Introduction
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are commonly encountered in outpatient clinics. The major STIs primarily addressed in both domestic and international treatment guidelines include syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection [1–4]. Recently, the incidence and significance of Mycoplasma genitalium have been on the rise [5]. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly affected access to healthcare services, thereby altering the epidemiology of major STIs. It has notably impacted access to HIV services, influencing transmission rates [6,7]. Additionally, there has been a decline in the incidence of new HIV cases in Korea after COVID-19 [8]. Some studies suggest that this reflects a genuine reduction in incidence rates [8]. The impact on other STIs within the country remains unclear.
This review focuses on syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, M. genitalium, and HSV. While genital warts or condyloma acuminata are also prevalent STIs [9], they will be addressed separately at a later date.
Ethics statement
As this study is a literature review, it did not require institutional review board approval or individual consent.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a disease that has been known for centuries, with documented cases appearing in European and various other countries' records from the 11th to 15th centuries [10]. Historical documents from the Joseon Dynasty in Korea also contain references to syphilis.
In Korea, syphilis is classified under the Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act as both a Category 4 communicable disease (Article 2, Item 5) and a STI (Item 10). It is monitored alongside six other STIs—gonorrhea, chlamydia infection, chancroid, genital herpes, condyloma acuminatum, and human papillomavirus infection—through designated sentinel surveillance institutions. However, starting in 2024, it has been reclassified as a nationally notifiable infectious disease (category 2 communicable disease), and data on its occurrence will be collected once again [11]. The surveillance system for syphilis has seen several changes over the years. Initially introduced in 2001, the sentinel surveillance system managed syphilis until 2010. It then transitioned to full-scale surveillance following a reorganization of the legal classification system for infectious diseases in 2010, only to revert to sentinel surveillance in 2020.
The prevalence of syphilis in Korea from 2017 to 2020 is detailed below. In 2019, comprehensive surveillance identified 1,750 syphilis cases, with 1,276 cases (72.9%) occurring in males and 474 cases (27.1%) in females. The age group of 20–40 years had the highest incidence, with 1,281 cases (73.2%), while those aged 60 and older accounted for 192 cases (11.0%). Regarding the stage of the disease, there were 1,176 cases of primary syphilis, 554 cases of secondary syphilis, and 23 cases of congenital syphilis. After shifting to sentinel surveillance in 2020, a total of 330 cases were reported, comprising 228 cases (69.1%) in males and 102 cases (30.9%) in females. The 20–40 age group represented 251 cases (76.1%), and the 60 and older age group had 30 cases (9.1%). The breakdown by stage included 191 cases of primary syphilis, 136 cases of secondary syphilis, and 3 cases of congenital syphilis. These data were sourced from the Weekly Health and Disease Report of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Since the transition to sentinel surveillance in 2021, there has been a noticeable change in the number of reported cases. From 2020 to 2023, the reported cases of primary syphilis were 191, 248, 254, and 280, respectively, while secondary syphilis cases were 136, 140, 138, and 131 for the same years (Fig. 1). Starting in 2024, with the resumption of full-scale surveillance, it will be possible to compare these figures with previous data. Fig. 1 also presents a detailed breakdown of the number of cases for each stage of syphilis.
