 , Jiyoon Kim
, Jiyoon Kim
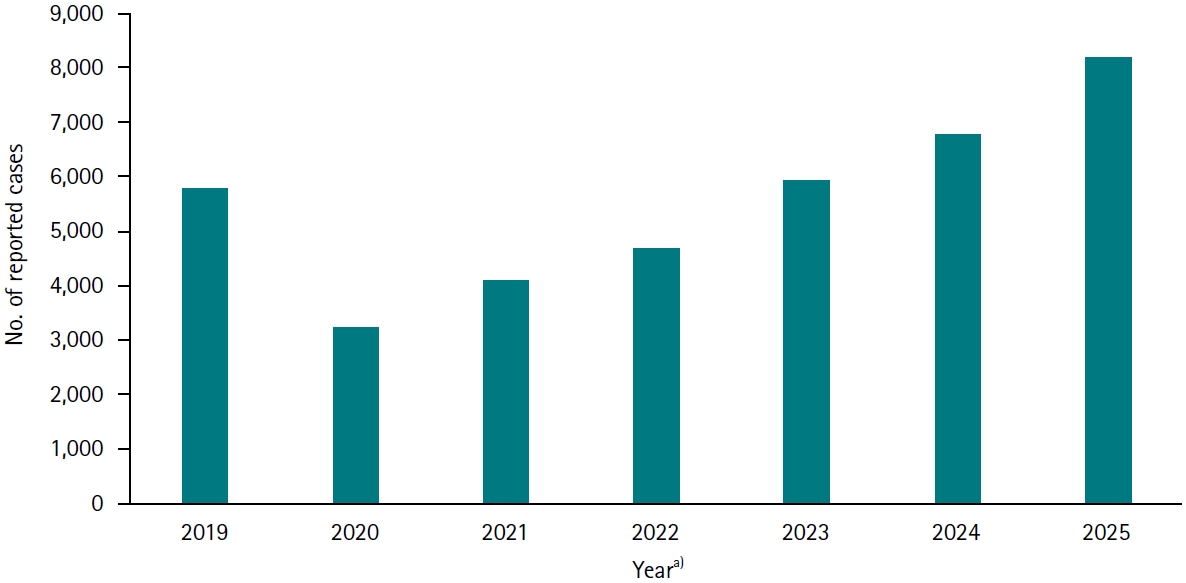

 , So Young Lee
, So Young Lee
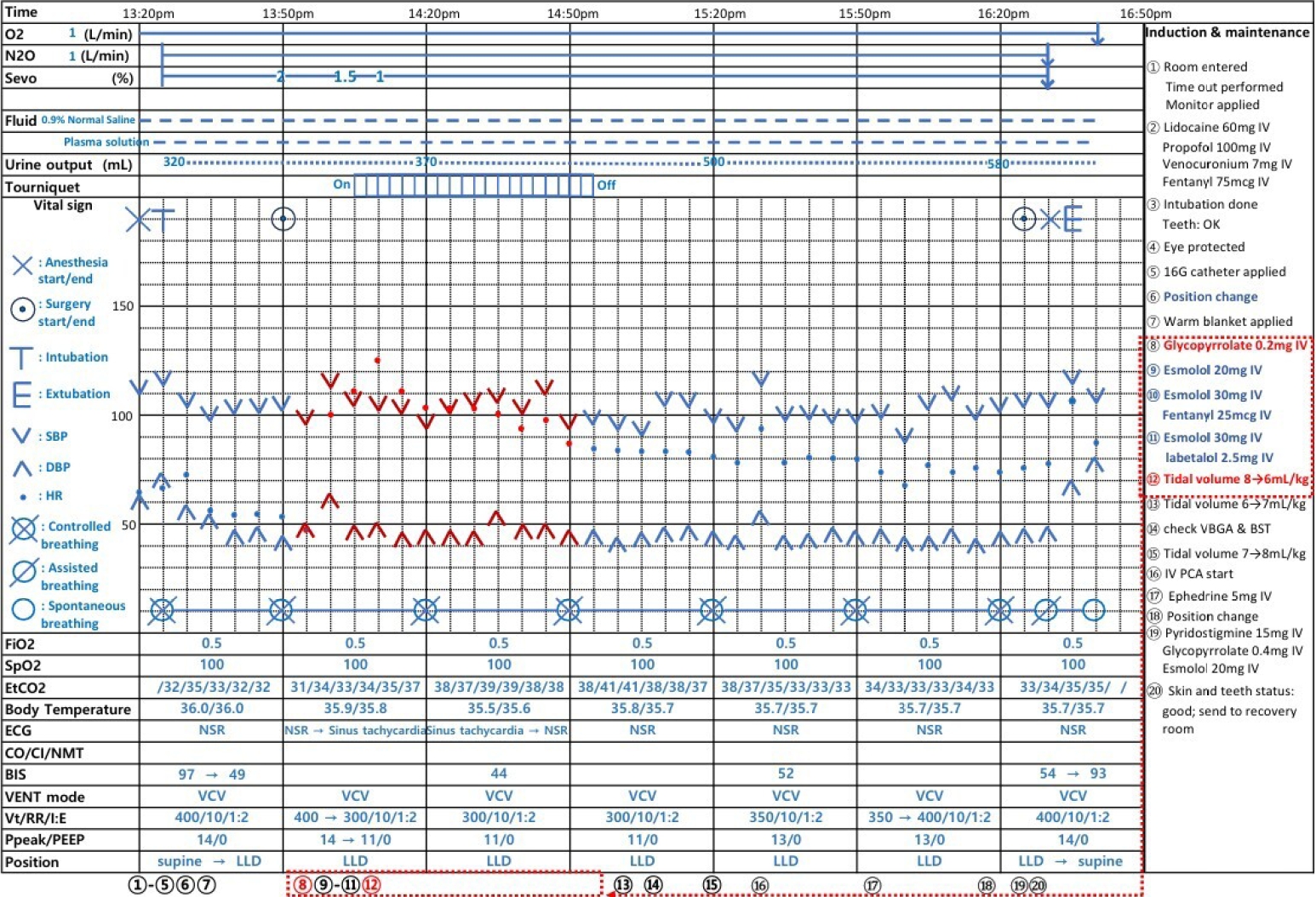
 , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Ju-Ran Byeon
, Ju-Ran Byeon , Yehyun Park
, Yehyun Park , Eun Mi Song
, Eun Mi Song , Chung Hyun Tae
, Chung Hyun Tae , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung
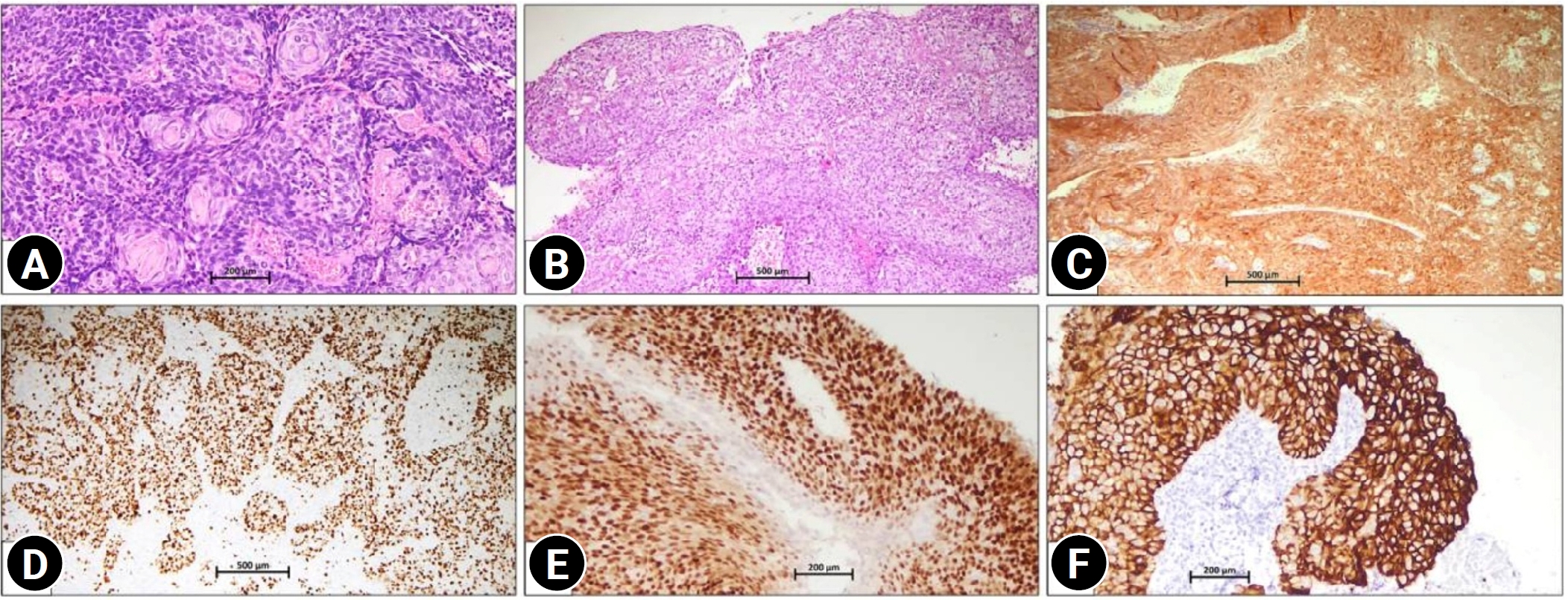
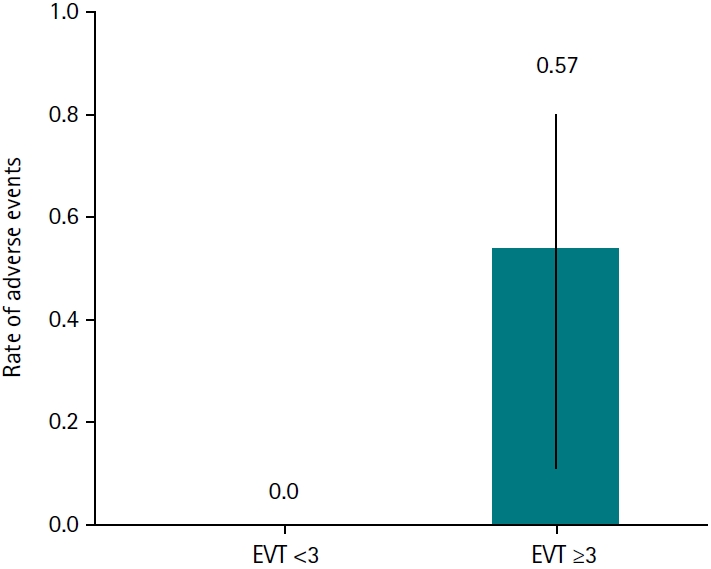
 , Jitendra Singh Nigam
, Jitendra Singh Nigam , Immanuel Pradeep
, Immanuel Pradeep , Ashutosh Rath
, Ashutosh Rath , Seetu Palo
, Seetu Palo , Naina Kumar
, Naina Kumar


 , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
 , Duck Sun Ahn
, Duck Sun Ahn
Citations

 , Oh Haeng Lee
, Oh Haeng Lee , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
Citations

