 , YangIm Hur
, YangIm Hur
 , Gyu Bae Lee
, Gyu Bae Lee , Jihyun Yoon
, Jihyun Yoon , Yang-Hyun Kim
, Yang-Hyun Kim
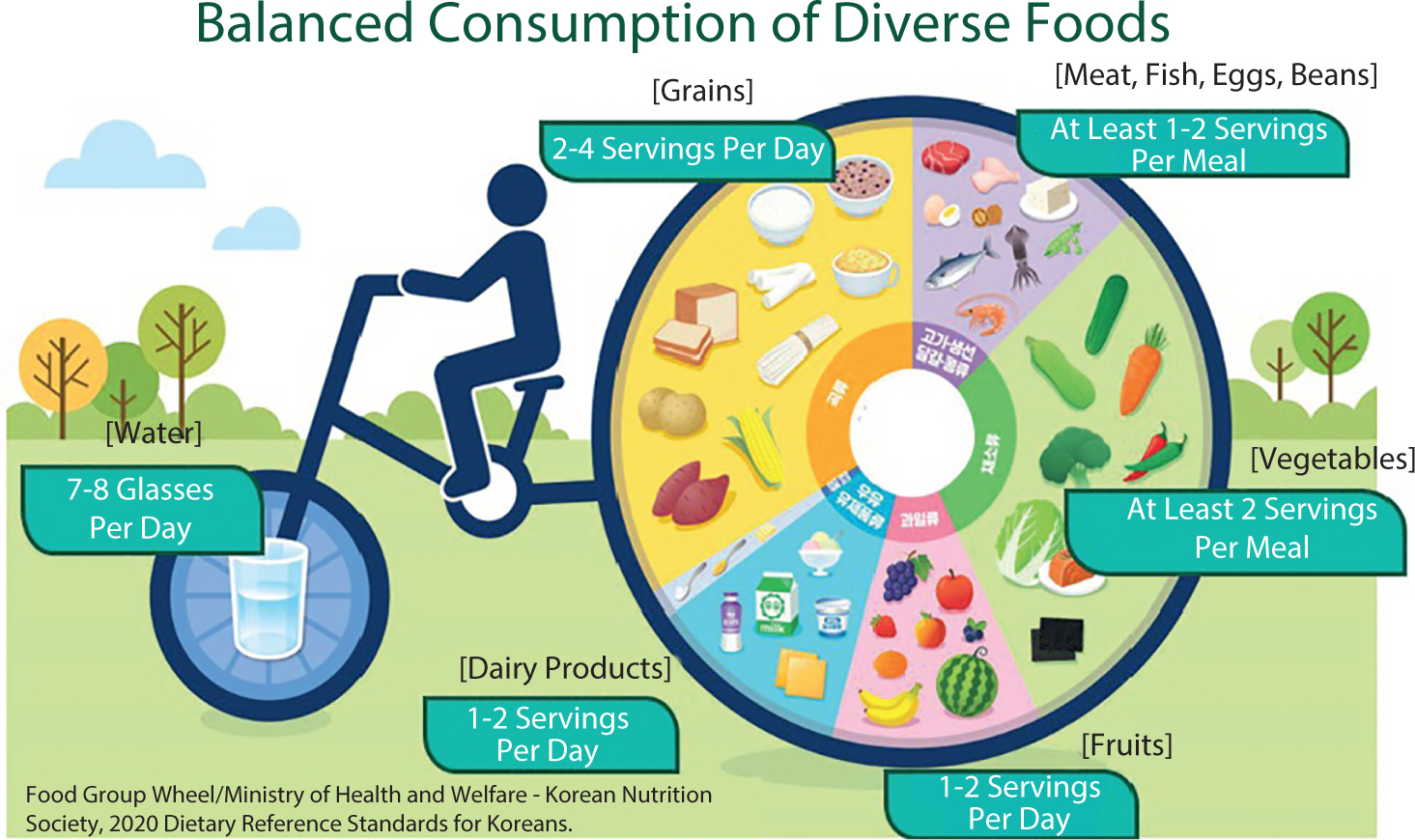
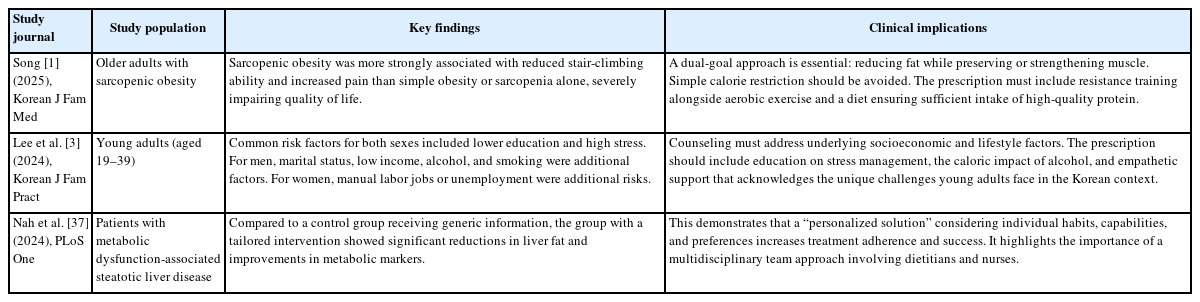
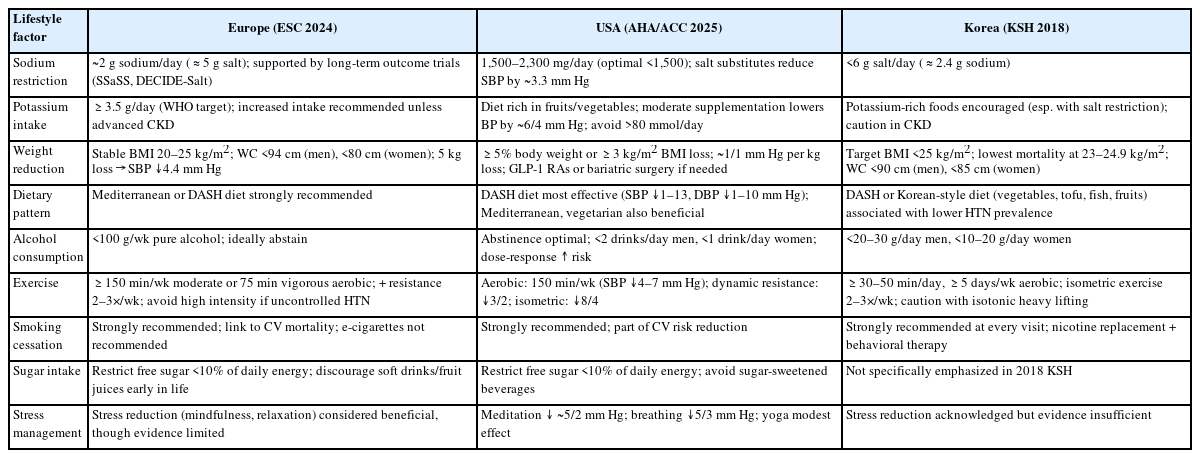
Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by environmental, genetic, dietary, and hormonal factors. This underscores the importance of postoperative nutritional management in supporting recovery, minimizing complications, and enhancing long-term outcomes. This review synthesizes clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and observational studies to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary interventions for breast cancer patients following surgery. Post-surgical nutritional care is centered around three primary objectives: supporting wound healing through high-quality protein intake, maintaining optimal nutritional status to prevent malnutrition, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of recurrence. To achieve these objectives, postoperative dietary strategies focus on several key components: ensuring adequate hydration for metabolic processes and tissue repair, consuming a balanced diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits to mitigate oxidative stress, incorporating whole grains to support overall healing, and maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality protein from sources such as fish, meat, and dairy products to aid tissue repair and immune system recovery. Patients are also advised to avoid alcohol, limit saturated fats, and reduce intake of salty, sugary, and smoked foods to minimize inflammation. As research progresses, the implementation of personalized dietary plans remains essential for optimizing recovery outcomes in breast cancer patients.
 , Kyunghee Jung-Choi
, Kyunghee Jung-Choi , Bo Young Kim
, Bo Young Kim , Kyoung Ae Kong
, Kyoung Ae Kong
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of unhealthy dietary habits by maternal educational level and how the effect of maternal education changed between 2009 and 2019.