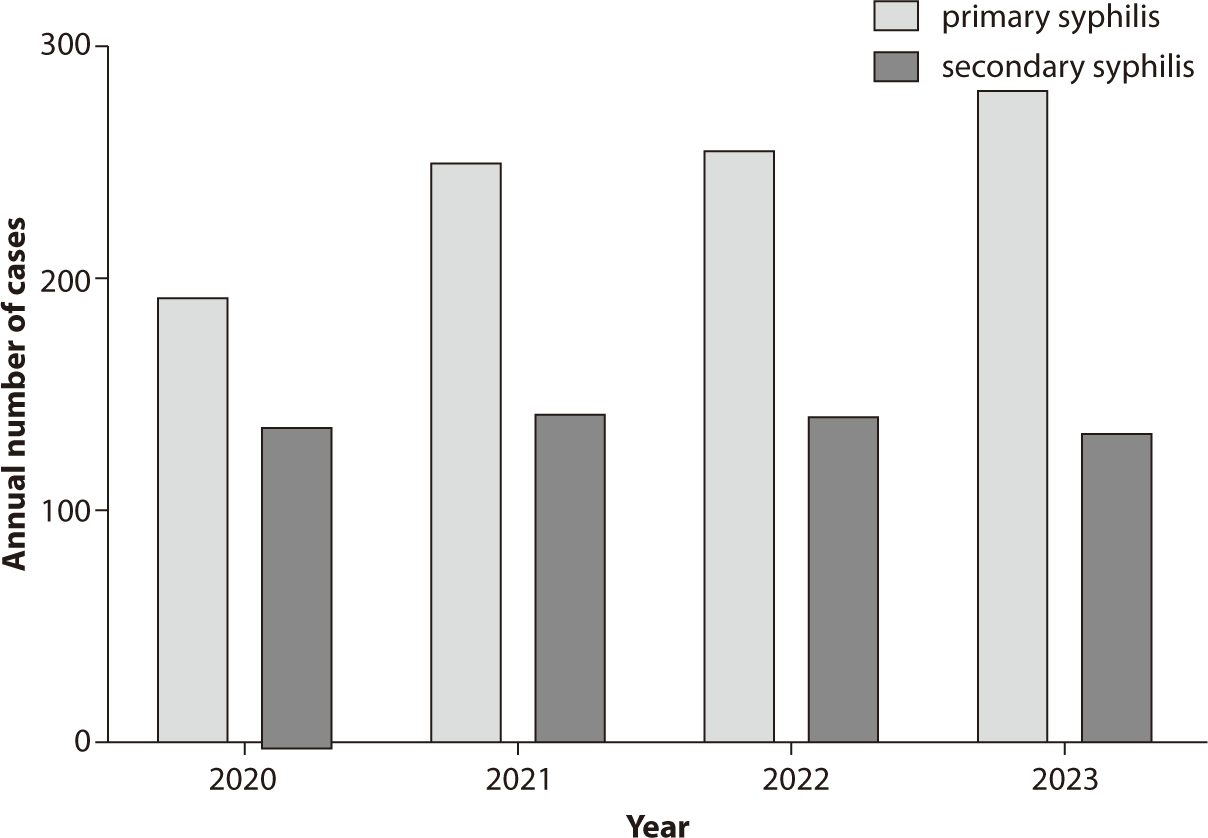
Syphilis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact or from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy. This disease is caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Although less common, transmission can also occur through blood transfusions or organ transplants. Additionally, there is a minimal risk of transmission through needlestick injuries in certain stages of the disease [12].
The clinical presentation of syphilis can be broadly divided into symptomatic periods and asymptomatic latent syphilis periods. The clinical course of syphilis is categorized into symptomatic phases and periods of asymptomatic latent syphilis. The symptomatic stages include primary, secondary, and tertiary syphilis, with periods of latent syphilis occurring between these stages. Primary syphilis, the initial stage of infection, typically presents as a single painless ulcer, known as a chancre, at the site of T. pallidum entry. This sore usually appears within 9 to 90 days after exposure and may be accompanied by localized swelling of lymph nodes. While the ulcer is generally painless, it can occasionally be painful. The ulcer characteristic of primary syphilis typically heals spontaneously.
Secondary syphilis typically develops 4–10 weeks after the appearance of the primary lesion and can affect the entire body. The symptoms of secondary syphilis are diverse, with a characteristic rash being a common feature. This rash, frequently involving the palms and soles, is observed in 48%–70% of patients with secondary syphilis. Other manifestations may include abdominal pain, hepatitis, pulmonary nodules, and alopecia. Additionally, condyloma lata, presenting as wart-like lesions, may also occur. Although many patients receive treatment during the secondary stage, the condition might resolve on its own without antibiotics; however, if left untreated, it can progress to latent syphilis. During this stage, the bacteria may infiltrate the central nervous system, potentially leading to meningitis. Approximately 70% of cases of untreated or latent syphilis remain symptom-free, but some may advance to tertiary syphilis. Tertiary syphilis can involve cardiovascular syphilis, neurosyphilis, and gummatous syphilis. Neurosyphilis is divided into two primary forms: meningeal neurosyphilis, which can present with cranial nerve dysfunction, meningitis, stroke, and changes in hearing or vision, and tabes dorsalis, characterized by demyelination of the dorsal columns and associated with ataxia, diminished reflexes, impaired proprioception, neuropathic pain, and paralysis. Typically, neurosyphilis develops 10–30 years after the initial infection [13].
