and better treatment adaptation, thereby further improving patient care and outcomes.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy enables the modulation of radiation beams to conform more precisely to the shape of the tumor, thereby protecting surrounding healthy tissues and reducing complications [7–9]. However, this technique requires meticulous treatment planning and the implementation of rigorous quality assurance protocols, which can be challenging [10,11]. Stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy administer high doses of radiation with sub-millimeter accuracy to treat small, well-defined tumors in the brain and body, respectively. The primary challenge in these therapies is managing patient movement and ensuring accurate targeting. These issues can be addressed using advanced imaging technologies and motion management techniques [12,13]. IGRT employs advanced imaging technologies to enhance the precision of radiation delivery by compensating for patient movement and anatomical changes during treatment [14]. The advantage of IGRT is its ability to adapt treatment in real-time. However, challenges include integrating imaging and treatment systems and maintaining consistent image quality [15]. Respiratory gating aligns radiation delivery with the patient's breathing cycle, minimizing exposure to moving organs such as the lungs and liver. The main challenges associated with respiratory gating include the need for advanced equipment and software, as well as requiring patient cooperation [16].
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into radiation oncology is becoming increasingly important due to various social and healthcare trends [17]. The global population is aging, which leads to a higher incidence of cancer in older age groups. As life expectancy increases, so does the demand for effective and efficient cancer treatments, placing significant burdens on healthcare systems worldwide [18]. To manage the increasing patient load effectively, it is essential to adopt advanced technologies [19].
Moreover, healthcare systems are under pressure to improve patient outcomes while controlling costs [20]. AI has the potential to meet these challenges by improving the accuracy of radiation therapy, shortening treatment durations, and reducing side effects. This can result in better resource utilization and heightened patient satisfaction [21]. Additionally, AI supports personalized medicine by offering treatments customized to the unique characteristics of each patient. By analyzing extensive datasets from diverse sources, AI can assist in creating more effective treatment plans that are specifically tailored to the genetic, phenotypic, and lifestyle factors of individual patients [22,23].
The necessity and justification for AI in radiation oncology extend beyond these practical improvements. The complexity and variability inherent in cancer treatments require sophisticated decision-making tools capable of analyzing vast amounts of data in real time—capabilities that surpass human limits. AI excels in integrating and interpreting multi-dimensional data from various imaging modalities and patient records, significantly enhancing clinical decision-making. This reduces errors and improves treatment outcomes. Additionally, AI supports continuous learning and adaptation in treatment protocols, allowing them to evolve with new medical insights and tailored to individual patient responses. Therefore, the integration of AI not only enhances efficiency but also elevates the standard of personalized patient care, rendering it an essential component in contemporary radiation oncology.
Ethics statement
As this study is a literature review, it did not require institutional review board approval or individual consent.
Opportunities for artificial intelligence integration
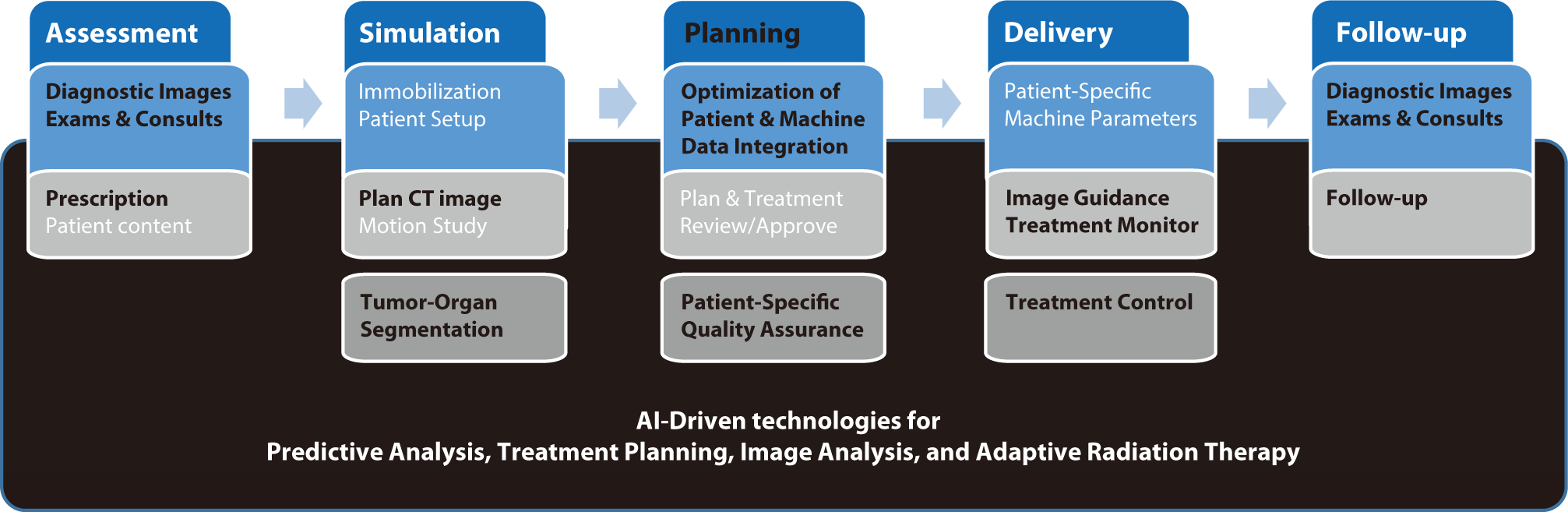
AI offers significant opportunities in various facets of radiation oncology, such as treatment planning, image analysis, adaptive radiation therapy (ART), and predictive analytics. In these domains, AI can enhance clinical workflows, shorten treatment durations, and deliver more personalized and effective treatments.
