Most-read are based on citations from 2024 ~ 2026.
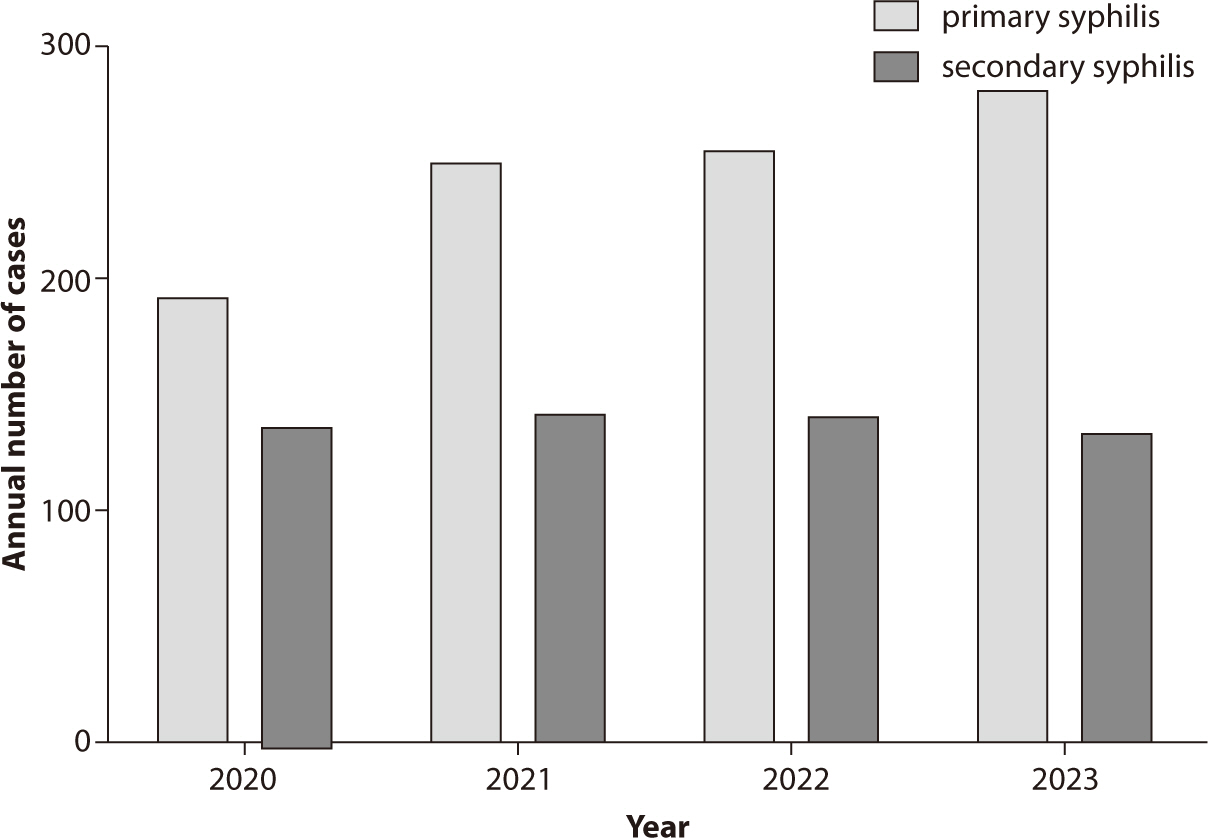

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) continue to pose significant public health
challenges in Korea, with syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia,
Citations


FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) is an innovative approach that delivers ultra-high dose rates exceeding 40 Gy in less than a second, aiming to widen the therapeutic window by minimizing damage to normal tissue while maintaining tumor control. This review explores the advancements, mechanisms, and clinical applications of FLASH-RT across various radiation sources. Electrons have been predominantly used due to technical feasibility, but their limited penetration depth restricts clinical application. Protons, offering deeper tissue penetration, are considered promising for treating deep-seated tumors despite challenges in beam delivery. Preclinical studies demonstrate that FLASH-RT reduces normal tissue toxicity in the lung, brain, skin, intestine, and heart without compromising antitumor efficacy. The mechanisms underlying the FLASH effect may involve oxygen depletion leading to transient hypoxia, reduced DNA damage in normal tissues, and modulation of immune and inflammatory responses. However, these mechanisms are incompletely understood, and inconsistent results across studies highlight the need for further research. Initial clinical studies, including treatment of cutaneous lymphoma and bone metastases, indicate the feasibility and potential benefits of FLASH-RT in patients. Challenges for clinical implementation include technical issues in dosimetry accuracy at ultra-high dose rates, adaptations in treatment planning systems, beam delivery methods, and economic considerations due to specialized equipment requirements. Future directions will involve comprehensive preclinical studies to optimize irradiation parameters, large-scale clinical trials to establish standardized protocols, and technological advancements to overcome limitations. FLASH-RT holds the potential to revolutionize radiotherapy by reducing normal tissue toxicity and improving therapeutic outcomes, but significant research is required for real-world clinical applications.
Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Treatment should be initiated for all suspected, clinical, or confirmed cases of scabies. Patients affected should be adequately isolated, and high-risk groups with close contact histories should be treated regardless of their symptoms. Optimal treatment strategies can be selected based on age, clinical subtype, and the patient's health status. In Korea, commercially available preparations for scabies treatment include topical 5% permethrin, topical 10% crotamiton, and oral ivermectin. Topical 5% permethrin is the first-line selective treatment for both classic and crusted scabies. Alternative treatments include topical 10% crotamiton and oral ivermectin. After completing treatment, follow-up visits at 2 and 4 weeks are recommended to monitor the therapeutic response. Treatment is considered to have failed if scabies mites or burrows are detected, new clinical characteristics develop, or there is an aggravation of pruritus. Scabies itch should be adequately managed with emollients, oral antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids. Preventive measures, including personal hygiene, patient education, and environmental control, should besd implemented to reduce the transmission of scabies.
 , Ssirai Kim, Sun Young Lee
, Ssirai Kim, Sun Young Lee
This study reviewed quantitative research on the health of sexual and gender minorities (SGMs) in Korea and aimed to propose a role for healthcare professionals in improving their health and access to medical care. We searched PubMed through February 29, 2024 for articles published since 2000, using terms related to SGMs and the keyword “Korea.” This process yielded 33 quantitative studies on Korean SGMs. Of these, 17 focused on sexual minorities and 16 on gender minorities. The findings indicate that Korean SGMs experience many symptoms of depression and anxiety, as well as high rates of suicidal ideation, planning, and attempts. They also report diminished health-related quality of life. SGM individuals who have faced discrimination or pressure to change their sexual or gender identity face an elevated risk of mental health issues. To improve the health of Korean SGMs and improve their access to healthcare, we recommend several approaches. First, more research on the health of Korean SGMs is necessary. Second, education and training programs for health professionals are essential to promote their understanding of SGM health issues and their advocacy for SGM health. Third, strategies are required to develop and implement program interventions that improve SGM health, such as increasing the availability of gender-affirming care, which is known to benefit the health of transgender and gender-diverse individuals. Finally, healthcare professionals should actively advocate for SGM health and call for shifts in public perception and institutional change, grounded in a broad understanding of SGMs and their health needs.
Citations