Diagnosing syphilis is complex. The most definitive method involves direct evidence of the syphilis bacterium. However, because Treponema is difficult to culture, a culture-based diagnosis is not feasible. Although dark-field microscopy can visualize Treponema from lesion samples, this method is rarely used today. In cases of primary syphilis, samples from chancres can be tested using PCR or other nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) to detect Treponema. Additionally, multiplex PCR tests, which diagnose multiple STIs simultaneously, can also detect syphilis from urine samples.
However, in cases of secondary, tertiary, and latent syphilis, it is not feasible to obtain samples that confirm the presence of the pathogen. Therefore, the diagnosis relies on a combination of tests. For initial screening, non-treponemal tests such as the Venereal Disease Research Laboratories test or the rapid plasma reagin test are employed. If these tests yield positive results, confirmation is sought through treponemal tests, including the T. pallidum latex agglutination, T. pallidum hemagglutination assay, or the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption immunoglobulin test.
Both the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2021 treatment guidelines and Korea's 2023 treatment guidelines recommend the same treatment [2]. Penicillin injections are the first-line treatment for syphilis at all stages [14]. Benzathine penicillin G is the drug of choice for all cases except neurosyphilis. Thanks to its depot effect, it can be administered once a week. Benzathine penicillin G must be given intramuscularly, not intravenously. For primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis, a single dose of 2.4 million units of benzathine penicillin G is administered. For late latent syphilis, 2.4 million units are administered weekly for three weeks. Alternatively, doxycycline 100 mg taken twice daily for 14–28 days can be used, but it is contraindicated during pregnancy, where penicillin is the only option.