AI can optimize radiation treatment planning by automating complex tasks, reducing planning time, and enhancing accuracy [24]. Machine learning algorithms can analyze extensive datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters, potentially leading to personalized treatment plans that maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects [25]. Over the past few decades, AI has been progressively integrated into radiation treatment planning. Initially, simple rule-based systems supported clinical decision-making. As computational power and data availability have increased, more sophisticated machine learning algorithms, including artificial neural networks, have been developed. These algorithms, which initially supported basic tasks, have now evolved to handle complex treatment planning scenarios. Current research in AI for radiation treatment planning focuses on developing algorithms that can analyze large datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters. Machine learning models are trained using historical treatment data, patient outcomes, and imaging data to enhance the precision and accuracy of treatment plans [26]. Studies have demonstrated that AI can significantly reduce the time required for planning while maintaining or improving the quality of the plans. Research is also exploring how to integrate AI with ART to continuously update treatment plans based on real-time patient data [27]. The automated generation of radiation fluence is a critical component of treatment planning, determining the intensity and distribution of radiation beams to achieve the desired dose distribution within the target area while sparing healthy tissues. AI has played a crucial role in improving the accuracy and efficiency of fluence map optimization. Deep learning techniques can predict optimal fluence patterns based on patient-specific anatomical and dosimetric data, reducing the complexity and time required for manual adjustments [28,29].
Several commercial products have incorporated AI into radiation treatment planning. For example, Varian's Ethos Therapy [30,31] and Elekta's MOSAIQ Plaza [32] utilize AI to improve treatment planning and adaptive therapy. These systems automate aspects of the planning process, optimize dose distribution, and adjust treatment plans in response to anatomical changes or variations in tumor size during treatment.
AI-driven image analysis can significantly enhance the accuracy of tumor detection and segmentation [33]. Deep learning algorithms are capable of processing imaging data from various modalities, including CT, MRI, and PET scans, to provide precise tumor delineation, which is crucial for effective radiation targeting [34,35]. The journey of AI-based image analysis in radiation oncology is marked by significant milestones. Initially, basic image processing techniques were employed to improve image quality and enhance tumor visualization. With the advent of machine learning, more advanced algorithms were developed to automate tumor detection and segmentation tasks. Early methodologies heavily relied on handcrafted features, but they were soon surpassed by deep learning algorithms capable of autonomously learning features from data [36]. Current research in AI-based image analysis focuses on increasing the precision and efficiency of tumor detection and segmentation [37,38]. Deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks, are widely used to analyze imaging data from CT, MRI, and PET scans [39]. These models have demonstrated an exceptional ability to distinguish tumors from adjacent healthy tissues, often surpassing the accuracy and consistency of human experts [40]. Additionally, research in multimodal image analysis indicates that AI can combine data from various imaging modalities to enhance diagnostic accuracy and inform treatment planning [41].