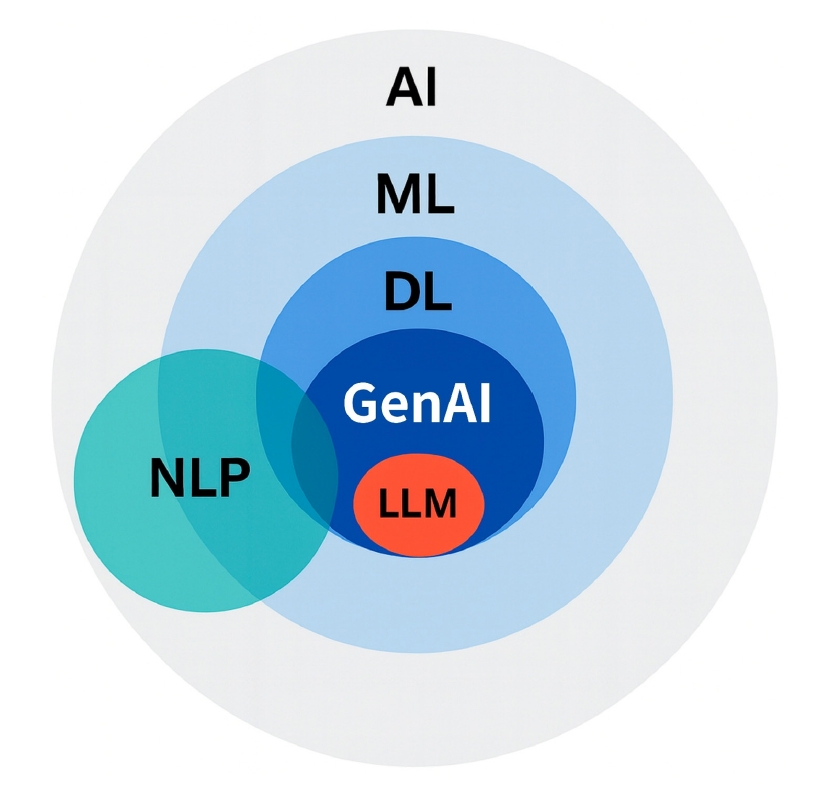
 , Jihyun Ahn
, Jihyun Ahn
Citations



 , Jiyoon Kim
, Jiyoon Kim



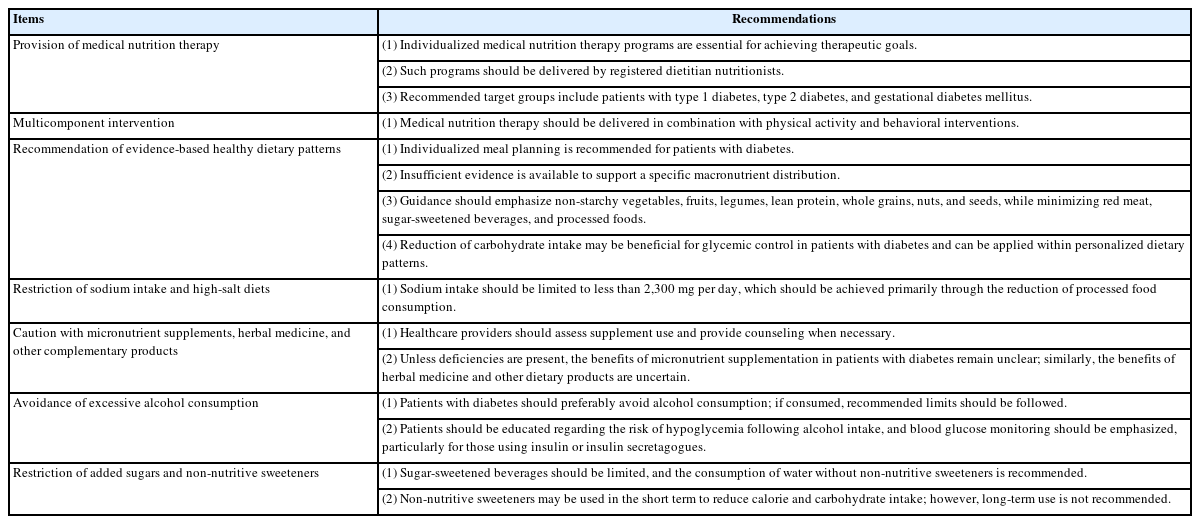
 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim
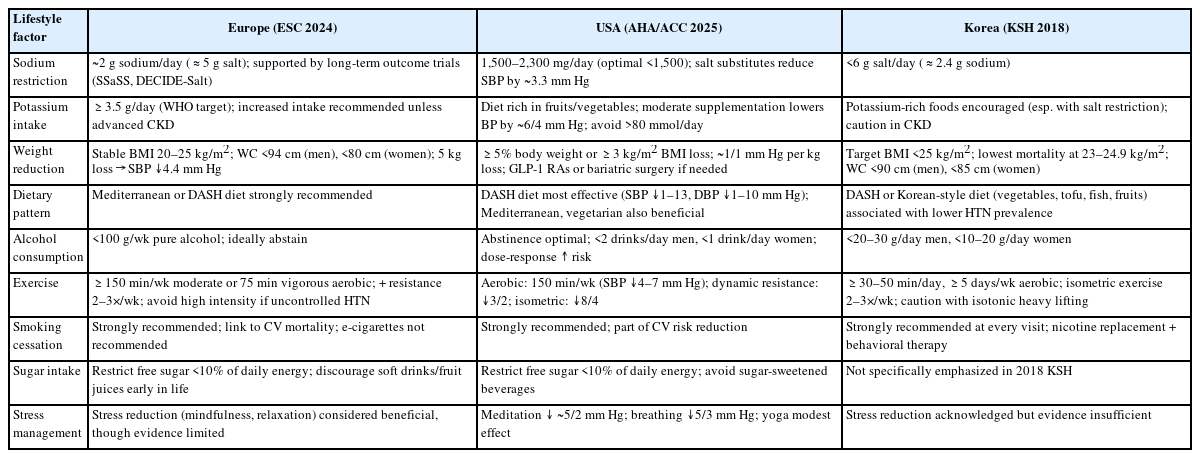
 , Gyu Bae Lee
, Gyu Bae Lee , Jihyun Yoon
, Jihyun Yoon , Yang-Hyun Kim
, Yang-Hyun Kim
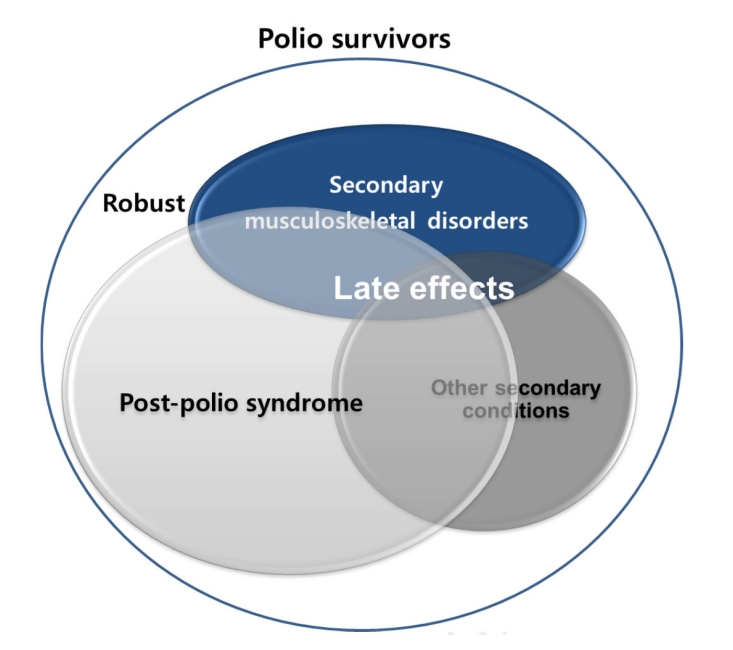
 , Ga-Yang Shim
, Ga-Yang Shim
 , Jae-Young Lim
, Jae-Young Lim