A characteristic reaction known as the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may occur following the treatment of spirochetal infections, including syphilis [15]. This inflammatory response is triggered by the release of cytokines and typically manifests within 24 hours of treatment, presenting symptoms such as myalgia and fever.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, similar to syphilis, is one of the oldest known STIs. The systematic recording and management of gonorrhea in Korea commenced during the Japanese colonial period and persisted through the American military government period following liberation. Since that time, reports on domestic prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility have been published [16].
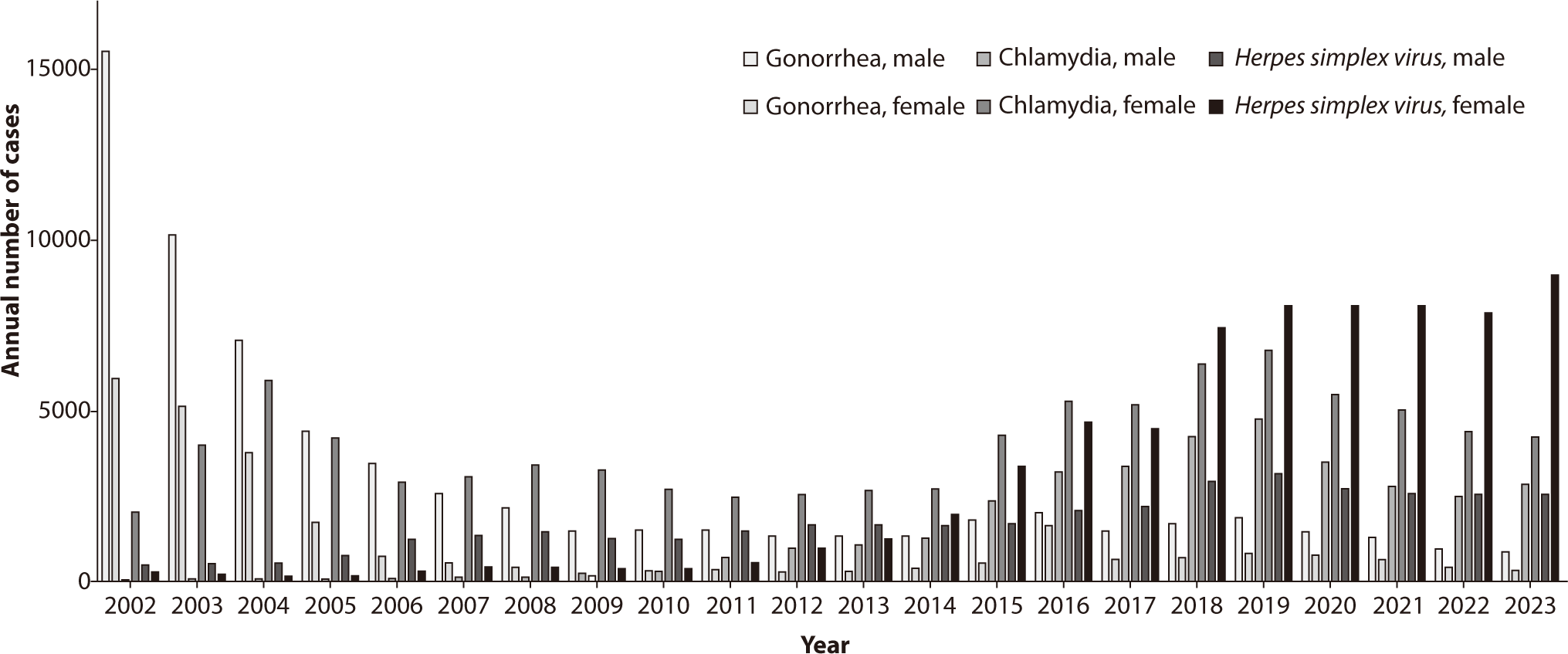
The annual incidence of gonorrhea in Korea is shown in Figs. 2, 3. In 2023, sentinel surveillance reported 1,204 cases of gonorrhea, indicating a decreasing trend in its incidence. A particularly concerning issue is the antibiotic resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacterium responsible for gonorrhea. There has been a significant global increase in resistance to fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, and a rising trend in resistance to azithromycin [17]. Additionally, strains resistant to ceftriaxone, considered a last-resort treatment for gonorrhea, have recently been identified, particularly in countries such as the United Kingdom and Japan. Extensively drug-resistant N. gonorrhoeae has also emerged, leading to treatment failures with the combined therapy of ceftriaxone and azithromycin [18–20]. In Korea, the antibiotic resistance rates of N. gonorrhoeae have shown concerning trends: resistance to ciprofloxacin increased from 26% in 2000 to 83% in 2006 among strains collected during that period. During the same timeframe, no resistance to ceftriaxone or cefixime was reported. Resistance to tetracycline was noted to be between 93%–100% [21]. From data collected between 2011 and 2013, 3% of the strains were resistant to ceftriaxone, 9% to cefixime, 38% showed intermediate resistance or resistance to azithromycin, and 97% were resistant to ciprofloxacin [22]. Antibiotic resistance testing on N. gonorrhoeae conducted by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention from 2013 to 2015 indicated that almost no strains were susceptible to ciprofloxacin and tetracycline. While susceptibility to ceftriaxone and cefixime was still maintained, resistance to cefixime showed an increasing trend. Furthermore, there was an upward trend in the number of strains exhibiting simultaneous resistance to multiple antibiotics from 2013 to 2015.
