Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer, accounting for 75%–80% of primary liver malignancies [1]. HCC mostly develops in the background of chronic liver disease, the most common etiologies being HBV or HCV infection, and chronic alcohol abuse. During the recent year, metabolic syndrome has become another major risk factor for HCC, even in Asian countries [2,3].
The clinical outcome of patients with HCC is generally poor, mainly due to difficulties in early detection and limited treatment options for advanced disease [4,5]. Currently, systemic therapy, such as receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy, is the treatment of choice for the patients with unresectable HCC [5]. However, the efficacy of systemic therapy in HCC is still unsatisfactory with survival benefit of 1–3 months, objective response rate less than 30%, and a high incidence of adverse events [6,7]. In this context, understanding the heterogeneity of HCC will play a key role in developing effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, by offering potential predictive biomarkers and personalized approaches for HCC management.
Ethics statement
It is a literature database-based review; therefore, neither approval by the institutional review board nor obtainment of informed consent was required.
Morpho-molecular heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma
HCC is typically composed of tumor cells showing hepatocytic differentiation with variable degrees of atypia [8]. While HCC recapitulates the cytoarchitectural morphology of the liver to varying extents, there are alterations in the hepatic microarchitecture such as loss of portal tracts, reduction or loss of the reticulin framework, and thickening of the hepatic plates. Neoangiogenesis occurs in HCCs, in the form of sinusoidal capillarization and unpaired arteries [8]. These changes also result in the characteristic imaging features, such as the early enhancement on contrast enhanced CT/MRI.
However, there is considerable heterogeneity of HCC, in the microscopic growth patterns, cytological features, and histological grade. About 50% of HCCs demonstrate mixed patterns of growth: trabecular, pseudoglandular, solid, and macrotrabecular (Fig. 1) [9]. In addition, while most HCCs demonstrate cytological features that recapitulate those of normal hepatocytes (i.e. polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm), some HCCs show extensive areas with clear cell change, fatty change, and cholestasis. Cytoplasmic inclusions (e.g., hyaline bodies, Mallory-Denk bodies, and pale bodies) may also be seen in some tumor cells [8]. Histological grading is currently performed according to either the four-tiered modified Edmondson and Steiner system or the three-tiered World Health Organization (WHO) grading system [9–11].
Recent advances in genomic techniques have unraveled the heterogeneity in the mutational landscape of HCC [12,13]. The most frequently mutated genes include TERT promoter, TP53, CTNNB1, ARID1A, ARID2, JAK1, ALB, AXIN1, NFE2L2, and RPS6KA3 [12]. In addition, gene expression profiling studies have suggested several molecular subclasses of HCC that correlate with the clinicopathological features, providing the foundation for an integrated morphological-molecular classification of HCC [14]. In the past two decades, there have been many efforts to establish a subclassification system that better categorizes HCCs with distinct clinical, histological, and molecular features (Table 1) [13,15–19]. HCC can be subclassified into two major groups, the proliferative class and the non-proliferative class. The proliferative class is characterized by high chromosomal instability and TP53 mutations, and is associated with poor histological differentiation, frequent vascular invasion, increased alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level, and overall poor clinical outcome [16,18]. On the other hand, the non-proliferative class displays chromosomal stability and a well-differentiated phenotype with less frequent vascular invasion [16,18]. CTNNB1-mutated HCCs belong to the latter group: these demonstrate frequent cholestasis and less immune cell infiltration on histology [14,20].
| Classification system | Proliferative class | Non-proliferative class |
|---|---|---|
| Lee et al. [15] | Cluster A | Cluster B |
| Boyault et al. [16] | G1, G2, G3 | G4, G5, G6 |
| Chiang et al. [17] | Proliferation | Interferon, Poly7, CTNNB1 |
| Hoshida et al. [18] | S1, S2 | S3 |
| TCGA Research Network [13] | Immune high and intermediate | Immune excluded |
| Sia et al. [19] | iClust1, iClust3 | iClust2 |
| Clinical features | Poor clinical outcome, high AFP, HBV, frequent vascular invasion | Improved clinical outcome, low AFP, HCV, low vascular invasion |
| Histological features | Poorly differentiated | Well differentiated |
| Molecular alterations | Chromosomal instability, TP53 mutations, FGF19 amplification | Chromosomal stability, CTNNB1 mutations, TERT promoter mutations |
Currently, approximately 35% of HCC can be further subclassified into histological subtypes with distinct morphological, clinicopathological and molecular characteristics [9]. The following section will summarize the clinicopathological and molecular features of these different subtypes.
Steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma
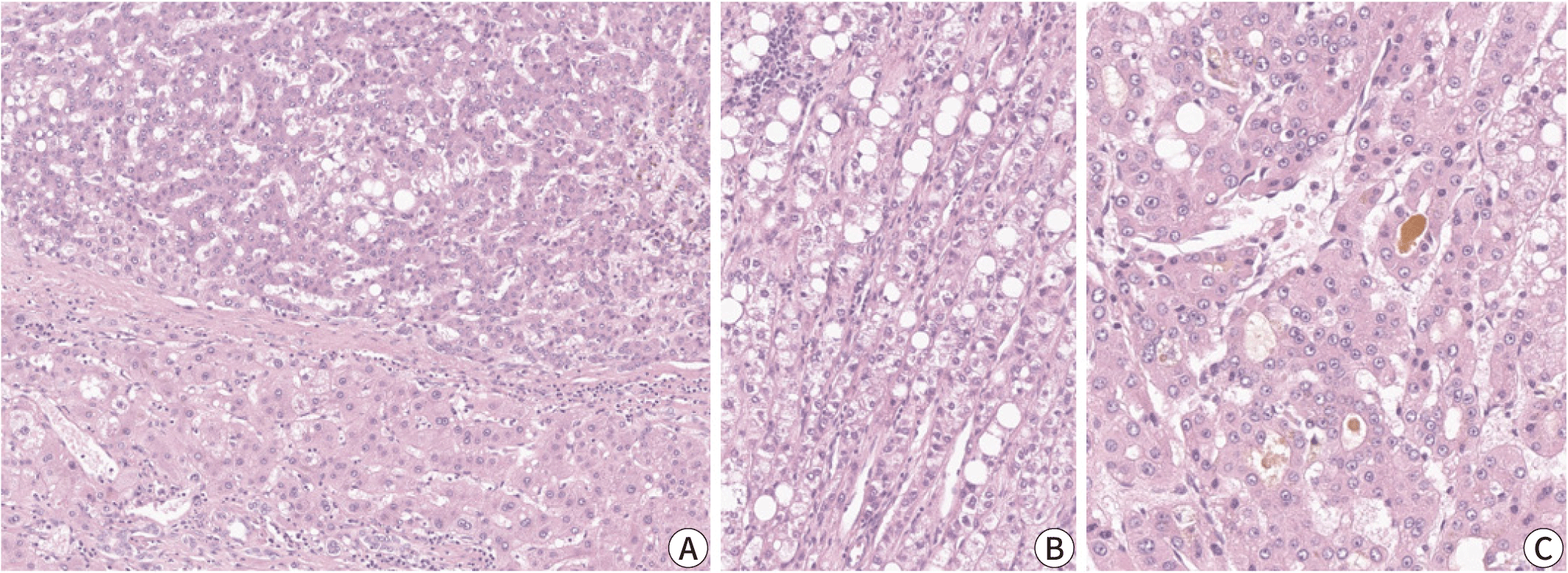
The steatohepatitic subtype of HCC demonstrates the key histological features of non-neoplastic steatohepatitis, including steatosis, pericellular fibrosis, cell ballooning, inflammation, and Mallory-Denk bodies, and these features occupy a major portion (>50%) of the tumor (Fig. 2) [21]. This subtype has been more frequently identified in patients with underlying metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and alcohol abuse, and its relative frequency has been reported to be between 5% and 20% [3,21]. Steatohepatitic HCC has been associated with less frequent vascular invasion and satellite nodules; however, its prognosis appears to be similar to that of conventional HCC [14]. Key molecular alterations associated with steatohepatitic HCC include IL-6/JAK/STAT activation, while CTNNB1, TERT promoter and TP53 mutations have been found to be less frequent in these tumors [14].
Clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma
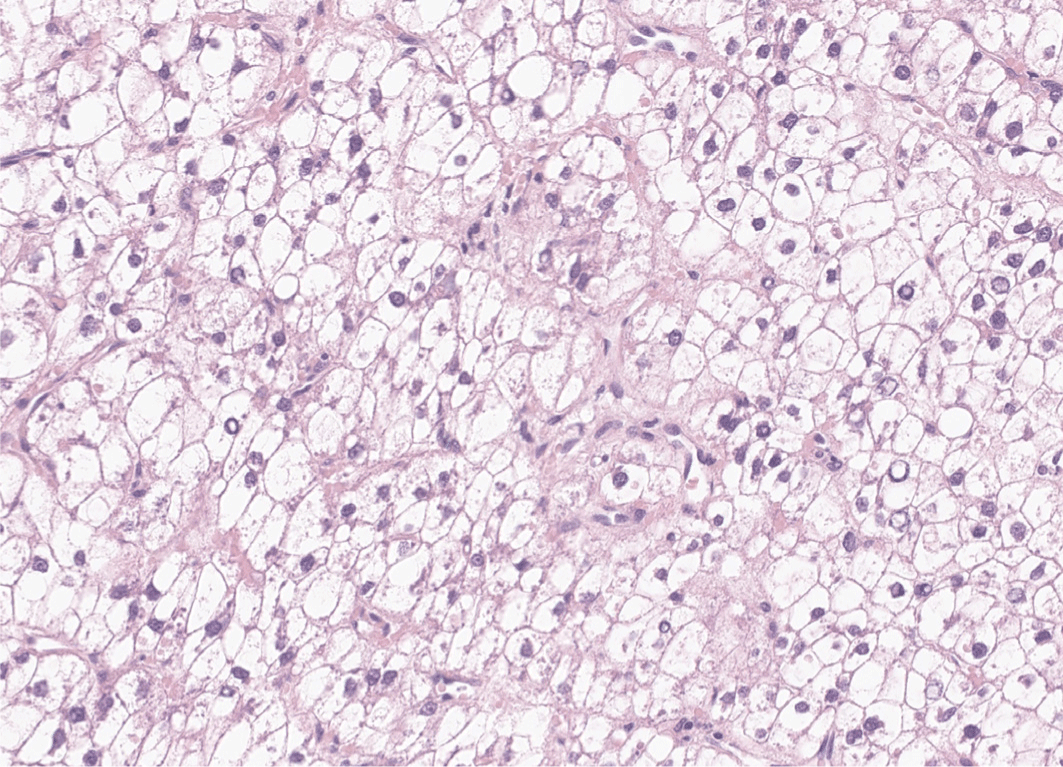
By definition, in clear cell HCCs, more than 80% of tumor cells demonstrate abundant clear cytoplasm (Fig. 3). The clear cytoplasm is a result of glycogen accumulation; however, some tumor cells may appear clear due to lipid droplets, and some degree of steatosis is acceptable for this diagnosis [22]. The relative frequency of clear cell HCC has been estimated to be around 3%–7%. Clear cell HCCs are generally well-differentiated tumors with a favorable prognosis [23]. One study has reported that clear cell HCCs demonstrate higher frequency of IDH1 mutation, although this mutation is not sufficient to define the subtype [24].