 , Juhee Seo
, Juhee Seo , Hyun Jung Park
, Hyun Jung Park

Heart failure (HF) represents a serious public health concern, characterized by substantial morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in pharmacological management, a gap persists in understanding and accounting for sex-related differences in HF treatment. This review was performed to clarify the impact of sex on the clinical outcomes of HF medications. Insights from various clinical trials and studies have highlighted differences between men and women in drug responses and adverse effects, indicating the need for a more nuanced approach to HF management. Promoting greater representation of women in clinical trials and the development of research methodologies that consider sex differences are crucial steps in advancing precision medicine. Such efforts ensure that therapeutic strategies are optimally tailored to the unique biological and genetic profiles of each person. Ultimately, this review emphasizes the vital need for a more inclusive and personalized approach to HF pharmacotherapy, underscoring the critical role of sex-related differences in shaping effective and individualized treatment pathways.
Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the parasite
Citations

 , Eun-Kyoung Pang
, Eun-Kyoung Pang
Citations



Citations

 , Karina Sylvana Gani
, Karina Sylvana Gani , Erica Kholinne
, Erica Kholinne
A Bankart lesion is a tear of the labrum, the ring of cartilage that encircles the shoulder joint socket, that can occur when the shoulder is dislocated. This injury frequently affects young athletes and is associated with shoulder instability. This review was performed to provide an overview of anterior shoulder instability, with an emphasis on rehabilitation and the return to sports following arthroscopic Bankart repair. We searched the Google Scholar and PubMed academic databases through February 18th, 2024, utilizing keywords including “arthroscopic Bankart repair” and “return to sports”. Our findings indicate that athletes who undergo arthroscopic Bankart repair exhibit higher rates of returning to sports compared to those who receive other anterior shoulder stabilization procedures. Several factors are considered when determining readiness to return to athletics, including time elapsed since surgery, type of sport, strength, range of motion, pain, and proprioception. Surgeons typically advise athletes to wait approximately 6 months after surgery before resuming sports activities. They also recommend that athletes regain at least 80% of the strength of the uninjured shoulder or achieve strength levels comparable to those prior to the injury. Additionally, patients are expected to attain a full range of motion without pain, which should be symmetrical to the uninjured side, and demonstrate improved proprioception in the shoulder. The sport in which an athlete participates can also influence the timeline for return. Those involved in overhead sports, like baseball or tennis, often experience lower success rates in returning to their sport compared to athletes from other disciplines.
Citations

 , Erik von Elm
, Erik von Elm , Douglas G. Altman
, Douglas G. Altman , Peter C. Gøtzsche, Cynthia D. Mulrow
, Peter C. Gøtzsche, Cynthia D. Mulrow , Stuart J. Pocock
, Stuart J. Pocock , Charles Poole
, Charles Poole , James J. Schlesselman
, James J. Schlesselman , Matthias Egger
, Matthias Egger
의학 연구의 대부분은 관찰 연구이다. 관찰 연구의 보고는 종종 불충분한 품질을 보이기도 한다. 부실한 보고는 연구의 강점과 약점을 평가하고 연구
결과의 일반화 가능성을 평가하는 데 방해가 된다. 방법론 전문가, 연구자, 편집자 그룹은 경험적 근거와 이론적 고려 사항을 고려하여 관찰 연구
보고의 질을 개선하기 위한 역학 STROBE 권고안을 개발했다. STROBE statement은 논문의 제목, 초록, 서론, 방법, 결과 및
토론 부분에 대한 22개 항목의 체크리스트로 구성되어 있다. 18개 항목은 코호트연구, 환자 대조군 연구, 단면연구에 공통으로 적용되며, 4개
항목은 세 가지 연구설계 각각에 따라 다르다. STROBE statement는 저자에게 관찰 연구에 대한 보고를 개선하는 방법에 대한 지침을
제공하고 심사자, 편집자 및 독자가 연구를 비판적으로 평가하고 해석하는 데 도움이 된다. 이 설명 문서는 STROBE statement의 사용,
이해 및 보급을 향상 시키는 것이 목적이다. 각 체크리스트 항목의 의미와 근거가 제시되어 있다. 각 항목에 대해 하나 또는 여러 개의 출판된
예시 논문과 가능한 경우 관련 경험적 연구 및 방법론 문헌에 대한 내용이 참고사항으로 제공된다. 유용한 흐름도의 예도 포함되어 있다. 본 문서
및 관련 웹사이트(
Citations

Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by environmental, genetic, dietary, and hormonal factors. This underscores the importance of postoperative nutritional management in supporting recovery, minimizing complications, and enhancing long-term outcomes. This review synthesizes clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and observational studies to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary interventions for breast cancer patients following surgery. Post-surgical nutritional care is centered around three primary objectives: supporting wound healing through high-quality protein intake, maintaining optimal nutritional status to prevent malnutrition, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of recurrence. To achieve these objectives, postoperative dietary strategies focus on several key components: ensuring adequate hydration for metabolic processes and tissue repair, consuming a balanced diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits to mitigate oxidative stress, incorporating whole grains to support overall healing, and maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality protein from sources such as fish, meat, and dairy products to aid tissue repair and immune system recovery. Patients are also advised to avoid alcohol, limit saturated fats, and reduce intake of salty, sugary, and smoked foods to minimize inflammation. As research progresses, the implementation of personalized dietary plans remains essential for optimizing recovery outcomes in breast cancer patients.
 , Heisook Lee
, Heisook Lee
This review aims to highlight the importance of research on structural, functional, molecular-biological, and disease-specific sex differences in the brain, and to examine current bibliometric indicators related to research on sex differences. The Web of Science Core Collection was searched for related articles from 2010 to 2023. Structural and functional brain differences according to sex, including variations in communication patterns between hemispheres, may play a role in mental disorders. Sex differences in neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and γ-aminobutyric acid contribute to disparities in mental health, addiction, and neurodevelopmental conditions. Neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia exhibit sex-based differences in prevalence, symptoms, brain changes, and neurotransmitter disruptions under hormonal influence. There is a growing body of research on depression, adolescence, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and cognition, highlighting the importance of considering sex/gender factors. Recent studies on sex differences in brain diseases have identified variations in brain structure, function, and neurophysiological substances, as well as in hormones and genes between the sexes. The incidence of psychiatric disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer’s disease is increasingly being linked to sex differences, and the need for research into the mechanisms underlying these differences is gaining recognition. However, there remains a significant gap in sex-specific neuroscience research related to the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and management of these conditions. Advancing inclusive research will require comprehensive training, a consensus on methodology, diverse perspectives through collaborative frameworks, governmental/institutional support, and dedicated funding to create suitable research environments and implementation strategies.
Citations

