
 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim
 , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
 , Wookeun Lee
, Wookeun Lee , Tae-Dong Jeong
, Tae-Dong Jeong , Hae-Sun Chung
, Hae-Sun Chung , Ki-Sook Hong
, Ki-Sook Hong
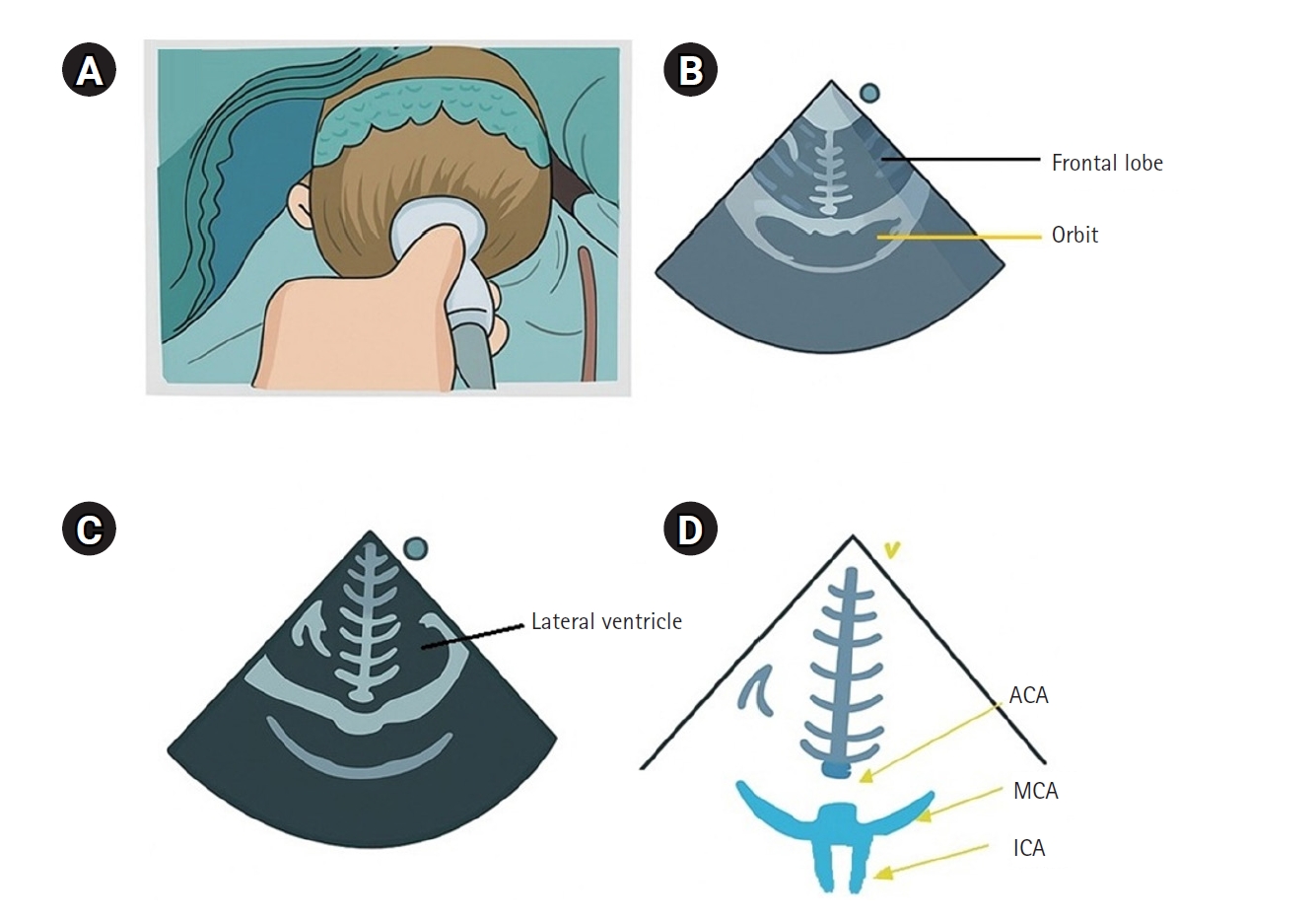
Six sigma is a quality management system for the assessment of precision and accuracy. We aim to apply the six sigma rule to quality control (QC) of point-of-care (POC) glucose meters in a tertiary hospital.
Thirty POC glucose meters installed at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital were monitored between January 2013 and March 2014. The QC data from the POC glucose meters at low and high levels were collected. The monthly mean, standard deviation, bias, coefficient of variation, and mean sigma metrics were calculated. The correlation between accuracy and precision was assessed based on the percentage bias and coefficient of variation. Comprehensive instructions on the QC and maintenance of the devices were provided in the departments with poor sigma scores. A follow-up assessment was performed after the intervention.