 , Rebecca C. Richmond
, Rebecca C. Richmond , Benjamin A. R. Woolf
, Benjamin A. R. Woolf , Neil M. Davies
, Neil M. Davies , Sonja A. Swanson
, Sonja A. Swanson , Tyler J. VanderWeele
, Tyler J. VanderWeele , Nicholas J. Timpson
, Nicholas J. Timpson , Julian P. T. Higgins
, Julian P. T. Higgins , Niki Dimou
, Niki Dimou , Claudia Langenberg
, Claudia Langenberg , Elizabeth W. Loder
, Elizabeth W. Loder , Robert M. Golub
, Robert M. Golub , Matthias Egger
, Matthias Egger , George Davey Smith
, George Davey Smith , Jeremy Brent Richards
, Jeremy Brent Richards
 , YangIm Hur
, YangIm Hur

Citations

 , Abdulraheem Almokhtar
, Abdulraheem Almokhtar , Hashem Bukhary
, Hashem Bukhary , Raed Sharaf
, Raed Sharaf , Khalid Alhomayani
, Khalid Alhomayani
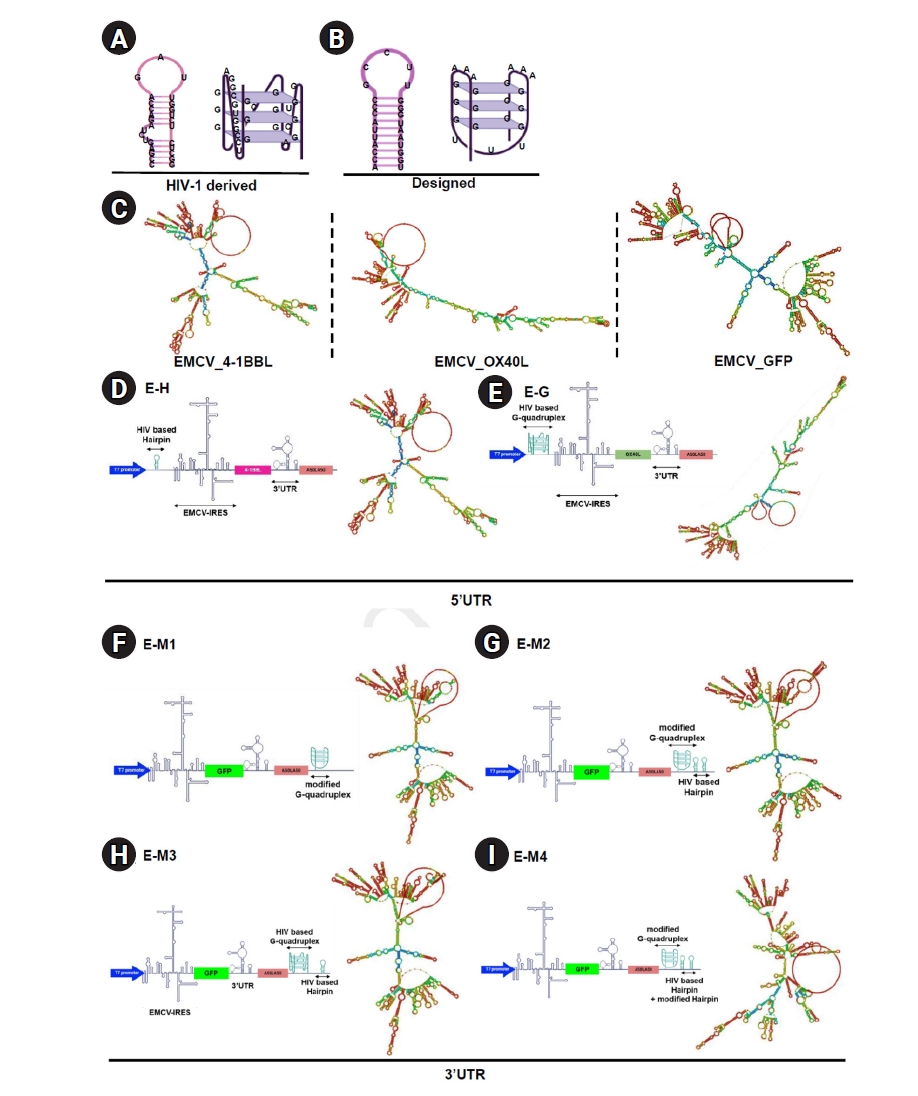
 , So-Hee Hong
, So-Hee Hong

 , An-Wen Chan
, An-Wen Chan , Gary S. Collins
, Gary S. Collins , Asbjørn Hróbjartsson
, Asbjørn Hróbjartsson , David Moher
, David Moher , Kenneth F. Schulz
, Kenneth F. Schulz , Ruth Tunn
, Ruth Tunn , Rakesh Aggarwal
, Rakesh Aggarwal , Michael Berkwits
, Michael Berkwits , Jesse A. Berlin
, Jesse A. Berlin , Nita Bhandari
, Nita Bhandari , Nancy J. Butcher
, Nancy J. Butcher , Marion K. Campbell
, Marion K. Campbell , Runcie C. W. Chidebe
, Runcie C. W. Chidebe , Diana Elbourne
, Diana Elbourne , Andrew Farmer
, Andrew Farmer , Dean A. Fergusson
, Dean A. Fergusson , Robert M. Golub
, Robert M. Golub , Steven N. Goodman
, Steven N. Goodman , Tammy C. Hoffmann
, Tammy C. Hoffmann , John P. A. Ioannidis
, John P. A. Ioannidis , Brennan C. Kahan
, Brennan C. Kahan , Rachel L. Knowles
, Rachel L. Knowles , Sarah E. Lamb
, Sarah E. Lamb , Steff Lewis
, Steff Lewis , Elizabeth Loder
, Elizabeth Loder , Martin Offringa
, Martin Offringa , Philippe Ravaud
, Philippe Ravaud , Dawn P. Richards
, Dawn P. Richards , Frank W. Rockhold
, Frank W. Rockhold , David L. Schriger
, David L. Schriger , Nandi L. Siegried
, Nandi L. Siegried , Sophie Staniszewska
, Sophie Staniszewska , Rod S. Taylor
, Rod S. Taylor , Lehana Thabane
, Lehana Thabane , David Torgerson
, David Torgerson , Sunita Vohra
, Sunita Vohra , Ian R. White
, Ian R. White , Isabelle Boutron
, Isabelle Boutron
Citations