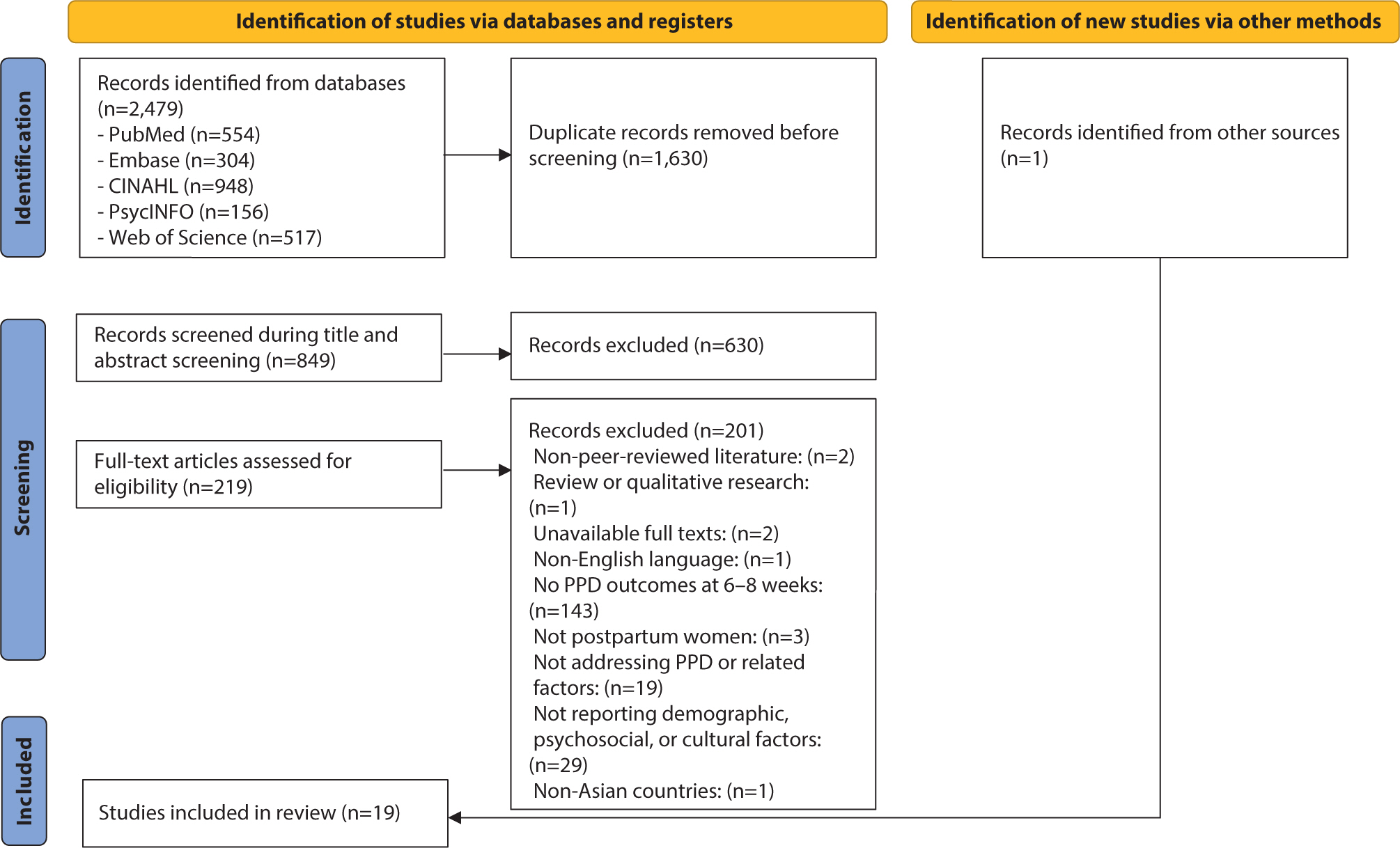
The prevalence of postpartum depression (PPD) in Asia is reported to range from 13.53% to 22.31%. However, there remains a gap in the identification of PPD, particularly regarding cultural cutoff points. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to determine the prevalence and associated factors of PPD in Eastern, South-eastern, Western, and Southern Asian countries and analyze the cutoff points of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) used across these countries. Following Arksey and O'Malley’s five-step scoping review framework, the population was defined as mothers, the concept as the EPDS, and the context as the Asian region. A literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. The data analysis focused on demographic characteristics, EPDS cutoffs and features, PPD prevalence, and its associated factors. Nineteen studies were selected. Most countries used translated versions of the EPDS with demonstrated reliability and validity. The cutoff scores varied, with most using scores of 10 or higher. The prevalence of PPD ranged from 5.1% to 78.7%. Key associated factors for PPD included cultural factors such as relationships with in-laws and preferences for the newborn’s sex. To improve the accuracy of PPD screening in Asia, the EPDS should be used consistently, and appropriate cutoff criteria must be established. In addition, prevention strategies and programs that reflect the cultural characteristics and social context of Asia need to be developed for the early detection and prevention of PPD.
Citations


Citations


Citations

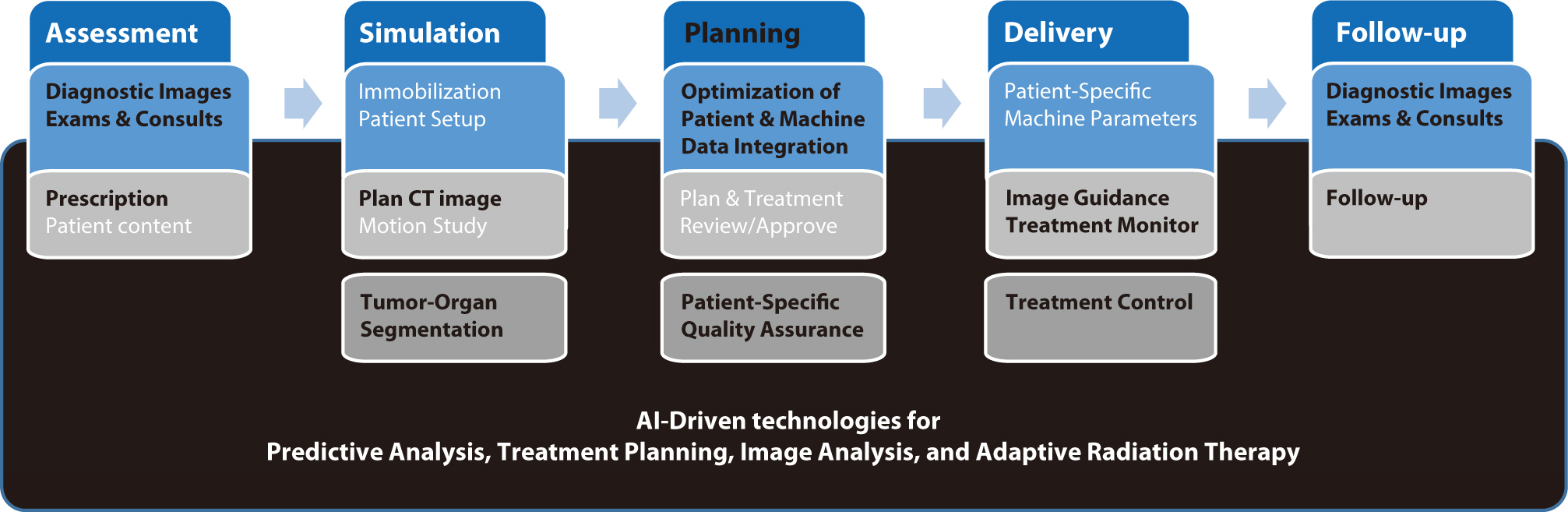
 , YoungMoon Goh
, YoungMoon Goh , Jungwon Kwak
, Jungwon Kwak
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various medical fields, including radiation oncology. This review explores the integration of AI into radiation oncology, highlighting both challenges and opportunities. AI can improve the precision, efficiency, and outcomes of radiation therapy by optimizing treatment planning, enhancing image analysis, facilitating adaptive radiation therapy, and enabling predictive analytics. Through the analysis of large datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters, AI can automate complex tasks, reduce planning time, and improve accuracy. In image analysis, AI-driven techniques enhance tumor detection and segmentation by processing data from CT, MRI, and PET scans to enable precise tumor delineation. In adaptive radiation therapy, AI is beneficial because it allows real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on changes in patient anatomy and tumor size, thereby improving treatment accuracy and effectiveness. Predictive analytics using historical patient data can predict treatment outcomes and potential complications, guiding clinical decision-making and enabling more personalized treatment strategies. Challenges to AI adoption in radiation oncology include ensuring data quality and quantity, achieving interoperability and standardization, addressing regulatory and ethical considerations, and overcoming resistance to clinical implementation. Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is crucial to overcoming these obstacles. By addressing these challenges, AI can drive advancements in radiation therapy, improving patient care and operational efficiencies. This review presents an overview of the current state of AI integration in radiation oncology and insights into future directions for research and clinical practice.
Citations


