Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Red Cross Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2014. Ewha Womans University School of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
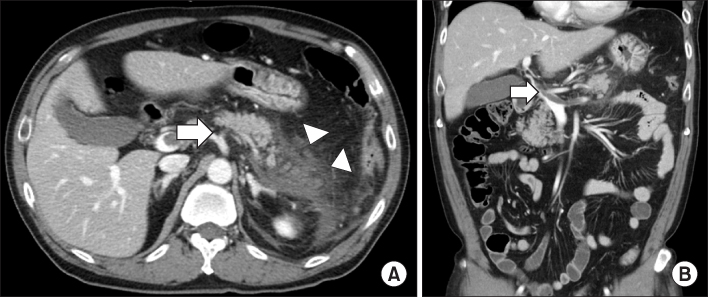
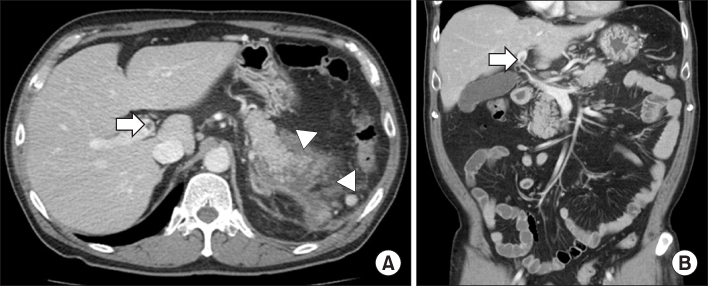

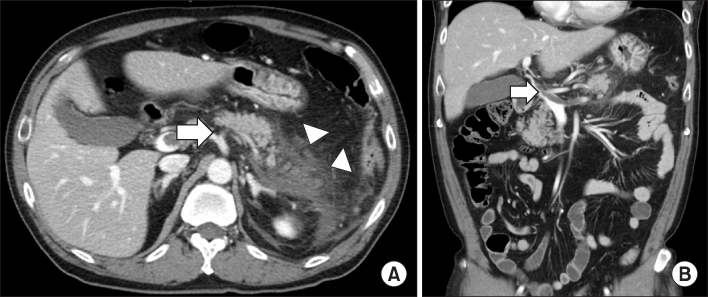
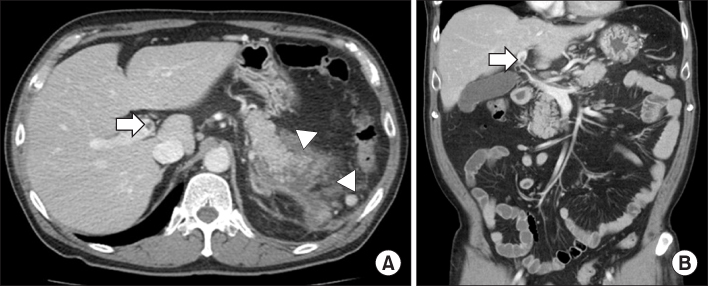
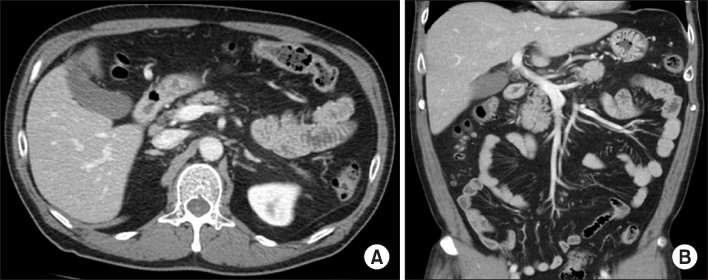
Summary of the reported cases of venous thrombosis in acute pancreatitis in Korea
PV, portal vein; SMV, superior mesenteric vein; SV, splenic vein; LMWH, low molecular weight heparin.
PV, portal vein; SMV, superior mesenteric vein; SV, splenic vein; LMWH, low molecular weight heparin.