 , Somi Jeong
, Somi Jeong , Seung-Jung Kim
, Seung-Jung Kim , Ara Ko
, Ara Ko , Hyeonji Jeon
, Hyeonji Jeon
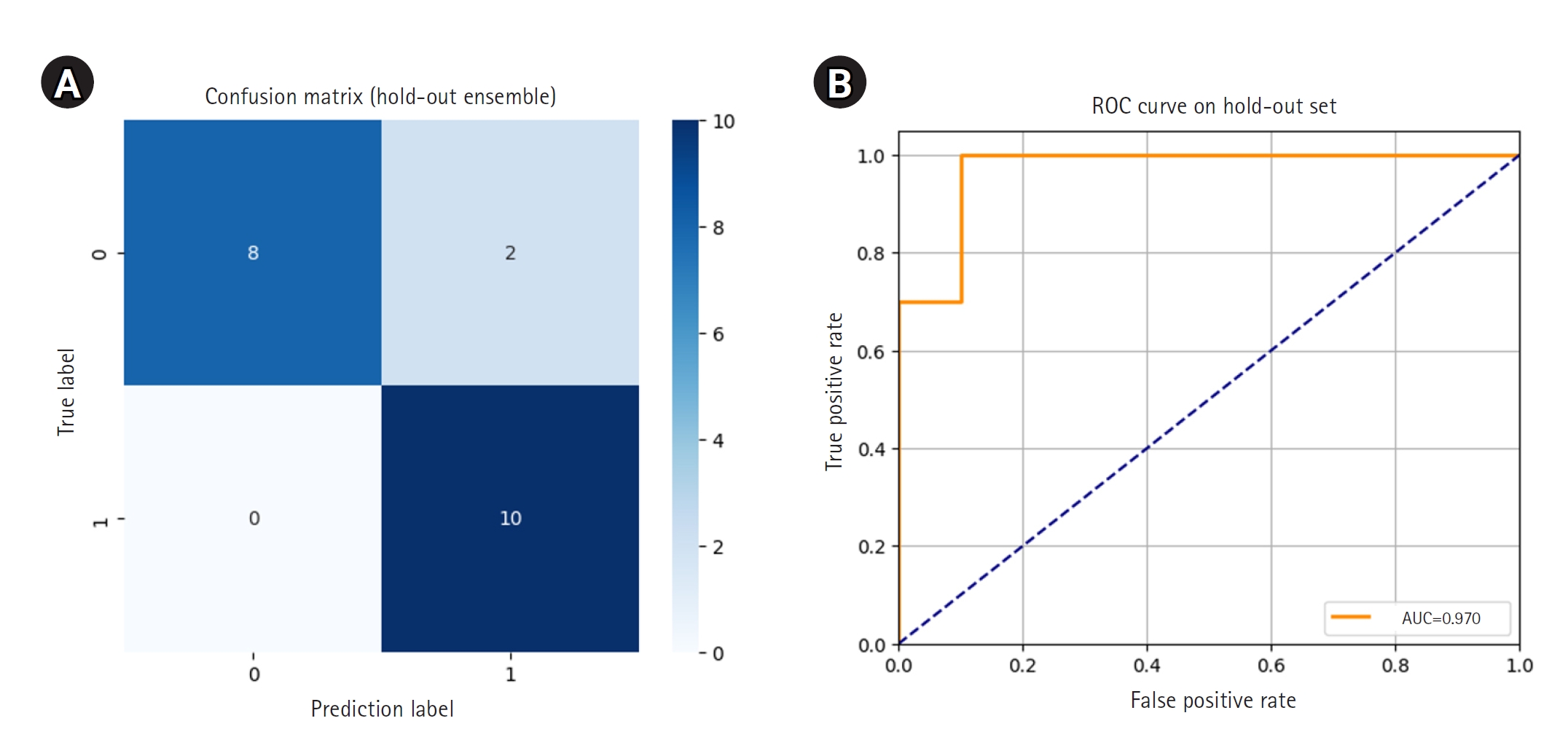
 , Sohyun Ahn
, Sohyun Ahn , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
Citations