The segmentation of tumors and surrounding normal organs is a critical task in radiation therapy, requiring accurate delineation of tumor boundaries and normal tissues to ensure effective treatment planning [42]. Manual segmentation is traditionally labor-intensive and prone to inter-observer variability. However, AI-based segmentation techniques streamline this process, providing consistent and rapid results. Advanced algorithms, such as U-Net and its variants, have become the standard for medical image segmentation, known for their ability to accurately identify tumor boundaries [43]. These models utilize an encoder-decoder architecture to capture the complex spatial hierarchies within images, ensuring precise segmentation. Commercial applications of AI-based image analysis in radiation oncology are already making an impact. For example, IBM Watson for Oncology leverages AI to analyze medical images and provide insights for treatment planning [44]. Similarly, Varian's ARIA oncology information system integrates AI to enhance treatment planning and execution [45]. Siemens Healthineers also offers AI-based tools for advanced image analysis and interpretation within its syngo.via platform [46].
In ART, treatment plans are adjusted based on changes in patient anatomy and tumor size throughout the course of treatment. AI improves ART by swiftly analyzing imaging data and making real-time adjustments to the treatment plan, thus increasing the accuracy and effectiveness of the treatment. The concept of ART has significantly evolved over the past few decades. Initially, radiation treatment plans were static and did not accommodate anatomical changes during the treatment course. As technology progressed, the necessity for more adaptive approaches became apparent, leading to the development of ART [47]. Early implementations of ART involved periodic imaging and manual adjustments, which were time-consuming and could not be performed in real-time. Current research and development in ART focus on utilizing AI to automate and improve the adaptability of treatment plans [48]. AI-based ART systems employ advanced imaging technologies, such as daily cone-beam CT scans, to monitor tumor size and anatomical changes in patients. Machine learning algorithms then analyze these imaging data to predict anatomical changes and adjust radiation dose distributions accordingly. This capability for real-time adaptation ensures that radiation doses are precisely targeted to the tumor, minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues and enhancing overall treatment outcomes [49–51].
Several commercial products have integrated AI to improve ART. Notably, Varian's Ethos Therapy system and Elekta's Unity system stand out. Varian's Ethos utilizes AI to analyze daily imaging and dynamically adjust treatment plans, offering personalized therapy for each session [49]. Similarly, Elekta's Unity combines a high-field MRI scanner with a linear accelerator to provide real-time imaging and adaptation during treatment sessions [52]. These systems mark significant progress in the field of commercial ART, facilitating more accessible and practical real-time adaptive therapy. As we look to the future, ART is poised to continue its evolution through the further integration of AI and advanced imaging technologies.
AI can analyze historical patient data to predict treatment outcomes and potential complications. Predictive analytics can guide clinical decision-making, allowing for more informed and personalized treatment strategies [53,54]. The application of predictive analytics in radiation oncology has advanced significantly over the years. Initially, treatment decisions were primarily based on empirical data and clinical experience. With the advent of data collection and storage technologies, large databases became available, enabling the identification of patterns and correlations through statistical methods. However, traditional methods were limited in handling complex, high-dimensional data. Current predictive analytics research focuses on leveraging AI to analyze large-scale historical patient data [55]. Machine learning algorithms, including deep learning and ensemble methods, are used to predict various clinical outcomes, including tumor response, survival rates, and potential side effects. These models process diverse data types, including demographic information, genetic profiles, imaging data, and treatment histories, to provide comprehensive predictions. Studies have shown that AI-based predictive models can outperform traditional statistical methods in terms of accuracy and robustness [56].
Several commercial products have integrated AI-based predictive analytics to support clinical decision-making in radiation oncology. For instance, IBM Watson for Oncology utilizes AI to analyze patient data and provide evidence-based treatment recommendations [57]. Similarly, the RayStation treatment planning system employs machine learning models to predict patient-specific treatment outcomes and optimize treatment plans [58]. Looking ahead, predictive analytics is poised to revolutionize clinical practice in radiation oncology. Researchers are focusing on improving the interpretability of AI models, which will enable clinicians to better understand and trust their predictions. Furthermore, the integration of predictive analytics with other AI-based technologies, such as image analysis and ART, is expected to streamline treatment workflows and improve efficiency. The adoption of federated learning, which allows AI models to be trained on data from multiple institutions without the need to share patient data, is anticipated to improve the generalizability and reliability of predictive models. The elements discussed in the "Opportunities for AI Integration" section are depicted in Fig. 1.