Citations

 , Woong Sub Koom
, Woong Sub Koom , Hong In Yoon
, Hong In Yoon , Kyung Hwan Kim
, Kyung Hwan Kim , Chan Woo Wee
, Chan Woo Wee , Jaeho Cho
, Jaeho Cho , Yong Bae Kim
, Yong Bae Kim , Ki Chang Keum
, Ki Chang Keum , Ik Jae Lee
, Ik Jae Lee
Carbon-ion radiotherapy (CIRT) offers superior dose distributions and greater biological effectiveness than conventional photon-based radiotherapy (RT). Due to its higher linear energy transfer and relative biological effectiveness, CIRT is particularly effective against radioresistant tumors and those located near critical organs. Since the first dedicated CIRT facility was established in Japan in 1994, CIRT has demonstrated remarkable efficacy against various malignancies, including head and neck tumors, skull base and upper cervical spine tumors, non-small-cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and bone and soft tissue sarcomas. This narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of the current status of CIRT, highlighting its clinical indications and future directions. According to clinical studies, CIRT achieves high local control rates with manageable toxicity across multiple cancer types. For instance, in head and neck tumors (e.g., adenoid cystic carcinoma and mucosal melanoma), CIRT has achieved local control rates exceeding 80%. In early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer, CIRT has resulted in local control rates over 90% with minimal toxicity. Moreover, CIRT has shown promise in treating challenging cases of hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic cancer, where conventional therapies are limited. Nonetheless, the global adoption of CIRT remains limited due to high costs and complexity. Future directions include conducting randomized controlled trials to establish high-level evidence, integrating new technologies such as ultrahigh-dose-rate (FLASH) therapy, and expanding CIRT facilities globally with strategic planning and cost-effectiveness analyses. If these challenges are addressed, CIRT is poised to play a transformative role in cancer treatment, improving survival rates and the quality of life.
Citations

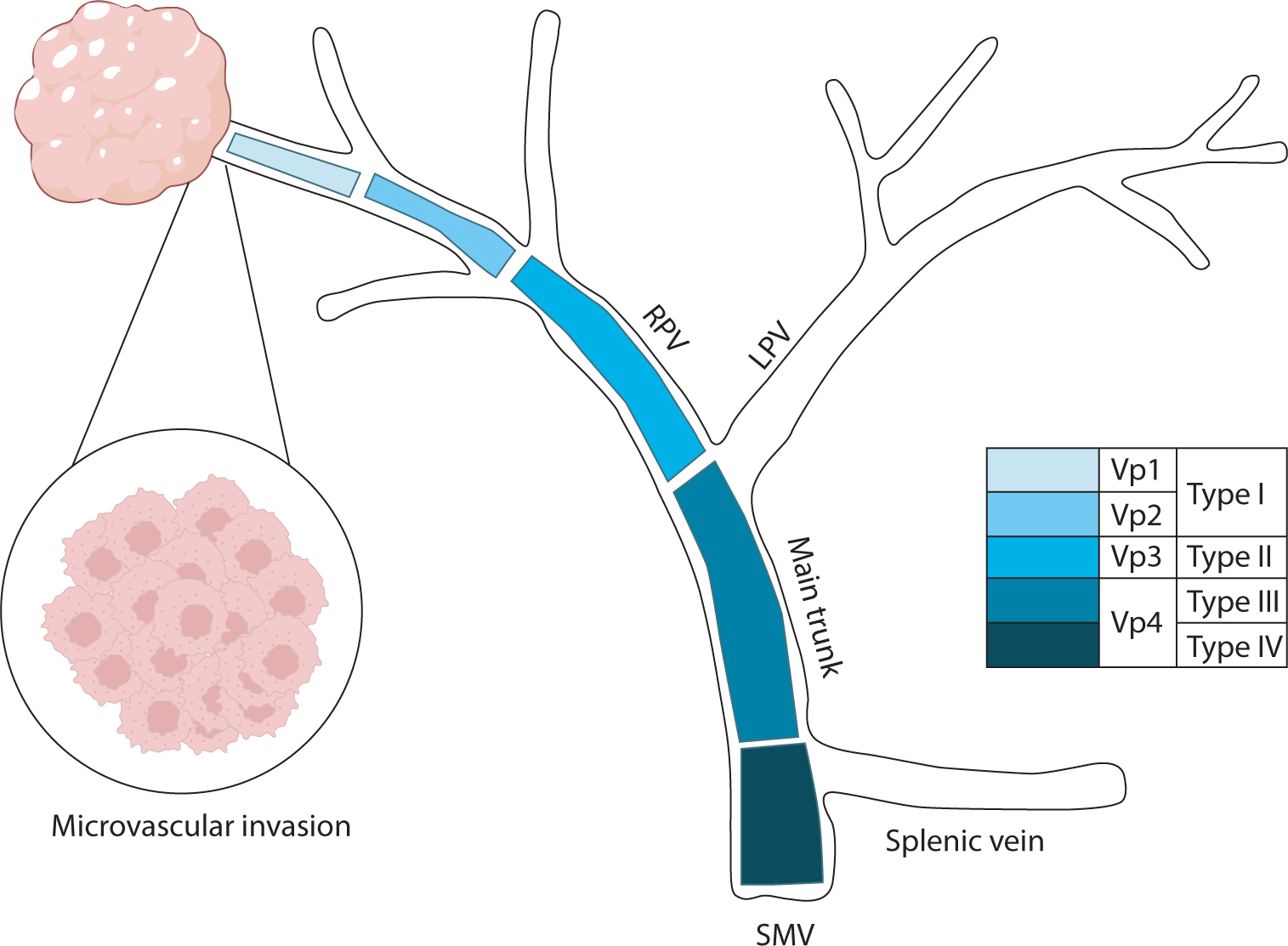
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.
Citations

This review examines the challenges associated with occupational disease surveillance in Korea, particularly emphasizing the limitations of current data sources such as the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance (IACI) statistics and special health examinations. The IACI system undercounts cases due to its emphasis on severe diseases and restrictions on approvals. Special health examinations, although they cover a broad workforce, are constrained by their annual scheduling, which leads to missed acute illnesses and subclinical conditions. The paper also explores the history of occupational disease surveillance in Korea, highlighting the fragmented and disease-specific approach of earlier systems. The authors introduce the newly established Korea Occupational Disease Surveillance Center (KODSC), a comprehensive nationwide system designed to gather, analyze, and interpret data on occupational diseases through a network of regional centers. By incorporating hospital-based surveillance and focusing on acute poisonings and other sentinel events, the KODSC aims to overcome the limitations of previous systems and promote collaboration with various agencies. Although it is still in the early stages of implementation, the KODSC demonstrates potential for improving data accuracy and contributing valuable insights for public health policy.
Citations