Using data from the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey conducted between 2009 and 2019, we assessed the prevalence of each unhealthy dietary habit (insufficient consumption of milk and fruit/vegetable, breakfast-skipping, and frequent consumption of fast food, soft drinks, and instant noodles) and the prevalence difference between maternal middle/high school and college graduate groups in four periods. The models included maternal educational level, four periods and the interaction between them, sex, and grade. In addition, we estimated the ORs of unhealthy dietary habits between the two maternal educational groups at each period.
Throughout the study period, unhealthy dietary habits were consistently more prevalent among mothers with lower education levels. Between 2009–2010 and 2017–2019, the prevalence of unhealthy dietary habits increased, with a particular increase in that of frequent consumption of fast food and soft drink. The prevalence differentials between the middle school and college graduate group decreased or did not differ, while those between the high school and college graduate groups increased over time. A similar trend was observed in the relative scale.
Considering the increase in the prevalence of unhealthy dietary habits and the prevalence differentials by maternal educational level, targeted efforts are needed not only for all adolescents and their parents but also for those with low socioeconomic status to improve the dietary habits of adolescents.
Citations

 , Kyoung Tae Noh
, Kyoung Tae Noh , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim
Cancer prevention by vegetable diet has received considerable attention in recent years. In the past these attributes of vegetables were based more on beliefs than on scientific evidences. But over the past few decades many studies have been performed about that. Cancer preventive components of many vegetables have been studied in experimental carcinogenesis models. These studies have reported on these components influence carcinogenesis during initiation and promotion phases of cancer development. Also, epidemiological studies and clinical trials have reported cancer preventive effects of vegetables. However, there is no comprehensive summary of cancer preventive effects with the types of vegetables. In this review, we classified the vegetables and described the mechanism of action of active components of vegetables, experimental studies, and clinical trials. Results revealed a negative correlation between consumption of vegetables and cancer risk. But we can't still conclude the effects of vegetables yet, so further studies would be necessary for final conclusion.
Citations