Challenges in artificial intelligence integration
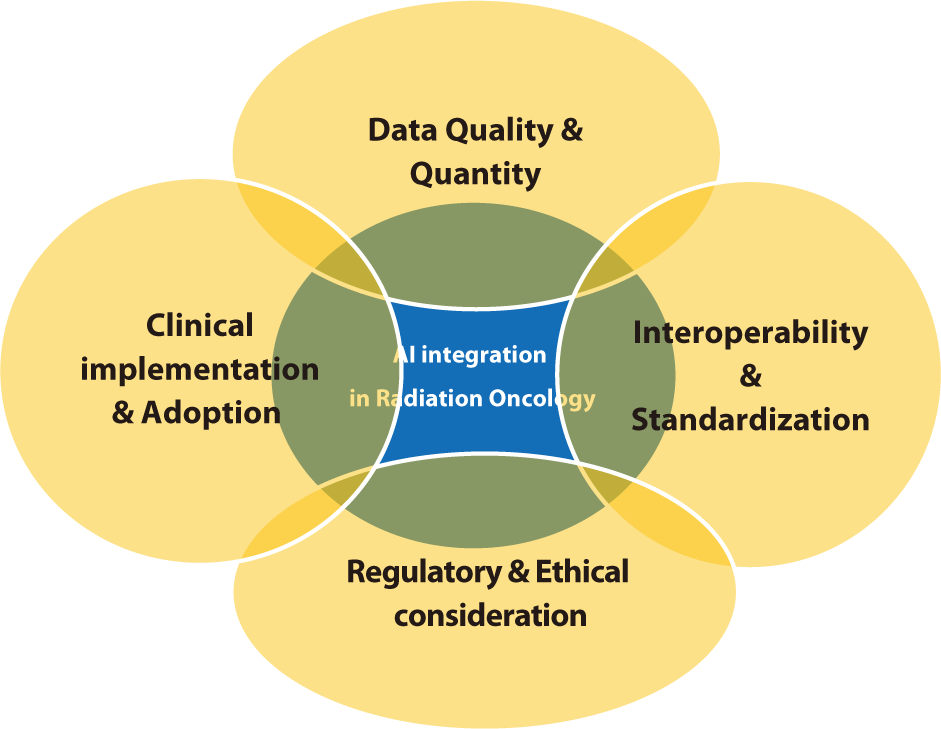
Integrating AI into radiation oncology involves multiple challenges that need to be addressed to fully harness its potential. These challenges encompass technical, clinical, and ethical aspects, necessitating collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and policymakers.
The effectiveness of AI models is heavily influenced by the quality and quantity of the data used for training [59–61]. Challenges such as inconsistent data quality, missing data, and limited access to large annotated datasets are significant obstacles [62]. AI algorithms depend on robust datasets that accurately reflect diverse patient populations and clinical scenarios. However, acquiring such datasets is often challenging due to privacy concerns, variations in data collection protocols, and the absence of standardized data formats. Research has indicated that biases in training data can result in AI models that fail to generalize effectively across different patient groups. It is crucial to ensure data quality and to develop techniques for managing missing or incomplete data to build dependable AI systems. Moreover, large datasets from multiple institutions are necessary to train models that are effective in various clinical environments. Collaborative initiatives to share data while safeguarding patient privacy are vital for the progress of AI in radiation oncology [63].
Radiation oncology systems frequently utilize various software and data formats, which can lead to interoperability issues [64]. To facilitate the seamless integration of AI tools across different platforms and institutions, it is crucial to standardize data formats and protocols [65]. The lack of interoperability may impede the efficient deployment of AI technologies, as it poses challenges in integrating and analyzing data from disparate systems. These interoperability challenges are further exacerbated by the use of diverse imaging modalities, treatment planning systems, and electronic health records in radiation oncology. Developing common data standards, such as Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM), is essential for enabling data exchange and integration [66,67]. Encouraging the widespread adoption of these standards throughout the industry will help surmount obstacles to AI implementation and enhance the effectiveness of AI tools in clinical settings.
Integrating AI into radiation oncology introduces several regulatory and ethical challenges, including concerns about patient privacy [68], data security, and the necessity for rigorous validation of AI models. Regulatory frameworks need to adapt to address these issues and ensure AI is used safely and effectively in clinical settings. Current regulations may not adequately capture the complexities of AI technologies, necessitating updates to existing guidelines and the creation of new standards. Ethical considerations are also paramount in the integration of AI [69–71]. It is crucial to obtain patient consent and safeguard data privacy, particularly when handling sensitive health information. Additionally, the potential for AI to reinforce existing biases in healthcare must be addressed, as biased algorithms could worsen health disparities. Developing AI models that are transparent and explainable will foster trust between clinicians and patients, facilitating their understanding and acceptance of AI-driven decisions.
