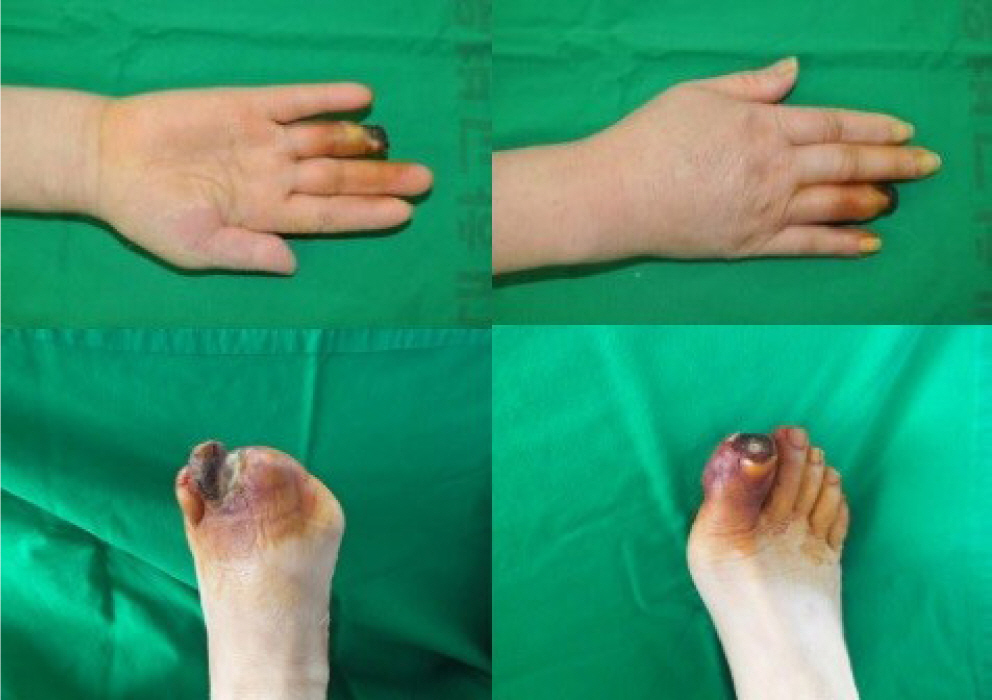
Symmetrical peripheral gangrene is a severe condition marked by symmetric acral necrosis without obstruction of the major blood vessels. This case report examines the critical decisions involved in choosing between early and delayed amputation, as well as determining the extent of the necessary amputation. We present three cases: one involving antiphospholipid syndrome, another with disseminated intravascular coagulation, and a third associated with diabetes mellitus. All three cases ultimately required amputation due to symmetrical peripheral gangrene. In the first two cases, amputation was delayed, which is typically advantageous as it allows for the clear demarcation of necrotic tissue. However, in the third case, where infection was evident, immediate amputation was necessary despite the patient's overall poor health.
 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Mi Yeon Kim
, Mi Yeon Kim , Min Sun Ryu
, Min Sun Ryu , So Young Ahn
, So Young Ahn , Hyoung Won Cho
, Hyoung Won Cho , In Sook Kang
, In Sook Kang , Seong Eun Kim
, Seong Eun Kim
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is characterized by raised levels of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), in association with thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Development of APS is related with idiopathic origin, autoimmune disease, malignancy and, on rare occasions, infection. However, in secondary APS combined with bacterial infections, aPL is usually shown with low titer and rarely associated with thrombotic events. A 52-year-old male was admitted due to pneumonia and multiple hepatosplenic abscesses. He had been treated with proper antibiotics, but he presented ascites and sudden variceal bleeding because of portal vein thrombosis. The bleeding was controlled by endoscopic variceal ligation. Acute portal vein thrombosis was successfully managed by low molecular weight heparin and hepatosplenic abscesses were completely resolved by antibiotics. This case suggests that systemic bacterial infection in immunocompetent patients possibly develops into secondary APS.