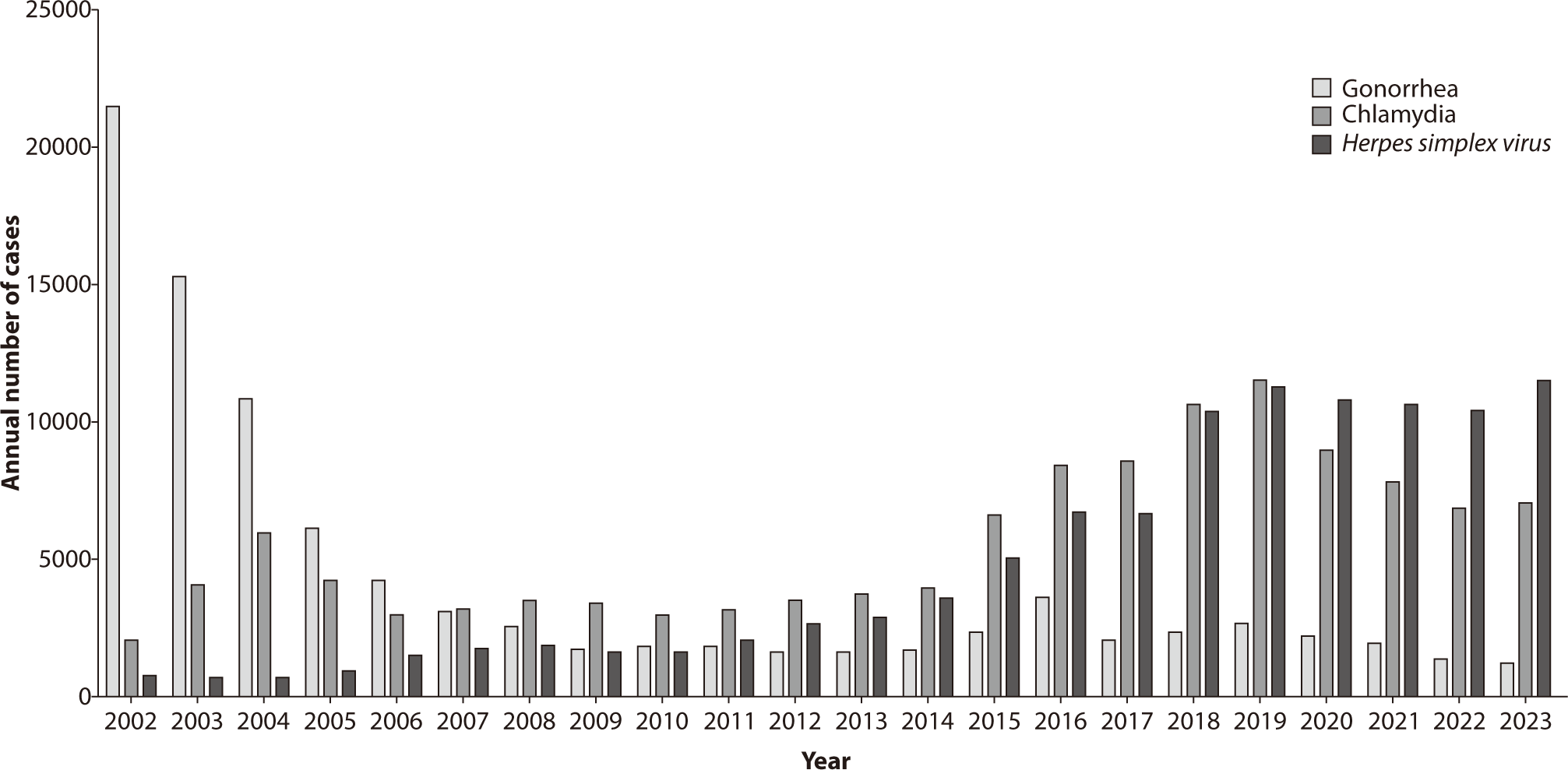
Gonorrhea can result in infections in the urogenital tract, oropharynx, and rectum. It can also cause bacteremia, which may manifest with skin lesions or arthritis. In women, between 86.4% and 92.6% of urogenital infections caused by gonorrhea are asymptomatic [23]. Although less precisely determined, a population-based multicenter study with 11,408 participants found that 55.7% to 86.8% of urogenital infections in men were asymptomatic [13,23].
The most common symptom of a gonorrhea infection is gonococcal urethritis, which typically manifests in men as urethral discharge and dysuria following an incubation period of 2 to 8 days. In women who exhibit symptoms, the infection may lead to vaginal discharge, itching, intermenstrual bleeding, or heavy menstrual periods. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) associated with gonorrhea can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain or pain during intercourse. Gonococcal pharyngitis may present with a sore throat, pharyngeal exudates, or swollen cervical lymph nodes, whereas gonococcal proctitis can lead to anorectal pain, a sensation of incomplete bowel evacuation, bleeding, or mucoid discharge. In Korea, cases of disseminated gonococcal infection have been reported, presenting as bacteremia and liver abscesses [24]. The typical presentation of disseminated gonococcal infection includes purulent arthritis, polyarthralgia, tenosynovitis, and skin rashes [25].
The diagnosis of gonorrhea involves identifying N. gonorrhoeae from the infected site. Traditionally, bacterial culture was the primary method used; however, NAATs have now become widely employed. Nevertheless, to determine antibiotic resistance, obtaining the pathogen through culture is necessary. Therefore, it is recommended to perform bacterial culture alongside NAATs when diagnosing gonorrhea. In men, first-void urine is commonly tested, and urethral swab tests are also an option. In women, vaginal swab tests are primarily used, although cervical swabs can also be taken. Recently, the use of self-collected samples has been introduced. The sensitivity of culture for detecting gonorrhea ranges from 50% to 85%, with lower sensitivity observed in non-genital sites and among asymptomatic patients [26].