Adopting AI tools in clinical settings necessitates significant changes in workflows and staff training. Resistance to change and skepticism regarding the reliability of AI can impede adoption [72]. It is crucial to implement comprehensive training programs and clearly communicate the benefits of AI to overcome these barriers. Research indicates that involving clinicians in the development and implementation of AI tools is essential for meeting clinical needs and ensuring seamless integration into existing workflows [73–75]. Providing ongoing education and support for healthcare professionals can foster trust in AI technologies and promote their adoption. Demonstrating the clinical and economic advantages of AI through pilot studies and real-world applications can also secure support from stakeholders. The issues discussed in the section "Challenges in AI Integration" are illustrated in Fig. 2.
Future directions
The future of AI in radiation oncology promises significant transformations in patient care. As AI technologies advance, several critical areas are poised to propel progress within the field. These areas encompass the creation of more advanced AI models, the integration of AI with other emerging technologies, the development of stringent standards and regulations, and a focus on collaborative and multidisciplinary approaches.
Future AI development will concentrate on creating more sophisticated models that can manage complex, high-dimensional data [76]. Advances in deep learning and reinforcement learning will enable the creation of models capable of predicting treatment outcomes with greater accuracy and adapting to new data in real time. These models will benefit from the ongoing expansion of available data, including multimodal datasets that integrate imaging, genomics, and clinical information. These comprehensive datasets will enable the development of personalized treatment plans specifically tailored to individual patients [77,78].
The integration of AI with other emerging technologies, such as radiomics, genomics, and wearable health devices, is expected to revolutionize radiation oncology [77]. Radiomics extracts a large number of features from medical images, which AI then uses to predict disease progression and treatment responses. Genomics offers insights into the genetic makeup of tumors, facilitating more targeted and effective treatments [79]. Wearable health devices continuously monitor patients' health indicators, supplying data that enables AI to dynamically adjust treatment plans in real-time [80].
To fully realize the potential of AI in radiation oncology, it is crucial to standardize and ensure interoperability across systems and institutions. The development and adoption of common data standards, such as DICOM, will facilitate the exchange and integration of data [81,82]. Additionally, it is essential to establish standardized protocols for the development, validation, and deployment of AI models to ensure that these tools are safe, reliable, and effective [83]. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is also working to establish standards that ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of AI in medical devices [84].
Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is essential for advancing AI in radiation oncology [76,85]. Multidisciplinary teams can leverage diverse expertise to create AI tools that address clinical needs and integrate smoothly into current workflows [86]. Collaborative research initiatives and shared databases facilitate the pooling of data and resources, which accelerates the development of robust AI models [82]. Promoting open science and data sharing while ensuring patient privacy will foster innovation and advance the field [87].
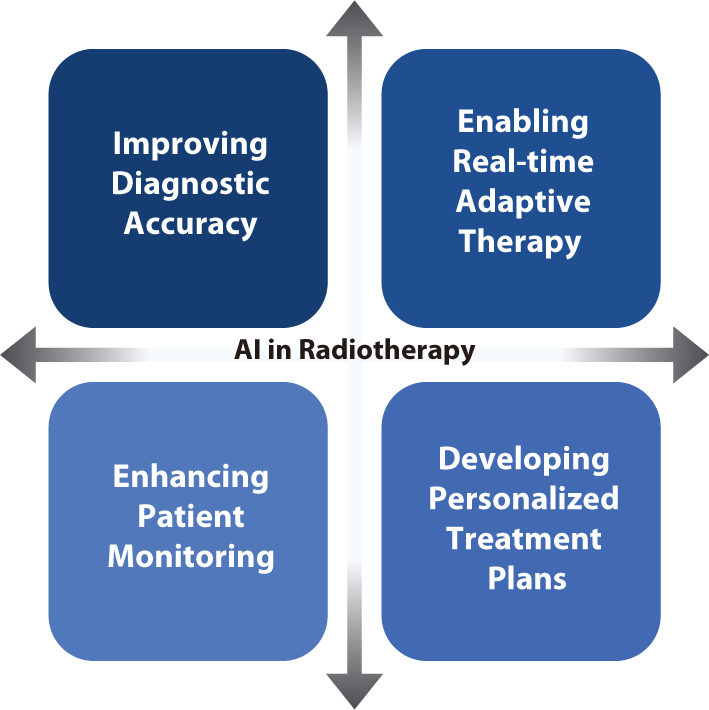
Developing explainable AI models is crucial for fostering trust between clinicians and patients [88]. Explainable AI offers insights into the decision-making processes of AI algorithms, thereby facilitating clinicians' understanding and validation of AI-based recommendations [89]. Increasing the transparency of AI systems will address concerns about bias and errors, ultimately encouraging the adoption of AI technologies in clinical settings [90,91]. AI has the potential to significantly improve the quality of clinical care while increasing efficiency. For instance, studies have demonstrated that AI can reduce the time needed for treatment planning and image analysis, allowing clinicians to devote more attention to patient care [92,93]. AI-based predictive analytics can identify patients at high risk of complications, enabling proactive interventions that improve outcomes [94,95]. Moreover, AI's capacity to continuously learn and adapt from new data ensures that treatment strategies are consistently updated with the latest medical knowledge and technological advancements [96]. In clinical settings, AI technologies have the potential to drive several key advancements in radiation oncology. These advancements include improving diagnostic accuracy, enabling real-time adaptive therapy, enhancing patient monitoring, and developing personalized treatment plans, all of which contribute to better patient outcomes and operational efficiencies [97–101].