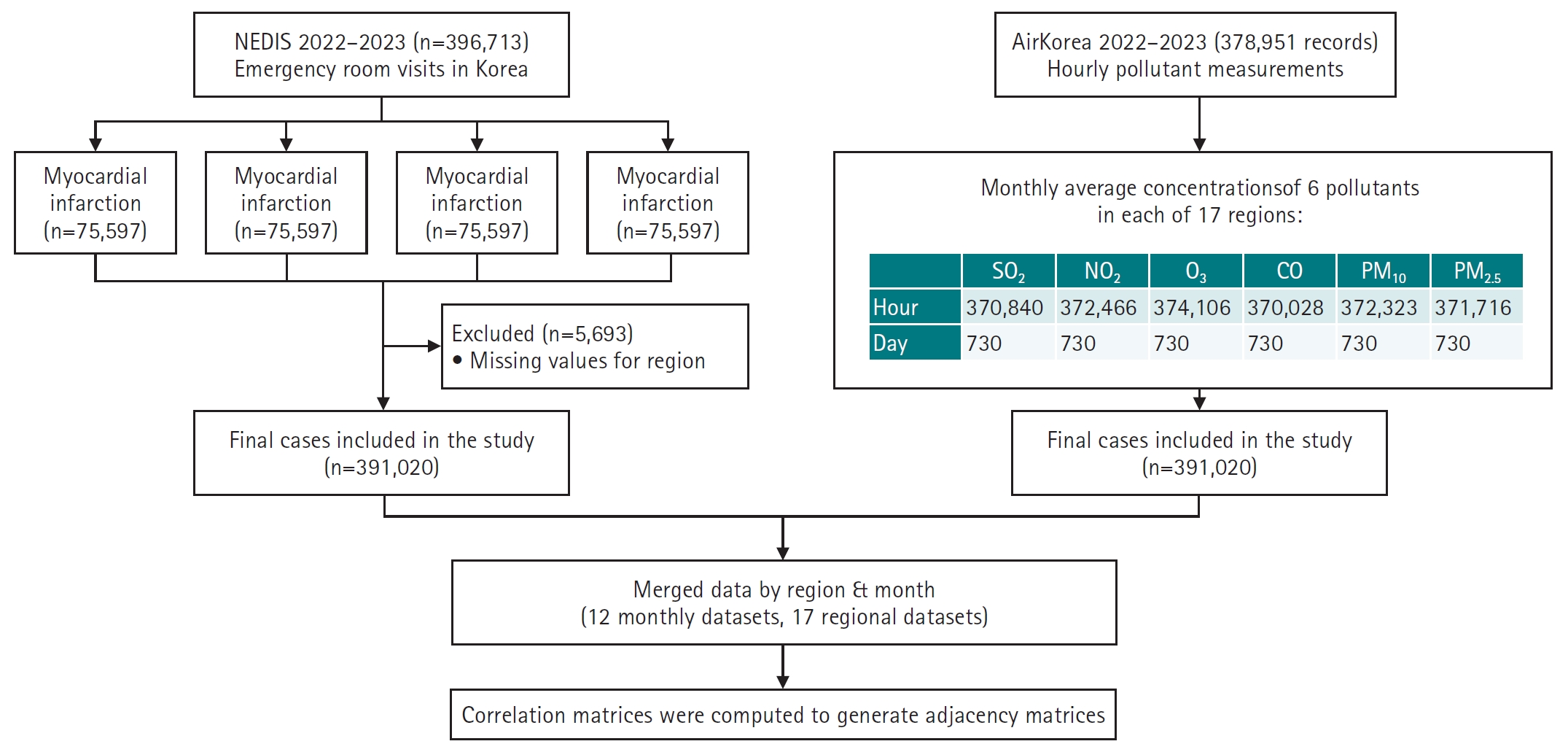
 , Seungpil Jeong
, Seungpil Jeong , Eunhee Ha
, Eunhee Ha
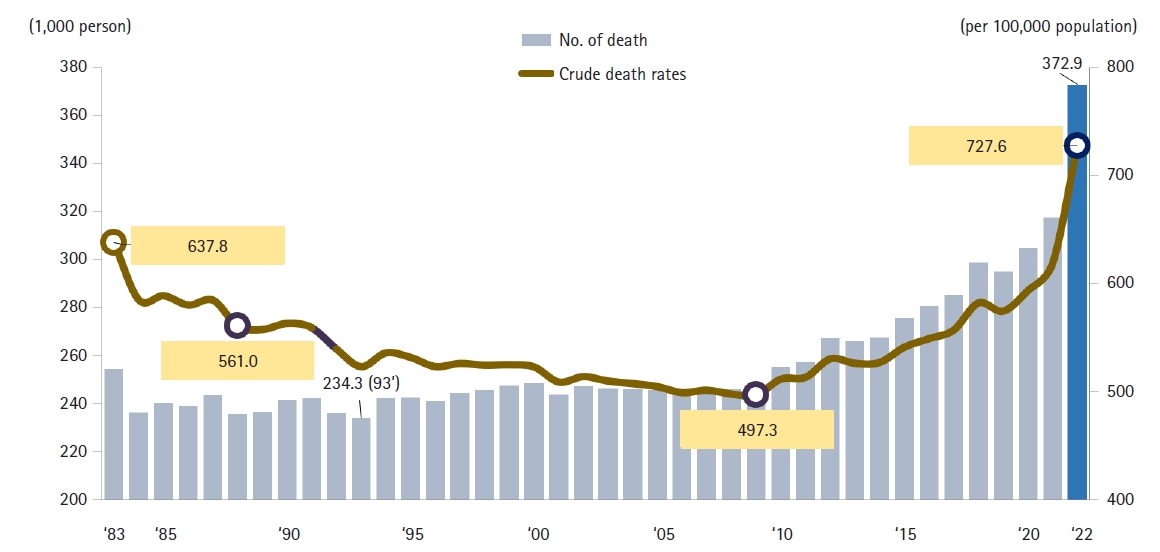
 , Juhee Seo