Macrotrabecular-massive hepatocellular carcinoma
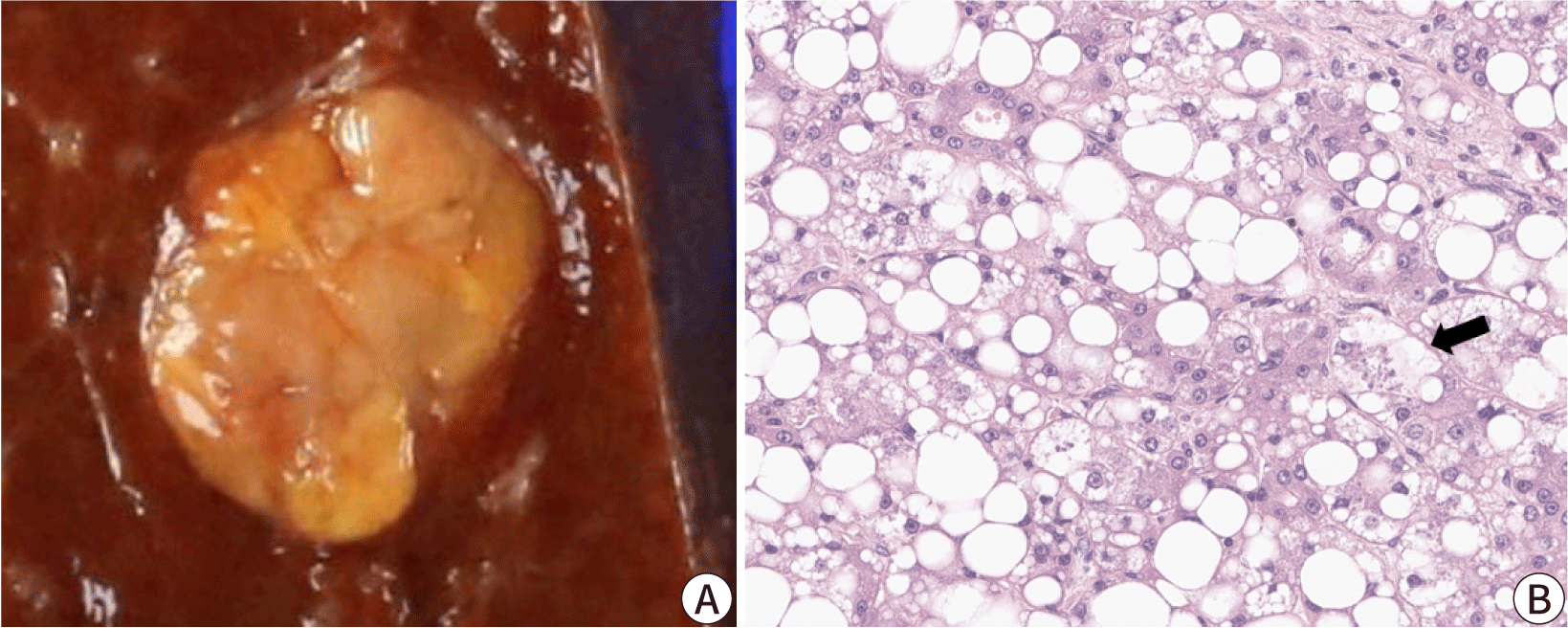
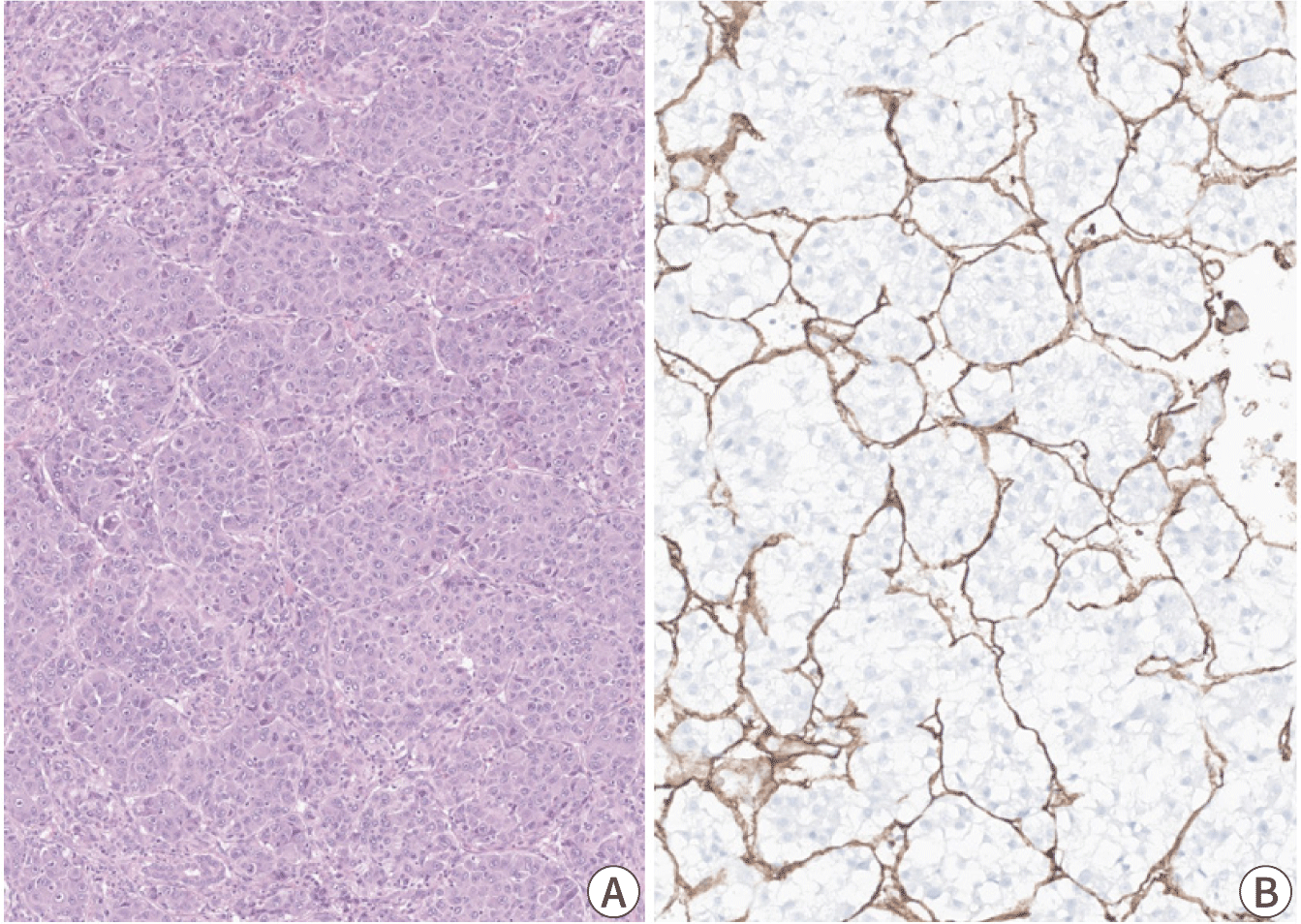
The macrotrabecular-massive subtype of HCC is an HCC in which more than 50% of the tumor cells assume a macrotrabecular growth pattern, defined as large trabeculae that are more than 6–10 cells thick (Fig. 4) [25]. This subtype accounts for approximately 5% of all HCCs and has been strongly associated with elevated serum AFP levels, high-grade cytological atypia, extensive lymphovascular invasion, more frequent distant metastasis, and a poor prognosis [25,26]. In addition, the vessels-encapsulating-tumor-clusters (VETC) pattern of neoangiogenesis, which has been associated with metastatic dissemination of HCC, is often enriched in this subtype (Fig. 4) [27,28]. TP53 mutations and FGF19 amplifications have been more frequently identified in the macrotrabecular-massive subtype of HCC [14].
Scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma
This subtype is characterized by dense intratumoral fibrous stroma (Fig. 5). The scirrhous subtype has a relative frequency of 4% and often mimics intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma on imaging [29]. Expression of immunohistochemical markers associated with stemness (e.g., cytokeratin ([CK]) 7, CK19, and epithelial cell adhesion molecule) is often seen in scirrhous HCCs, and increased expression of cholangiocarcinoma-like and stem-cell-like genes have been identified by gene expression profiling, consistent with the intermediate characteristic of this subtype [30,31]. Furthermore, scirrhous HCC is associated with frequent TSC1/TSC2 mutations and transforming growth factor-β signaling activation [14,30].