Citations

 , Minsung Kim
, Minsung Kim
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols are designed to minimize surgical stress, preserve physiological function, and expedite recovery through standardized perioperative care for primary colorectal surgery patients. This narrative review explores the benefits of current ERAS protocols in improving outcomes for these patients and provides insights into future advancements. Numerous studies have shown that ERAS protocols significantly reduce the length of hospital stays by several days compared to conventional care. Additionally, the implementation of ERAS is linked to a reduction in postoperative complications, including lower incidences of surgical site infections, anastomotic leaks, and postoperative ileus. Patients adhering to ERAS protocols also benefit from quicker gastrointestinal recovery, marked by an earlier return of bowel function. Some research indicates that colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery with ERAS protocols may experience improved overall survival rates. High compliance with ERAS protocols leads to better outcomes, yet achieving full adherence continues to be a challenge. Despite these advantages, implementation challenges persist, with compliance rates affected by varying clinical practices and resource availability. However, the future of ERAS looks promising with the incorporation of prehabilitation strategies and technologies such as wearable devices and telemedicine. These innovations provide real-time monitoring, enhance patient engagement, and improve postoperative follow-up, potentially transforming perioperative care in colorectal surgery and offering new avenues for enhanced patient outcomes.
Citations


Citations

Autism spectrum disorder involves challenges in social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Historically, males have received autism diagnoses at comparatively high rates, prompting an underrepresentation of females in research and an incomplete understanding of sex-specific symptom presentations and comorbidities. This review examines sex differences in the prevalence of common comorbidities of autism to inform tailored clinical practices. These conditions include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety disorders, conduct disorder, depression, epilepsy, intellectual disability, and tic disorders. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is prevalent in both sexes; however, females may more frequently exhibit the inattentive subtype. Anxiety disorders display inconsistent sex differences, while conduct disorder more frequently impacts males. Depression becomes more common with age; some studies indicate more pronounced symptoms in adolescent girls, while others suggest greater severity in males. Epilepsy is more prevalent in females, especially those with intellectual disabilities. Despite displaying a male predominance, intellectual disability may exacerbate the severity of autism to a greater degree in females. No clear sex differences have been found regarding tic disorders. Overall, contributors to sex-based differences include biases stemming from male-centric diagnostic tools, compensatory behaviors like camouflaging in females, genetic and neurobiological differences, and the developmental trajectories of comorbidities. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing sensitive diagnostics and sex-specific interventions. Inconsistencies in the literature highlight the need for longitudinal studies with large, diverse samples to investigate autism comorbidities across the lifespan. Understanding sex differences could facilitate earlier identification, improved care, and personalized interventions, thus enhancing quality of life for individuals with autism.
Citations

 , Won Woong Lee
, Won Woong Lee , Haewoo Lee
, Haewoo Lee , Jin Yong Jun
, Jin Yong Jun , Jin-Won Noh
, Jin-Won Noh
Citations


Citations


Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the leading cause of mortality worldwide, driven primarily by atherogenesis. Recent efforts to understand sex differences in CAD have revealed distinct patterns in disease burden, risk factors, and clinical presentations. This review examines these sex differences in CAD, underscoring the importance of customized diagnostic and management strategies. Although men typically have higher rates of CAD prevalence and incidence, women face unique challenges, such as delayed diagnosis, atypical symptoms, and lower rates of medication prescription. Hormonal, genetic, and lifestyle factors all play a role in these disparities, with estrogen notably reducing CAD risk in women. Nontraditional risk factors, including chronic inflammation, psychological stress, socioeconomic status, and reproductive history, also contribute to CAD development and are often neglected in clinical settings. Addressing these differences requires increased awareness, more accurate diagnosis, and equitable healthcare access for both sexes. Furthermore, greater inclusion of women in CAD research is essential to better understand sex-specific mechanisms and optimize treatment outcomes. Personalizing CAD management based on sex-specific knowledge has the potential to improve prognosis and decrease disease incidence for both men and women.
Citations


This study analyzed drug-induced death statistics in Korea between 2011 and 2021.
Cause-of-death statistics data from Statistics Korea were examined based on the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision.
In 2021, there were 559 drug-induced deaths, marking a 172.7% increase compared to 2011, which recorded 205 deaths. The rate of drug-induced deaths per 100,000 people was 1.1 in 2021, up 153.6% from 0.4 in 2011. The mortality rate for men aged 25−34 years and women aged 35−44 years each increased fourfold from 2011 to 2021: from 0.3 to 1.2 for the former and 0.3 to 1.3 for the latter. Of the drug-induced deaths in 2021, 75.0% (419/559) were due to intentional self-harm, and 10.4% (58/559) were accidental. The number of deaths attributed to medical narcotics in 2021 was 169, a 5.5-fold increase from 2011. The most commonly implicated drugs in these deaths were sedative-hypnotic drugs, benzodiazepines, and opioids. Sedative-hypnotic drugs and benzodiazepines were frequently involved in cases of intentional self-harm, while opioids and psychostimulants were more often associated with accidental deaths.
The death rate from drug-induced causes is considerably lower in Korea than in the United States (1.1 vs. 29.2). However, the number of such deaths has increased recently. Since these deaths occur predominantly among younger age groups and are often the result of intentional self-harm, there is a clear need for systematic management and the implementation of targeted policies.
Citations