The treatment guidelines for gonorrhea are regularly updated. The most recent guidelines from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), issued in 2021, recommend a single intramuscular dose of 500 mg of ceftriaxone for uncomplicated gonorrhea [2]. Additionally, if a chlamydial infection cannot be ruled out, administering doxycycline (100 mg) twice daily for 7 days is advised. There are notable differences between the U.S. and European guidelines, especially concerning the use of dual therapy [4]. While previous U.S. guidelines favored dual therapy, the current recommendations support monotherapy. The 2023 domestic guidelines also endorse a single intramuscular or intravenous dose of 500 mg ceftriaxone for uncomplicated urogenital, cervical, and rectal gonococcal infections in adults. Alternative treatments include a single intramuscular dose of 2 g of spectinomycin or a combination therapy consisting of 240 mg of intramuscular gentamicin and 2 g of oral azithromycin. For pharyngeal infections, however, both the U.S. and domestic guidelines continue to recommend a single intramuscular dose of 500 mg of ceftriaxone.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection caused by serovars D through K of Chlamydia trachomatis. Previously, it was often categorized with other infections such as non-gonococcal urethritis. However, it is now recognized as one of the most prevalent STIs. In the United States, data from 2019 reported 1,808,703 new cases, making chlamydia the most commonly reported STI [27]. In Korea, surveillance data indicated an increasing incidence of chlamydia infections until 2019, with 11,518 cases reported that year. Following the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, however, the number of reported cases declined to 7,064 in 2023 (Figs. 2, 3). This decrease may be attributed to factors such as reduced testing and healthcare access during the pandemic, changes in sexual behavior, or the reprioritization of healthcare resources. These factors have been noted in various international studies, although it was challenging to confirm with domestic data. Nonetheless, it is believed that the situation in the country would not have been significantly different.
Chlamydia can lead to urogenital, oropharyngeal, rectal, and ocular infections in both men and women. The majority of these cases are asymptomatic, with over 70% of urogenital infections in women and more than 80% in men presenting no symptoms. Similarly, around 90% of rectal and pharyngeal infections remain asymptomatic [28]. When symptoms do occur, chlamydia infections typically manifest as urethritis, characterized by dysuria and urethral discharge, cervicitis, PID, and proctitis, which includes pain, discharge, and bleeding. In men, the infection may also lead to epididymitis. Additionally, chlamydia can cause Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, a specific form of PID.
In neonates born vaginally to mothers with chlamydia, there is a risk of developing conjunctivitis or pneumonia. Additionally, a rare manifestation of chlamydia infection, known as lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), may also occur. LGV progresses through three stages: initially, a small, painless, temporary ulcer appears at the infection site. The second stage, which develops 2 to 6 weeks later, is marked by large, painful inguinal lymph nodes, with approximately 30% of these nodes spontaneously rupturing. If left untreated, the third stage involves chronic lymphadenitis, which leads to scarring, lymphedema, and genital elephantiasis [29].
Chlamydia is diagnosed by detecting the pathogen with NAATs from the suspected site of infection. The process for collecting samples is similar to that used for gonorrhea; however, since cultures are not conducted, NAATs are the sole diagnostic method employed.
The treatment for chlamydia is doxycycline. According to the updated 2021 guidelines from the U.S. CDC, doxycycline is now recommended as the first-line treatment [2], a decision supported by recent studies [30–32]. Domestic guidelines also endorse doxycycline, prescribing 100 mg twice daily for 7 days. Alternative treatments include azithromycin (1 g) or levofloxacin (500 mg), both administered for 7 days. A study conducted in Japan revealed that the antibiotic resistance rates for C. trachomatis were 2.0% for azithromycin and 2.4% for clarithromycin [33].
Mycoplasma genitalium
M. genitalium was not widely recognized as an infection in the past, but it has recently gained attention as a STI. In the 2015 guidelines from the U.S. CDC, M. genitalium was described as an "emerging pathogen of uncertain significance" [34]. However, with the accumulation of more data, recent guidelines now recommend treatment for it [2].