, Juhee Seo , Hyun Jung Park
, Hyun Jung Park
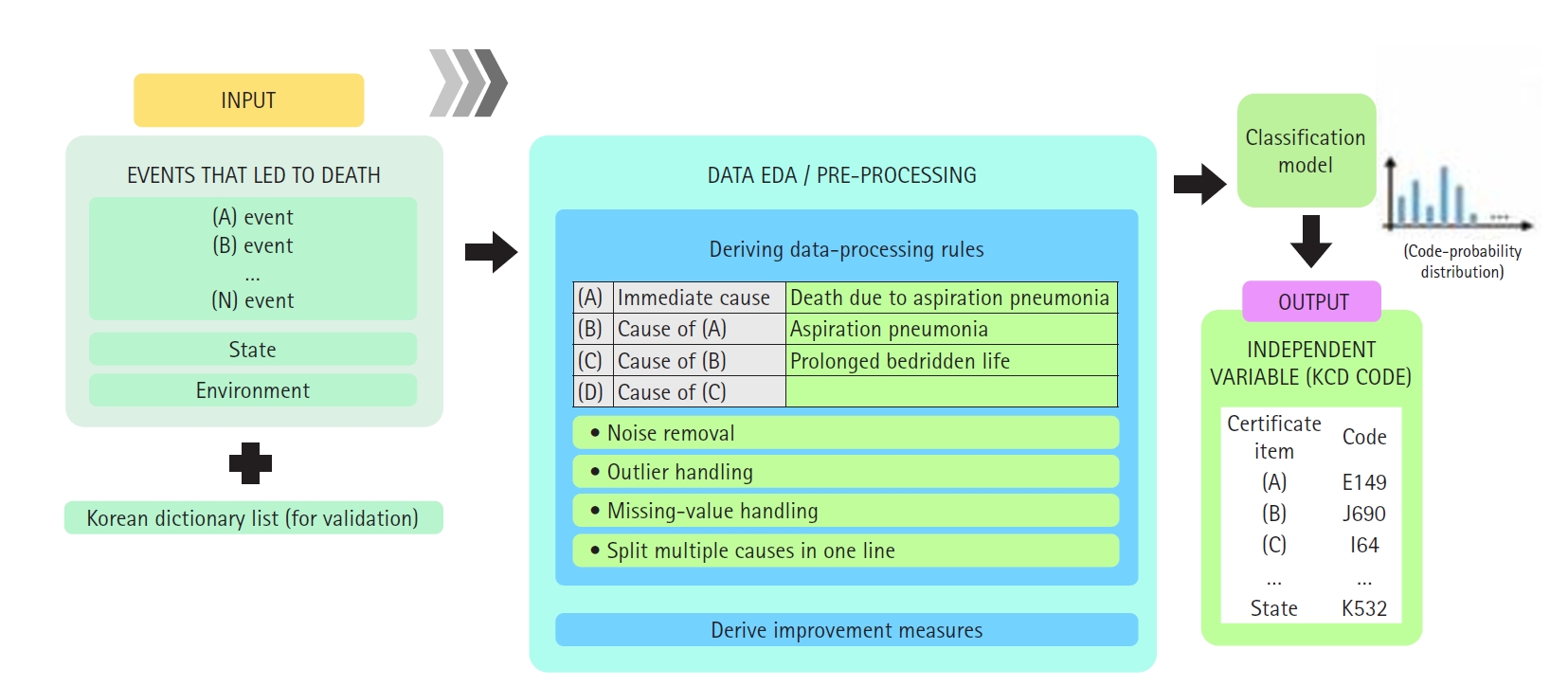
 , Gyeongmin Im
, Gyeongmin Im
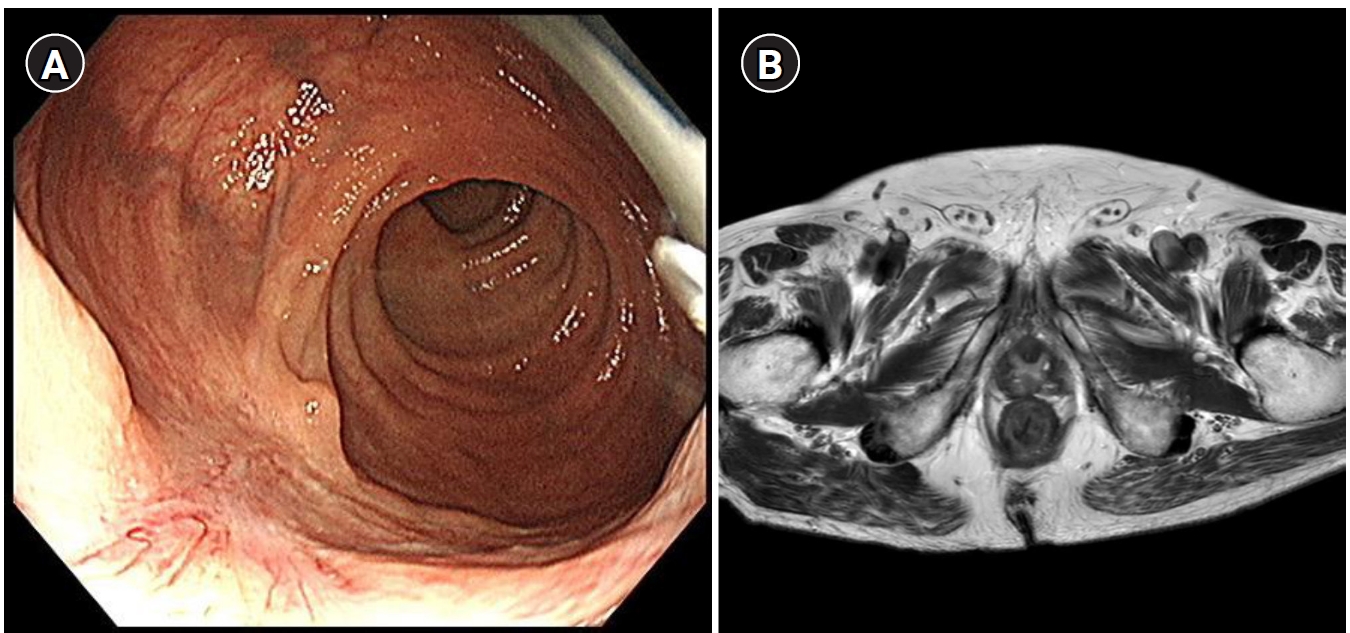