The mean sigma values for the low and high controls were 3.29 and 3.71, respectively. At the low and high controls, 36.6% and 10% of the glucose meters showed a sigma value <3. The causes of low sigma values included the use of expired control materials, prolonged air exposure of the sample strip, lack of user training, and errors in device maintenance. On follow-up monitoring for 3 months following QC intervention, 23.3% (low control) and 6.6% (high control) of the glucose meters scored a sigma value <3, indicating improved QC.
Sigma metrics-based QC can successfully improve accuracy and precision of POC glucose meters in an objective and quantitative manner and can be used for follow up after QC intervention.
Citations

 , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Ji Sun Jeong
, Ji Sun Jeong
We analyzed retrospectively incidence, management, and predictors of difficult intubation, which have been known through practical cases.
A total of 217 cases of difficult intubation (DI) between 2010 and 2014 were investigated. Risk factors such as age, body mass index, Mallampati score, thyromental distance, degree of mouth opening and range of neck motion, Cormack-Lehane grade, intubation and airway management techniques were investigated. The cases of each department were analyzed and the airway management techniques according to simplified risk scores (SRS) were also investigated.
The average incidence of DI was 0.49%. Patients undergoing surgery in the departments of oro-maxillo-facial surgery (1.35%), ophthalmologic surgery (0.96%), urologic surgery (0.80%), and head and neck surgery of ear-nose-throat (0.62%) showed the higher incidence of DI. Difficult mask ventilation (10 of 217, 4.6%) was occurred with DI. Higher SRS were related to high rates of video laryngoscope use and fiberoptic guided intubation. There was a decrease in the use of McCoy blades after 2013, an increase in the use of video laryngoscope, and a consistent rate of fiberoptic intubation.
It is not easy to check all the predictors of DI in a preanesthetic evaluation and the predictors are not accurate. The role of clinical preparation and practical management is important, and the most important thing is to establish a planned induction strategy. Multiple factors system, such as simplified risk factors should be used to evaluate patients to prepare for appropriate airway management techniques in case of DI.
Citations

 , Jisoo Lee
, Jisoo Lee
To examine the management status of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) taking glucocorticoids treated at a tertiary hospital rheumatology Practice.
A retrospective chart review was performed on 114 RA patients who were noted to be taking glucocorticoids during the period of 2000.7 to 2003.7, and who had been followed up for at least one year period. Use of bone densitometry and use of prescription medication for osteoporosis management were assessed.
Thirty one % of patients underwent bone densitometry, and 34% of patients received prescription medication for osteoporosis management. Sixty-six percent of patents who underwent bone densitometry showed osteoporosis with T score of less than 2.5, Osteoporosis medication was prescribed most often in the prednisolone exposure group of at least 7.5mg/d for at least 6 months. Factors associated with not receiving management for osteoporosis included male sex, young age, and premenopausal woman.
The use of bone densitometry and prescription medication for osteoporosis were suboptimal. Interventions to improve detection and prevention of glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis are necessary.
 , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi , Jung Eun Shin
, Jung Eun Shin , Mi Sun Ju
, Mi Sun Ju , Jung Hyun Chun
, Jung Hyun Chun , Kyung Eun Lee
, Kyung Eun Lee
This study is to compare the clinical and cost effectiveness of various pharmacologic therapies with of without endoscopic procedure in the Forrest II ulcer.
Between May 2001 and June 2002, total of 58 Forrest II bleeding activity patients (37 cases of NBVV, 6 adherent blood clots, 9 flat red spot, and 6 flat black spot) with gastric ulcer(32 cases) and duodenal ulcer(26 cases) were analyzed. UGI endoscopy was performed within 12 hours of the first bleeding episodes, and underwent repetitive endoscopy after 48h. All the patients were randomly assigned to receive somatostatin(group I), PPI(omeparzole : group II), only H2 blocker (famotidine, group III), or endoscopic injection therapy followed by famotidine (group IV). We compared with rebleeding rates, changes of ulcer size, and modified estimated costs for 3 day-hospital in four groups respectively.
1) Twelve patients experienced rebleeding(20.7%). 2) The rates of rebleeding were 16.6% (2/12) in group I, 28.6%(4/14) in group II, 5.9%(1/17) in group III, 26.7% in group IV. There was no significant difference in rebleeding rate among the groups, but there was low rebleeding tendency in group III, compared with group II(
In Forrest II bleeding ulcer, medical therapy, especially famotidine could be suggested prudently as a proper treatment modality for this lesion, considering the cost-effectiveness.