 , Claudia Santosa
, Claudia Santosa , Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne
, Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne , Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara
, Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara 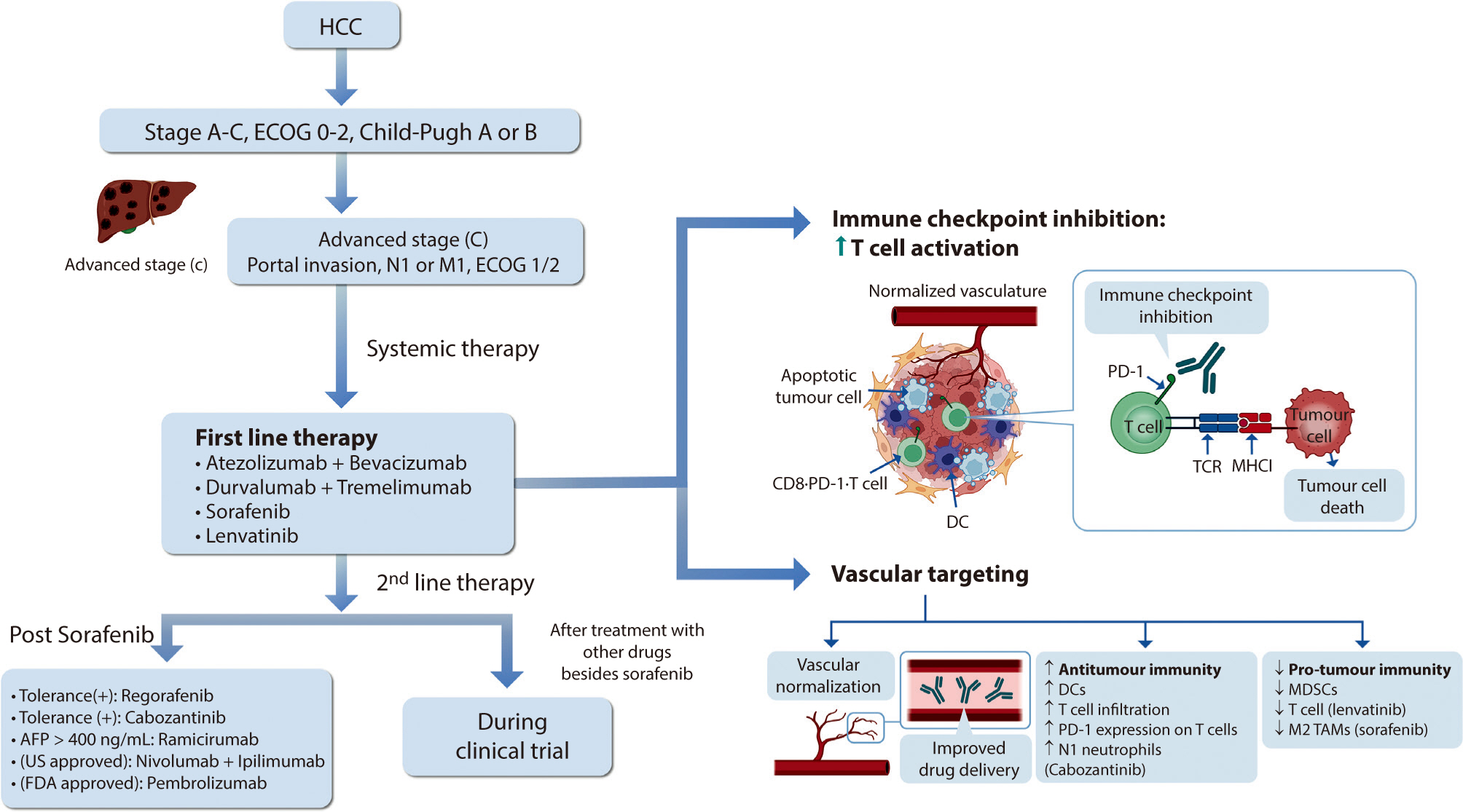
 , Jeong-Ju Yoo
, Jeong-Ju Yoo , Sang Gyune Kim
, Sang Gyune Kim , Young Seok Kim
, Young Seok Kim
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a critical health concern in Korea, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer mortality and imposing substantial economic burdens, particularly among the working-age population. This review examines recent advancements in treating advanced HCC, referencing the updated 2022 HCC guidelines and the Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer system. Historically, first-line systemic therapies included sorafenib and lenvatinib, with regorafenib, cabozantinib, or ramucirumab serving as second-line options. Since 2020, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown superior overall survival than sorafenib, leading to the adoption of combination therapies such as atezolizumab with bevacizumab and durvalumab with tremelimumab as first-line treatments. The IMbrave150 study demonstrated that atezolizumab–bevacizumab significantly extended median overall survival and progression-free survival, with the longest survival reported in any phase 3 trial for advanced HCC. Similarly, the HIMALAYA study indicated that durvalumab combined with tremelimumab significantly improved survival rates. Second-line therapies now include regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab, nivolumab with ipilimumab, and pembrolizumab, each offering benefits for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, these therapies are associated with side effects that require careful management. Traditional targeted therapies can lead to hypertension, cardiovascular events, and hand-foot skin reactions, whereas immune checkpoint inhibitors may cause immune-related adverse events affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. Clinicians must be well-versed in these treatments and their potential side effects to provide optimal patient care. The emergence of combination therapies targeting complex biological pathways signifies a new paradigm in HCC treatment, emphasizing the importance of continuous education and vigilant monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Citations

This review describes a psychological support service designed to address post-traumatic stress disorder in workers impacted by workplace injuries, assisting in their recovery and facilitating their return to work. It explores the rationale and context behind establishing trauma counseling centers for these individuals, along with the status, roles, future directions, and recommendations for these centers. The review details the operational framework and functions of the workplace injury trauma management program, the scope of the impacts of such injury, the groups targeted for crisis intervention, and the psychological interventions tailored to each stage of recovery. Initiated as a pilot project in 2018, trauma counseling centers for workers have gradually become more common, with 23 centers in operation across Korea as of 2024.
Citations

Health and safety issues in micro and small enterprises (MSEs) are recognized as a global challenge. This study aimed to examine Workers' Health Centers (WHCs) as a representative public organization providing occupational health services to MSEs in Korea. WHCs were established in 2011 after a trial period aimed at addressing occupational diseases in MSEs with limited resources. As of 2024, there are 24 WHCs, 22 branch offices, and 23 trauma counseling centers for workers. These health centers are managed by the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency, with their actual operation delegated to private organizations. Each WHC employs an average of 13 staff members and is organized into four specialized teams: cardiovascular disease prevention, workplace environment improvement, musculoskeletal disease prevention, and occupational stress management. These centers also offer common basic programs along with region-specific specialized initiatives. In 2023, the total cumulative number of users reached 203,877, with employees from MSEs comprising approximately 88.5% of the total. WHCs can thus be seen as playing a pivotal role as case managers of health requirements in the workplace by fostering strong relationships with MSEs and linking them to other relevant programs through a problem-solving-oriented approach. Given the limited resources of these enterprises, proactive policies and the equitable application of safety and health regulations are essential. A balanced strategy that combines regulatory enforcement with practical assistance is critical to ensure the success of WHCs in improving health and safety conditions in MSEs.

The availability of combined antiretroviral therapy has significantly reduced the number of new HIV infections and the associated mortality, and HIV infection has become a chronic disease with long-term survival. In Korea, more than 1,000 new HIV infections have been registered annually since 2013. After peaking at 1,223 in 2019, the number of new infections decreased between 2020 and 2023. In 2023, the majority of newly HIV-infected people were men, and the proportions of young people under 40 years, homosexual contacts and foreigners increased. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related deaths from opportunistic infections associated with immunosuppression and AIDS-defining cancers are gradually decreasing, whereas non-AIDS defining comorbidities such as non-AIDS defining cancers, cardiovascular disease and metabolic complications are emerging as major causes of death. Since the introduction of zidovudine, approximately 30 antiretroviral drugs have been approved for the treatment of HIV infection. Early and continuous antiretroviral treatment for all people living with HIV is an effective strategy for maintaining viral suppression and preventing transmission of HIV infection. In conclusion, achieving the 95–95–95 target among those living with HIV in Korea requires multifaceted efforts to improve early diagnosis, early and proper treatment of HIV infection including the management of chronic diseases, and adherence to antiretroviral therapy.
Citations

 , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
The capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) have recently surged, largely due to advancements in deep learning inspired by the structure and function of the neural networks of the human brain. In the medical field, the impact of AI spans from diagnostics and treatment recommendations to patient engagement and monitoring, considerably improving efficiency and outcomes. The clinical integration of AI has also been examined in specialties, including pathology, radiology, and oncology. General surgery primarily involves manual manipulation and includes preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care, all of which are critical for saving lives. Other fields have strived to utilize and adopt AI; nonetheless, general surgery appears to have retrogressed. In this review, we analyzed the published research, to understand how the application of AI in general surgery differs from that in other medical fields. Based on previous research in other fields, the application of AI in the preoperative stage is nearing feasibility. Ongoing research efforts aim to utilize AI to improve and predict operative outcomes, enhance performance, and improve patient care. However, the use of AI in the operating room remains significantly understudied. Moreover, ethical responsibilities are associated with such research, necessitating extensive work to gather evidence. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and leveraging lessons from AI success stories in other fields, AI tools could be specifically tailored for general surgery. Surgeons should be prepared for the integration of AI into clinical practice to achieve better outcomes; therefore, the time has come to consider ethical and legal implications.
Citations