Since M. genitalium is not a notifiable infection in Korea, nationwide incidence statistics are not compiled. A study conducted in Korea between 2012 and 2015 involving 14,932 soldiers with urological symptoms found that chlamydia was the most prevalent infection at 36.6%, followed by Ureaplasma urealyticum at 24.0%, and M. genitalium at 21.5%. N. gonorrhoeae accounted for 19.0% of the cases [35]. Another study, carried out from 2018 to 2020 on outpatients, identified M. genitalium in 3.27% of the cases, with the highest prevalence observed in the 20–29 age group [36].
The urogenital tract is the primary site of M. genitalium infection, although it can also occasionally cause proctitis. In cases of recurrent and persistent urethritis, M. genitalium is detected in approximately 30%–40% of instances. Although M. genitalium often remains asymptomatic, it is present in 30%–40% of men with persistent recurrent urethritis [37]. Symptoms during these episodes typically include dysuria and urethral discomfort. In women, M. genitalium is associated with cervicitis, PID, and infertility. The main symptoms in women are those related to cervicitis, such as post-coital bleeding, intermenstrual bleeding, and lower abdominal pain [38].
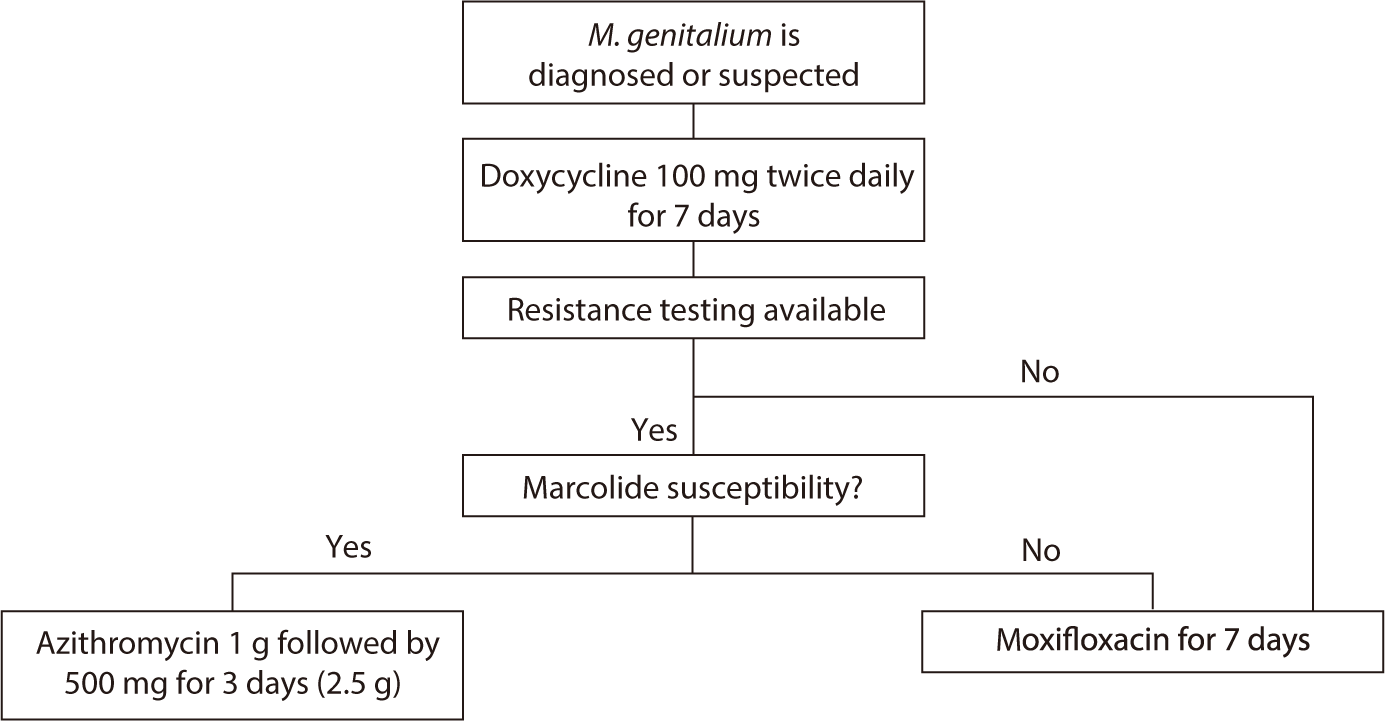
M. genitalium often fails to respond to treatment, primarily due to resistance to the medications used. Therefore, recent major guidelines recommend assessing resistance before selecting a treatment regimen for M. genitalium [2]. However, since macrolide resistance testing tools are not yet available domestically, these recommendations cannot be applied in the local context (Fig. 4).