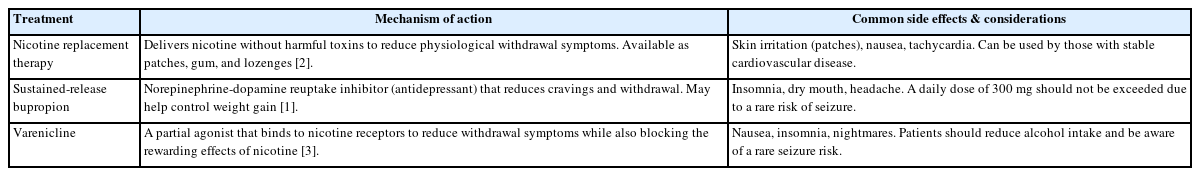
 , Jeong-Ho Chae
, Jeong-Ho Chae , Jung-Seok Choi
, Jung-Seok Choi , Yong Pil Chong
, Yong Pil Chong , Byung Chul Chun
, Byung Chul Chun , Eun Mi Chun
, Eun Mi Chun , Bo Seung Kang
, Bo Seung Kang , Dai Jin Kim
, Dai Jin Kim , Yeol Kim
, Yeol Kim , Jun Soo Kwon
, Jun Soo Kwon , Sang Haak Lee
, Sang Haak Lee , Won-Chul Lee
, Won-Chul Lee , Yu Jin Lee
, Yu Jin Lee , Jong Han Leem
, Jong Han Leem , Soo Lim
, Soo Lim , Saejong Park
, Saejong Park , Dongwook Shin
, Dongwook Shin , Hyeon Woo Yim
, Hyeon Woo Yim , Kwang Ha Yoo
, Kwang Ha Yoo , Dae Hyun Yoon
, Dae Hyun Yoon , Ho Joo Yoon
, Ho Joo Yoon
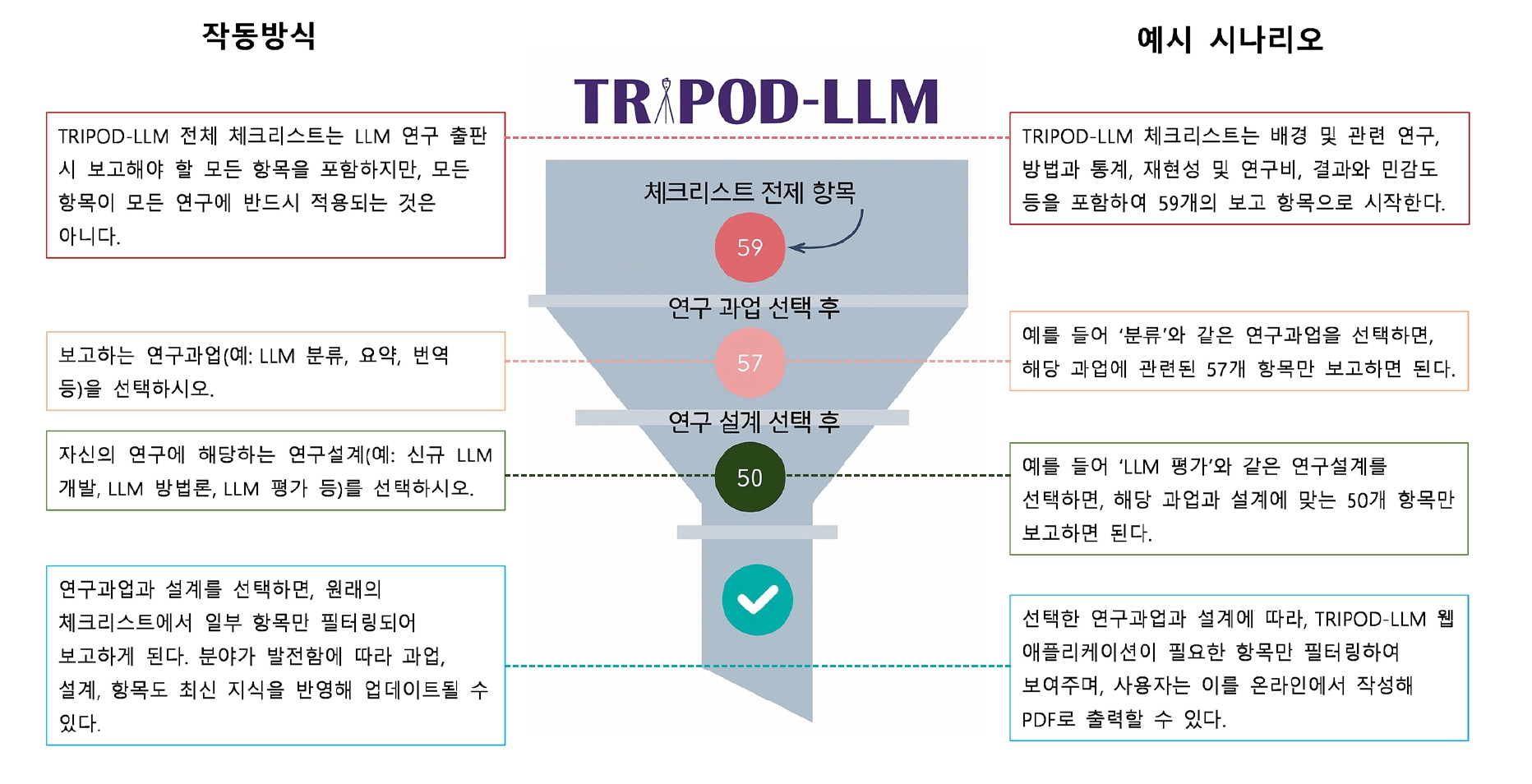
 , Majid Afshar
, Majid Afshar , Saleem Ameen
, Saleem Ameen , Yindalon Aphinyanaphongs
, Yindalon Aphinyanaphongs , Shan Chen
, Shan Chen , Giovanni Cacciamani
, Giovanni Cacciamani , Dina Demner-Fushman
, Dina Demner-Fushman , Dmitriy Dligach
, Dmitriy Dligach , Roxana Daneshjou
, Roxana Daneshjou , Chrystinne Fernandes
, Chrystinne Fernandes , Lasse Hyldig Hansen
, Lasse Hyldig Hansen , Adam Landman
, Adam Landman , Lisa Lehmann
, Lisa Lehmann , Liam G. McCoy
, Liam G. McCoy , Timothy Miller
, Timothy Miller , Amy Moreno
, Amy Moreno , Nikolaj Munch
, Nikolaj Munch , David Restrepo
, David Restrepo , Guergana Savova
, Guergana Savova , Renato Umeton
, Renato Umeton , Judy Wawira Gichoya
, Judy Wawira Gichoya , Gary S. Collins
, Gary S. Collins , Karel G. M. Moons
, Karel G. M. Moons , Leo A. Celi
, Leo A. Celi , Danielle S. Bitterman
, Danielle S. Bitterman
Citations