 , Sooyoung Huh
, Sooyoung Huh , Haesook Seo
, Haesook Seo
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the first seasonal influenza epidemic was declared in the 37th week of 2022 in Korea and has continued through the winter of 2023–2024. However, this finding has not been observed in the United States and Europe. The present study aimed to determine whether the prolonged influenza epidemic in Korea from 2022 to 2023 was caused by using a different influenza epidemic threshold compared to the thresholds used in the United States and Europe.
Korea, the United States, and Europe use different methods to set seasonal influenza epidemic thresholds. First, we calculated the influenza epidemic thresholds for influenza seasons using the different methods of those three regions. Using these epidemic thresholds, we then compared the duration of influenza epidemics for the most recent three influenza seasons.
The epidemic thresholds estimated by the Korean method were lower than those by the other methods, and the epidemic periods defined using the Korean threshold were estimated to be longer than those defined by the other regions’ thresholds.
A low influenza epidemic threshold may have contributed to the prolonged influenza epidemic in Korea, which was declared in 2022 and has continued until late 2023. A more reliable epidemic threshold for seasonal influenza surveillance needs to be established in Korea.
Citations

 , Taek Chung
, Taek Chung , Dong Kyu Kim
, Dong Kyu Kim , Hyungjin Rhee
, Hyungjin Rhee
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is a heterogeneous bile duct adenocarcinoma with a rising global incidence and a poor prognosis. This review aims to present a comprehensive overview of the most recent radiological research on iCCA, focusing on its histopathologic subclassification and the use of imaging findings to predict prognosis and inform treatment decisions. Histologically, iCCA is subclassified into small duct (SD-iCCA) and large duct (LD-iCCA) types. SD-iCCA typically arises in the peripheral small bile ducts and is often associated with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis. It presents as a mass-forming lesion with a relatively favorable prognosis. LD-iCCA originates near the hepatic hilum, is linked to chronic bile duct diseases, and exhibits more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes. Imaging is essential for differentiating these subtypes and assessing prognostic factors like tumor size, multiplicity, vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, enhancement patterns, and intratumoral fibrosis. Imaging-based prognostic models have demonstrated predictive accuracy comparable to traditional pathological staging systems. Furthermore, imaging findings are instrumental in guiding treatment decisions, including those regarding surgical planning, lymphadenectomy, neoadjuvant therapy, and the selection of targeted therapies based on molecular profiling. Advancements in radiological research have improved our understanding of iCCA heterogeneity, facilitating prognosis prediction and treatment personalization. Imaging findings assist in subclassifying iCCA, predicting outcomes, and informing treatment decisions, thus optimizing patient management. Incorporating imaging-based approaches into clinical practice is crucial for advancing personalized medicine in the treatment of iCCA. However, further high-level evidence from international multicenter prospective studies is required to validate these findings and increase their clinical applicability.
 , Karel G M Moons
, Karel G M Moons , Paula Dhiman
, Paula Dhiman , Richard D Riley
, Richard D Riley , Andrew L Beam
, Andrew L Beam , Ben Van Calster
, Ben Van Calster , Marzyeh Ghassemi
, Marzyeh Ghassemi , Xiaoxuan Liu
, Xiaoxuan Liu , Johannes B Reitsma
, Johannes B Reitsma , Maarten van Smeden
, Maarten van Smeden , Anne-Laure Boulesteix
, Anne-Laure Boulesteix , Jennifer Catherine Camaradou
, Jennifer Catherine Camaradou , Leo Anthony Celi
, Leo Anthony Celi , Spiros Denaxas
, Spiros Denaxas , Alastair K Denniston
, Alastair K Denniston , Ben Glocker
, Ben Glocker , Robert M Golub
, Robert M Golub , Hugh Harvey
, Hugh Harvey , Georg Heinze
, Georg Heinze , Michael M Hoffman
, Michael M Hoffman , André Pascal Kengne
, André Pascal Kengne , Emily Lam
, Emily Lam , Naomi Lee
, Naomi Lee , Elizabeth W Loder
, Elizabeth W Loder , Lena Maier-Hein
, Lena Maier-Hein , Bilal A Mateen
, Bilal A Mateen , Melissa D McCradden
, Melissa D McCradden , Lauren Oakden-Rayner
, Lauren Oakden-Rayner , Johan Ordish
, Johan Ordish , Richard Parnell
, Richard Parnell , Sherri Rose
, Sherri Rose , Karandeep Singh
, Karandeep Singh , Laure Wynants
, Laure Wynants , Patricia Logullo
, Patricia Logullo
Citations

Shoulder pain is a common complaint in primary care settings. The prevalence of shoulder pain is on the rise, especially in societies with aging populations. Like other joint-related conditions, shoulder pain is predominantly caused by degenerative diseases. These degenerative changes typically affect bones, tendons, and cartilage, with common conditions including degenerative rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Diagnosing these degenerative diseases in older adults requires a thorough understanding of basic anatomy, general physical examination techniques, and specific diagnostic tests. This review aims to outline the fundamental physical examination methods for diagnosing shoulder pain in older adult patients in primary care. The shoulder's complex anatomy and its broad range of motion underscore the need for a systematic approach to evaluation. Routine inspection and palpation can identify signs such as muscle atrophy, bony protrusions, or indications of degenerative changes. Assessing range of motion, and distinguishing between active and passive deficits, is crucial for differentiating conditions like frozen shoulder from rotator cuff tears. Targeted strength tests, such as the empty can, external rotation lag, liftoff, and belly press tests, are instrumental in isolating specific rotator cuff muscles. Additionally, impingement tests, including Neer’s and Hawkins’ signs, are useful for detecting subacromial impingement. A comprehensive understanding of shoulder anatomy and a systematic physical examination are vital for accurately diagnosing shoulder pain in older adults. When properly executed and interpreted in the clinical context, these maneuvers help differentiate between various conditions, ranging from degenerative changes to rotator cuff pathology.
The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive guide for managing older adult patients with shoulder diseases, specifically rotator cuff tears and osteoarthritis, and to explore effective nonsurgical treatment options. Chronic rotator cuff tears are typically degenerative, whereas acute tears result from trauma. A key feature of these tears is tendon degeneration accompanied by type III collagen predominance, predisposing tears to progression. Osteoarthritis in the glenohumeral joint arises from wear-and-tear changes that compromise cartilage integrity, leading to pain and restricted motion. Accurate clinical assessment and imaging, including plain radiographs, ultrasonography, and MRI, facilitate diagnosis and guide treatment. The physic-al examination emphasizes range of motion, rotator cuff strength, and scapular stability. Management strategies prioritize pain relief, function preservation, and improving mobility. Nonsurgical modalities, including exercise, manual therapy, and activity modification, constitute first-line treatments, especially for older adults. Pharmacological approaches involve NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, and neuropathic pain medications. Steroid injections have short-term benefits, but repeated treatments may compromise tissue integrity. Platelet-rich plasma is a regenerative option that may improve tendon healing, but mixed findings highlight the need for further investigation. A structured physical therapy program focusing on range of motion and strengthening is essential, with alternative interventions used judiciously. Patients should be counseled regarding the potential progression of tears and the possible need for future surgical intervention if nonsurgical methods are unsuccessful. Multimodal approaches, including joint mobilization and personalized exercise regimens, hold potential for optimizing functional outcomes and supporting independence in older adults.
Citations