If resistance testing is possible, administer doxycycline (100 mg) twice daily for 7 days initially. If the organism is susceptible to macrolides, azithromycin can be administered as a single 1 g oral dose followed by three additional 500 mg doses (totaling 2.5 g). In the presence of macrolide resistance, moxifloxacin (400 mg) taken orally for 7 days is recommended. If resistance testing is not available, the recommended approach is to administer doxycycline for one week followed by moxifloxacin for another week. The 2023 domestic guidelines suggest starting treatment with azithromycin (500 mg orally), followed by 250 mg daily for 4 days (total 1.5 g). In cases of treatment failure or recurrence, a 7-day course of doxycycline or minocycline is advised, followed by further treatment decisions based on macrolide susceptibility. If testing is not feasible or if macrolide susceptibility is confirmed, the recommended regimen is 1 g of azithromycin followed by 500 mg daily for 3 days (total 2.5 g), with a follow-up at 21 days to confirm cure. If macrolide resistance is detected, a 7-day course of moxifloxacin 400 mg is recommended.
Herpes simplex virus
HSV is categorized into type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2), both of which can cause genital herpes [39]. However, HSV-2 is primarily associated with anogenital herpes, whereas HSV-1 typically leads to cold sores around the lips. In Korea, the incidence of HSV-2 is monitored through a sample surveillance system. Data show that there were 6,657 cases in 2017, 10,347 cases in 2018, 11,229 cases in 2019, 10,759 cases in 2020, 10,637 cases in 2021, 10,403 cases in 2022, and 11,449 cases in 2023. Additionally, the number of cases reported per institution has been steadily increasing (Figs. 2, 3).
Most individuals infected with HSV remain asymptomatic, and the majority are unaware that they are carriers. During the initial infection, which follows an incubation period of approximately 4–7 days post-contact, patients develop multiple painful, bilateral, erythematous lesions. These lesions progress through stages including papules, vesicles, and ulcers, and typically last between 16.5 to 19.7 days [13,40]. Additionally, 39%–68% of patients report experiencing headaches, fever, and lymphadenopathy during this initial phase [13]. Following the initial outbreak, the virus enters a latent state where it remains asymptomatic. Symptomatic recurrences occur in about 40-50% of cases and are often preceded by prodromal symptoms localized to the affected area. These symptoms, which include itching or burning sensations, help patients recognize the onset of a new outbreak. Recurrences tend to be milder than the initial infection and usually resolve within 5–10 days.
Testing for HSV can be performed on samples from vesicular lesions using NAATs, such as PCR, which have very high sensitivity. A wet swab is the preferred method, but a dry swab can also be used. While viral culture is an option, it is less sensitive and more time-consuming than NAAT, and thus, it is not recommended as the sole testing method. Viral culture may be utilized in instances where the infection does not respond to treatment or antiviral resistance is suspected. Serological testing is valuable for identifying infections, especially latent infections in the absence of skin lesions, and is frequently employed in demographic studies.
Treatment for HSV includes oral or injectable antiviral medications. The primary antiviral drugs used are acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir. Although these medications do not cure HSV, they help reduce symptoms, shorten the duration of the disease, and decrease the recurrence rate. Despite the availability of various antiviral drugs, most share similar mechanisms of action and efficacy. For suspected initial infections, a 10-day course of antiviral treatment is recommended, which may be extended by an additional week if lesions persist. For recurrent lesions, a shorter course of treatment may be attempted. Topical antiviral treatment alone is not recommended due to its insufficient effectiveness.
Conclusion
This review highlights the evolving landscape of STIs in Korea. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the epidemiology of STIs, necessitating adaptations in healthcare delivery and public health strategies. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, particularly in gonorrhea and M. genitalium, underscores the importance of antimicrobial stewardship and the development of new therapeutic options. Continuing efforts in education, prevention, and research are essential to manage and mitigate the impact of STIs on public health.