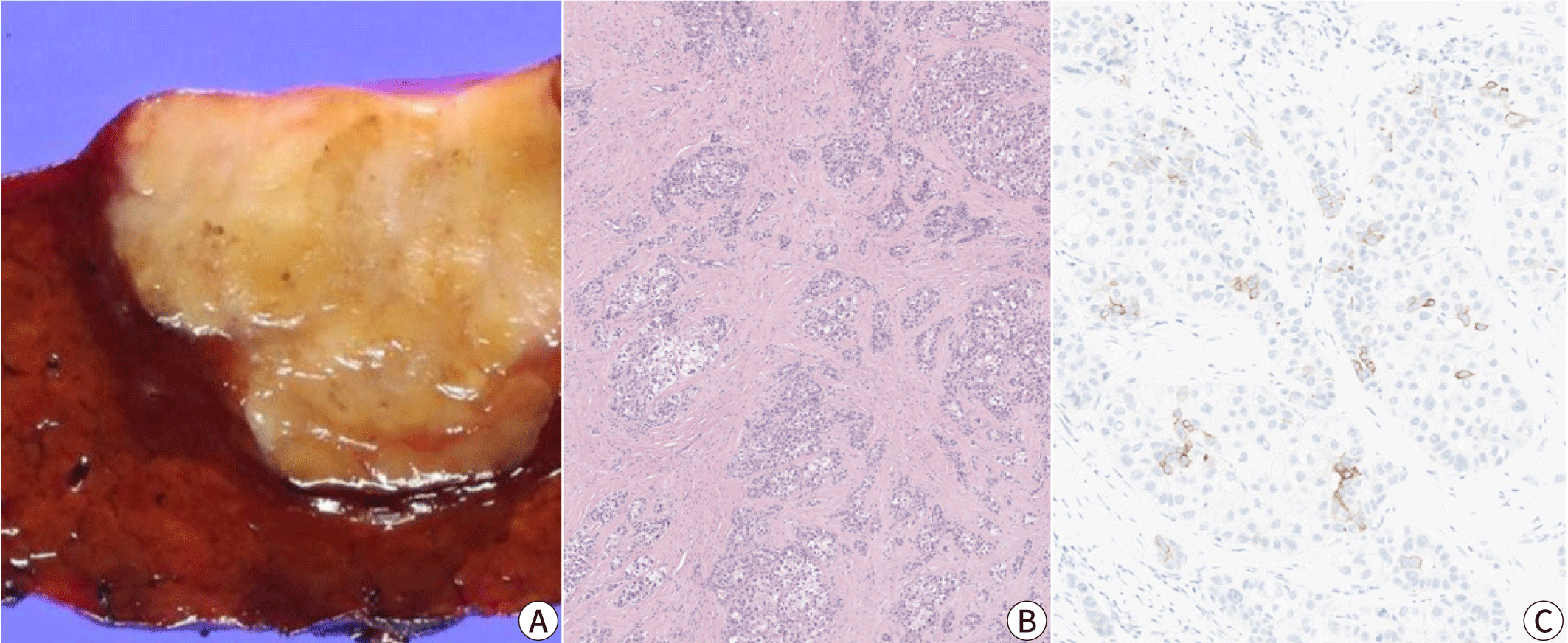
Lymphocyte-rich hepatocellular carcinoma
The lymphocyte-rich subtype demonstrates massive intratumoral infiltration of lymphocytes, which outnumber the tumor cells in most microscopic fields. This subtype is rare, accounting for less than 1% of all HCCs, but has received much attention as it has been associated with a favorable clinical outcome [32]. The lymphocyte-rich subtype is associated with increased programmed death-ligand 1 expression and focal amplification of chromosome 11q13.3, which is related to the immune checkpoint signature (CD274, PDCD1, BTLA, CTLA4, HAVCR2, IDO1, and LAG3) [32–35]. Interestingly, although this subtype is also known as “lymphoepithelioma-like HCC”, it is not associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection, unlike the lymphoepithelioma-like tumors arising in other organs, such as the nasopharynx and stomach [32].
Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma
Fibrolamellar carcinoma, or fibrolamellar HCC, consists of strands of large eosinophilic tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli, and separated by dense intratumoral bands of fibrosis [36]. Fibrolamellar carcinoma accounts for approximately 1% of all HCC, occurs in younger patients (median age of 25 years), and the background liver is non-cirrhotic [37]. The prognosis of fibrolamellar carcinoma appears to be better than that of conventional HCC arising in cirrhotic livers, but similar to that of HCC in non-cirrhotic livers [37]. DNAJB1-PRKACA gene fusion has been identified in >95% of cases, and fluorescence in situ hybridization for PRKACA gene rearrangement is a useful ancillary test in confirming the diagnosis [38]. Expression of CK7 and CD68 in the tumor cells is another characteristic of fibrolamellar carcinoma [38].