Citations

 , Pyoeng Gyun Choe
, Pyoeng Gyun Choe
The rise of multidrug-resistant organisms represents a serious global public health concern. In Korea, the increasing prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) is particularly concerning due to the difficulties associated with treatment. Data from the Korea Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System indicate a yearly increase in CRE cases, with carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales being the predominant type. The capacity of CRE to resist multiple broad-spectrum antibiotics leads to higher medical costs and mortality rates, underscoring the need for urgent action. Effective prevention is crucial to curbing CRE outbreaks and transmission. Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) play a key role and require commitment from healthcare professionals to minimize unnecessary antibiotic use, as well as from policymakers to ensure adherence to ASP guidelines. Given the complexity of CRE transmission, ASP efforts must be integrated with infection control strategies for maximum effectiveness. These strategies include adherence to standard and contact precautions, environmental disinfection, preemptive isolation, and comprehensive education and training for healthcare personnel. Additionally, surveillance testing for patients at high risk for CRE and the use of real-time diagnostic kits can facilitate early detection and reduce further transmission. Strategies for the prevention of CRE infection should be tailored to specific healthcare settings. Ongoing research is essential to update and refine infection control guidelines and effectively prevent CRE outbreaks.
Citations


Influenza presents a considerable disease burden, particularly among adults over 65 years old. In this population, the disease is associated with high rates of infection, hospitalization, and mortality. The objective of this study was to assess the impact of influenza on older adults and to evaluate the effectiveness of influenza vaccines within this demographic. A literature search was conducted using PubMed to identify relevant English-language studies published from January 2000 to January 2024. The analysis indicated that influenza-related hospitalization rates (ranging from 10.1 to 308.3 per 100,000 persons) and all-cause excess mortality rates (1.1 to 228.2 per 100,000 persons) were notably high in older adults, although these rates varied over time and by location. Hospitalization rates due to influenza increased considerably after the age of 50 years, with the highest rates observed in individuals aged 85 years and older. Excess mortality attributable to influenza also rose with age, with rates between 17.9 and 223.5 per 100,000 persons in those over 75 years old. The effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing severe infections requiring hospitalization was found to be only 37% in individuals aged 65 years and older. The unadjuvanted, standard-dose influenza vaccine had an estimated effectiveness of just 25% against laboratory-confirmed influenza and between 37% and 43.7% in preventing hospitalizations. Therefore, considering the substantial burden of influenza and the limited efficacy of standard vaccines, the use of highly immunogenic influenza vaccines should be prioritized for older adults.
Citations


This paper discusses the implications of South Korea's birth notification system and Protected Birth Act, which is set to take effect on July 19, 2024. The legislation aims to prevent infanticide and child abandonment by mandating birth reporting and allowing anonymous births for women in crisis. However, concerns have been raised about the Act's effectiveness in protecting both women and children, particularly regarding issues of disability and migrant families. This paper focuses on gender and healthcare issues, highlighting how the Act perpetuates discrimination against out-of-wedlock pregnancies and upholds normal family ideologies. It notes the absence of critical discussions on women's autonomy, safe pregnancy termination, and paternal responsibility. The importance of healthcare providers understanding and preparing for the Act's implementation is emphasized. The paper calls for strengthening social safety nets to improve healthcare access for vulnerable populations and eliminate discrimination against non-traditional families. Additionally, it addresses the need for comprehensive support systems for crisis pregnancies, including financial assistance, psychological support, parenting education, housing solutions, and expanded healthcare services. This paper acknowledges the Act's significance in providing a systematic state-level approach to protecting pregnant women in crisis, replacing the previous reliance on private organizations. Nonetheless, it also emphasizes the importance of continually reviewing and supplementing the system to address potential rights infringements and ensure its effectiveness. In conclusion, this paper advocates for ongoing discussions on gender and healthcare issues, and for future amendments to the law that reflect real-world circumstances and provide genuine protection for crisis pregnancies and infants.
Citations

 , Eun Mee Kim
, Eun Mee Kim
The Republic of Korea’s potential role in the peacebuilding process on the Korean Peninsula is explored, with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea’s earnest efforts to denuclearize and become a normal country. The paper focuses on the United Nations (UN) agencies in the peacebuilding process, considering the UN’s engagement in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea during the sanction years with humanitarian assistance, the UN’s legitimacy as an impartial international organization for assisting developing countries in forging peace and prosperity, and recently-adopted resolutions on sustaining peace and the Sustainable Development Goals. Policy recommendations are for the Republic of Korea to actively cooperate with the UN’s development and humanitarian agencies, conduct a thorough preparatory review and conduct research, and work towards expanding its engagement and role within key UN agencies.
Citations

Citations

 , Jeong-Ho Chae
, Jeong-Ho Chae , Jung-Seok Choi
, Jung-Seok Choi , Yong Pil Chong
, Yong Pil Chong , Byung Chul Chun
, Byung Chul Chun , Eun Mi Chun
, Eun Mi Chun , Bo Seung Kang
, Bo Seung Kang , Dai Jin Kim
, Dai Jin Kim , Yeol Kim
, Yeol Kim , Jun Soo Kwon
, Jun Soo Kwon , Sang Haak Lee
, Sang Haak Lee , Won-Chul Lee
, Won-Chul Lee , Yu Jin Lee
, Yu Jin Lee , Jong Han Leem
, Jong Han Leem , Soo Lim
, Soo Lim , Saejong Park
, Saejong Park , Dongwook Shin
, Dongwook Shin , Hyeon Woo Yim
, Hyeon Woo Yim , Kwang Ha Yoo
, Kwang Ha Yoo , Dae Hyun Yoon
, Dae Hyun Yoon , Ho Joo Yoon
, Ho Joo Yoon

Endocrine tumor syndromes constitute a group of disorders characterized by tumors in hormone-producing tissues. These conditions predominantly affect younger patients and often have a familial inheritance. Advances in molecular genetics in recent decades have facilitated the identification of several genes associated with these tumors. The recent World Health Organization classification of adrenocortical tumors integrates the latest developments in pathology, oncology, and molecular biology. In addition, this updated classification includes adrenal cortical diseases based on an understanding of germline susceptibility to these conditions and their clonal-neoplastic nature. Catecholamine-secreting tumors, including pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma, have been found to have a genetic predisposition in as many as 80% of cases. Compared to sporadic cases, endocrine tumor syndromes are more likely to present bilaterally and show synchronous or metachronous disease. This highlights the critical need for early diagnosis, intervention, and ongoing surveillance. This review focuses on the clinical manifestations and genetic basis of endocrine tumor syndromes originating from the adrenal glands.
Citations


Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is increasingly recognized as a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, driven by the global obesity epidemic. Projected to become the primary cause of HCC by 2030, MASH-HCC presents unique clinical challenges. This review examines its clinical management, including surveillance strategies and treatment advances, and discusses prospects to overcome existing challenges. MASH-HCC accounts for 10%–20% of HCC cases, particularly in Western countries, with a rising incidence due to obesity. Risk factors include cirrhosis, diabetes, obesity, alcohol, smoking, genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3), and microbiome alterations. The pathogenesis involves fibrosis, immune dysfunction (e.g., T-cell impairment), and molecular changes. Prevention focuses on lifestyle modifications. Surveillance in patients with MASH cirrhosis is crucial but is hindered by poor ultrasound sensitivity in obese patients, necessitating alternative methods. Treatment mirrors that of other HCC types, but comorbidities and potentially reduced efficacy of immunotherapy necessitate tailored approaches. MASH is becoming the leading cause of HCC, necessitating lifestyle interventions for prevention. Improved surveillance and early detection are critical but challenging due to obesity-related factors. Treatments align with those for other HCC types, but comorbidities and potential differences in immunotherapy efficacy due to T-cell dysfunction require careful consideration. Key needs include identifying molecular drivers in non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, developing preventive therapies, refining surveillance methods, and tailoring treatments. Trials should specifically report MASH-HCC outcomes to enable personalized therapies. Further research is needed to understand T-cell dysfunction, optimize immunotherapies, and identify predictive biomarkers.