Improving diagnostic accuracy: AI-based image analysis increasing the accuracy of tumor detection and segmentation, thereby improving the precision of radiation targeting. This increased precision minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues and increases treatment efficacy.
Enabling real-time adaptive therapy: AI rapidly analyzes daily imaging data and adjusts treatment plans in real time, enhancing the effectiveness of ART. This capability ensures that radiation doses are precisely targeted to the tumor, accommodating anatomical changes or variations in tumor size throughout the treatment course.
Enhancing patient monitoring: Wearable health devices coupled with AI analytics enable continuous monitoring of patients' health indicators. This allows timely interventions when adverse changes are detected. Such a predictive approach aids in managing side effects and enhances overall treatment outcomes.
Developing personalized treatment plans: AI analyzes extensive datasets to identify patterns and predict individual responses to different treatment modalities. This capability allows clinicians to create treatment plans that are tailored to each patient's unique genetic and clinical profile, thereby maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Looking ahead, integrating AI into clinical practice in radiation oncology necessitates careful consideration of ethical, regulatory, and practical issues. However, the potential benefits, such as improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies, make it a worthwhile endeavor. Collaborative efforts among multidisciplinary teams, the establishment of robust standards, and the continued advancement of AI technologies will shape the future of radiation oncology, ultimately transforming patient care. The themes explored in the "Future Directions" section are visualized in Fig. 3.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into radiation oncology offers significant opportunities to enhance the precision, efficiency, and outcomes of treatments. As AI technologies continue to advance, their potential to transform various aspects of radiation therapy becomes increasingly apparent. This review has highlighted key areas where AI can make substantial contributions, including treatment planning, image analysis, ART, and predictive analytics. Each area showcases AI's ability to improve clinical workflows, shorten treatment times, and deliver more personalized and effective treatments.
Despite these promising advancements, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential of AI in radiation oncology. Data quality and quantity are critical issues because robust and comprehensive datasets are necessary for effective AI models. Ensuring interoperability and standardization across different systems and institutions is also essential to facilitate seamless integration and data exchange. Additionally, regulatory and ethical considerations must be carefully addressed to protect patient privacy and ensure the safe deployment of AI technologies in clinical environments.
Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is essential for overcoming these challenges. By forming multidisciplinary teams, diverse expertise can be harnessed to create AI tools that not only meet clinical needs but also integrate seamlessly into existing workflows. Initiatives that promote collaborative research and shared databases will facilitate the pooling of data and resources, thereby accelerating the development of robust AI models. Encouraging open science and data sharing, while simultaneously protecting patient privacy, will drive innovation and advance the field. Moreover, the development of explainable AI models is crucial for promoting trust between clinicians and patients. Explainable AI offers insights into the decision-making processes of AI algorithms, enabling clinicians to more easily understand and validate AI-based recommendations. Increasing the transparency of AI systems will address concerns about bias and errors, ultimately encouraging the adoption of AI technologies in clinical practice.
The future of AI in radiation oncology is bright, and ongoing research and development are poised to overcome current challenges and unlock new opportunities. AI-driven improvements in diagnostic accuracy, real-time adaptive therapy, patient monitoring, and personalized treatment plans are poised to revolutionize the field, enhancing patient care and operational efficiencies. By emphasizing collaborative research, continuous learning, and patient-centric approaches, the field can surmount these challenges and realize transformative advancements in radiation therapy.