 , Karel G M Moons
, Karel G M Moons , Paula Dhiman
, Paula Dhiman , Richard D Riley
, Richard D Riley , Andrew L Beam
, Andrew L Beam , Ben Van Calster
, Ben Van Calster , Marzyeh Ghassemi
, Marzyeh Ghassemi , Xiaoxuan Liu
, Xiaoxuan Liu , Johannes B Reitsma
, Johannes B Reitsma , Maarten van Smeden
, Maarten van Smeden , Anne-Laure Boulesteix
, Anne-Laure Boulesteix , Jennifer Catherine Camaradou
, Jennifer Catherine Camaradou , Leo Anthony Celi
, Leo Anthony Celi , Spiros Denaxas
, Spiros Denaxas , Alastair K Denniston
, Alastair K Denniston , Ben Glocker
, Ben Glocker , Robert M Golub
, Robert M Golub , Hugh Harvey
, Hugh Harvey , Georg Heinze
, Georg Heinze , Michael M Hoffman
, Michael M Hoffman , André Pascal Kengne
, André Pascal Kengne , Emily Lam
, Emily Lam , Naomi Lee
, Naomi Lee , Elizabeth W Loder
, Elizabeth W Loder , Lena Maier-Hein
, Lena Maier-Hein , Bilal A Mateen
, Bilal A Mateen , Melissa D McCradden
, Melissa D McCradden , Lauren Oakden-Rayner
, Lauren Oakden-Rayner , Johan Ordish
, Johan Ordish , Richard Parnell
, Richard Parnell , Sherri Rose
, Sherri Rose , Karandeep Singh
, Karandeep Singh , Laure Wynants
, Laure Wynants , Patricia Logullo
, Patricia Logullo
Citations



Citations


Citations



Citations




Citations



Citations



Citations

Citations

 , Bruno B. Andrade
, Bruno B. Andrade , Ju Sang Kim
, Ju Sang Kim , Yoolwon Jeong
, Yoolwon Jeong
Citations

 , Joonil Hwang
, Joonil Hwang , Hai-Jeon Yoon
, Hai-Jeon Yoon , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn

Citations