CTNNB1-mutated hepatocellular carcinoma
CTNNB1 mutations have been reported in approximately 20%–40% of HCCs [39]. CTNNB1 encodes β-catenin, which plays a key role in the WNT signaling pathway that regulates liver function and zonation [40]. In addition, bile salt transporter expression is dysregulated in these tumors, histologically manifested by frequent intratumoral cholestasis. Some CTNNB1-mutated HCCs may be diagnosed by gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI, due to the upregulation of the organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 (OATP1B3) [41]. Histologically, CTNNB1-mutated HCCs are typically well-differentiated tumors with microtrabecular and/or pseudoglandular growth patterns, intratumoral cholestasis, and less immune cell infiltration compared to non-CTNNB1-mutated HCCs [14,20]. However, CTNNB1-mutated HCCs are not morphologically homogeneous, with approximately 40% not demonstrating the “classic CTNNB1 morphology” [42]. Immunohistochemical studies for β-catenin (nuclear expression) and glutamine synthetase (diffuse, strong and homogeneous expression) may serve as useful surrogate markers for CTNNB1 mutation.
Hepatocellular carcinoma with stemness-related marker expression
HCC with stemness-related marker expression, or progenitor HCC, is defined as HCC expressing stemness-related markers, e.g., CK19, in >5% of the tumor cells [15]. This subset of HCCs differ from combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma, as they are morphologically compatible with HCC, and there is no evidence of glandular differentiation or mucin production in these tumors. They are associated with increased serum AFP levels, frequent vascular invasion, poor histological differentiation, high recurrence rate, resistance to systemic chemotherapy and locoregional treatment, and overall poor prognosis [43]. HCCs with stemness-related marker expression more frequently demonstrate TP53 mutations and chromosomal instability, and increased PD-L1 expression [33,34].
Hepatocellular carcinomas with vessels-encapsulating-tumor-clusters pattern
The VETC phenotype is defined by the presence of VETC pattern in more than 55% of the tumor area, characterized by CD34-positive vessels that encapsulate and isolate individual tumor clusters, forming a cobweb-like pattern (Fig. 4) [27,28,44]. The VETC pattern is often found in the macrotrabecular-massive subtype of HCC (7.8%) and is associated with aggressive behavior and metastatic dissemination [27,28]. It has been reported that VETC pattern is related to a novel mechanism of metastasis, independent of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition [44]. Furthermore, patients with VETC-positive HCC have shown greater survival benefits from sorafenib therapy compared to those with VETC-negative HCC, suggesting that the VETC pattern may serve as a potential predictive marker for sorafenib response [28]. Correlation between the VETC pattern on histology and a rim arterial phase hyperenhancement in arterial phase imaging suggests a role for imaging in the prognostication of HCC [45].
Other rare histological subtypes of HCC have been described. The chromophobe subtype of HCC has tumor cells with clear to pale cytoplasm and mainly bland nuclei with focal areas of striking nuclear atypia [46]. Chromophobe subtype is strongly associated with alternative lengthening of telomeres, a telomerase-independent mechanism of telomere maintenance, which can be detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization [46]. Its prognosis is currently known to be similar to that of conventional HCC [47]. Neutrophil-rich HCC is characterized by marked intratumoral neutrophilic infiltration, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production by tumor cells, and a poor prognosis [47]. The tumor cells are often poorly differentiated, and focal sarcomatoid differentiation can be observed [48].
Conclusion
Recent molecular studies have significantly enhanced our understanding of the morphological and molecular heterogeneity of HCC, providing the foundation for more effective and personalized treatment strategies. Pathologists are becoming increasingly aware of the histomorphological heterogeneity of HCC, and the specification of the various subtypes of HCC has helped pathologists understand the histology of HCC in more detail and the various differential diagnoses and diagnostic pitfalls for each variant. The correlation between the histomorphology and the molecular and biological features suggests the role of histology in the prediction of therapeutic response and prognosis. This may be further facilitated by the recent advances in digital pathology and artificial intelligence-based biomarker research.

