Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2015, The Ewha Medical Journal
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
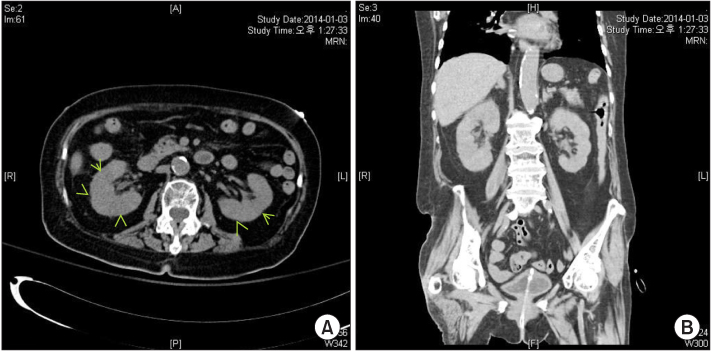
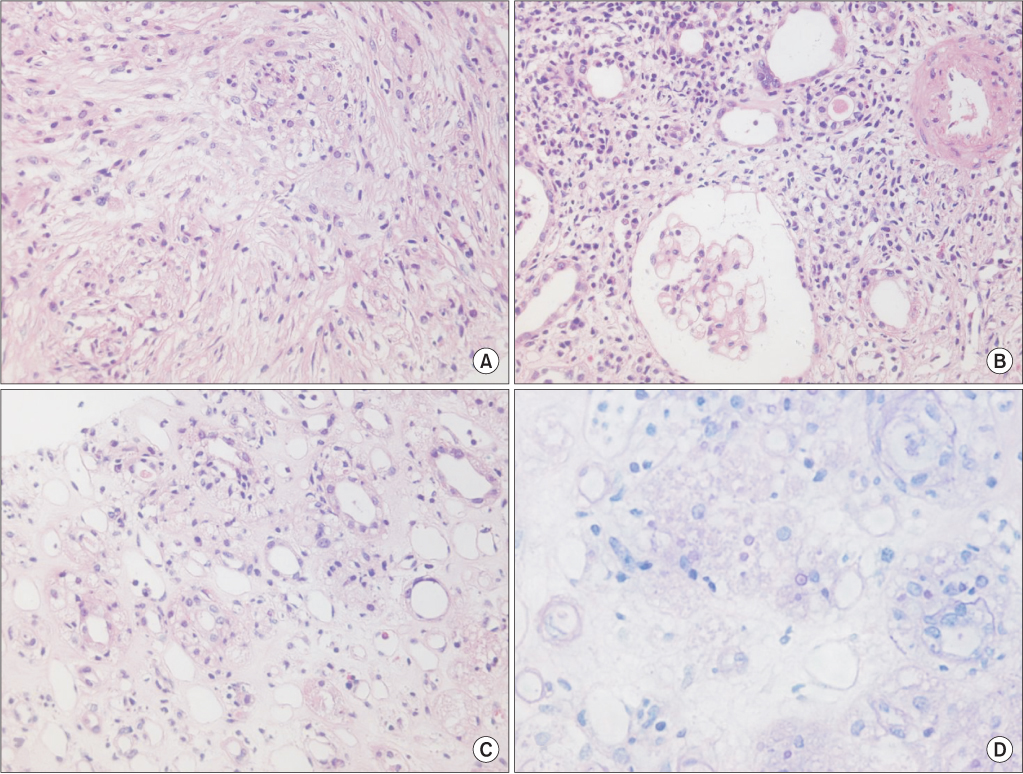
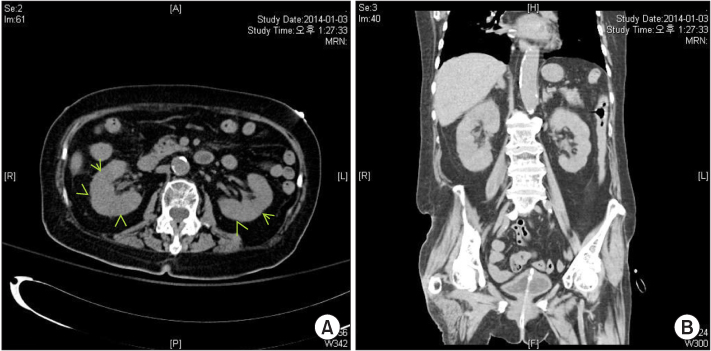
BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cr, serum creatinine level; WBC, white blood cell count; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; NM, not mentioned; E.coli, Escherichia coli; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; CLD, chronic liver disease; TMP/SMX, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole; CP, chronic pancreatitis; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; Tx, treatment; OA, osteoarthritis; WNL, within normal limits; MG, Myasthenia gravis; PD, Parkinson' s disease.
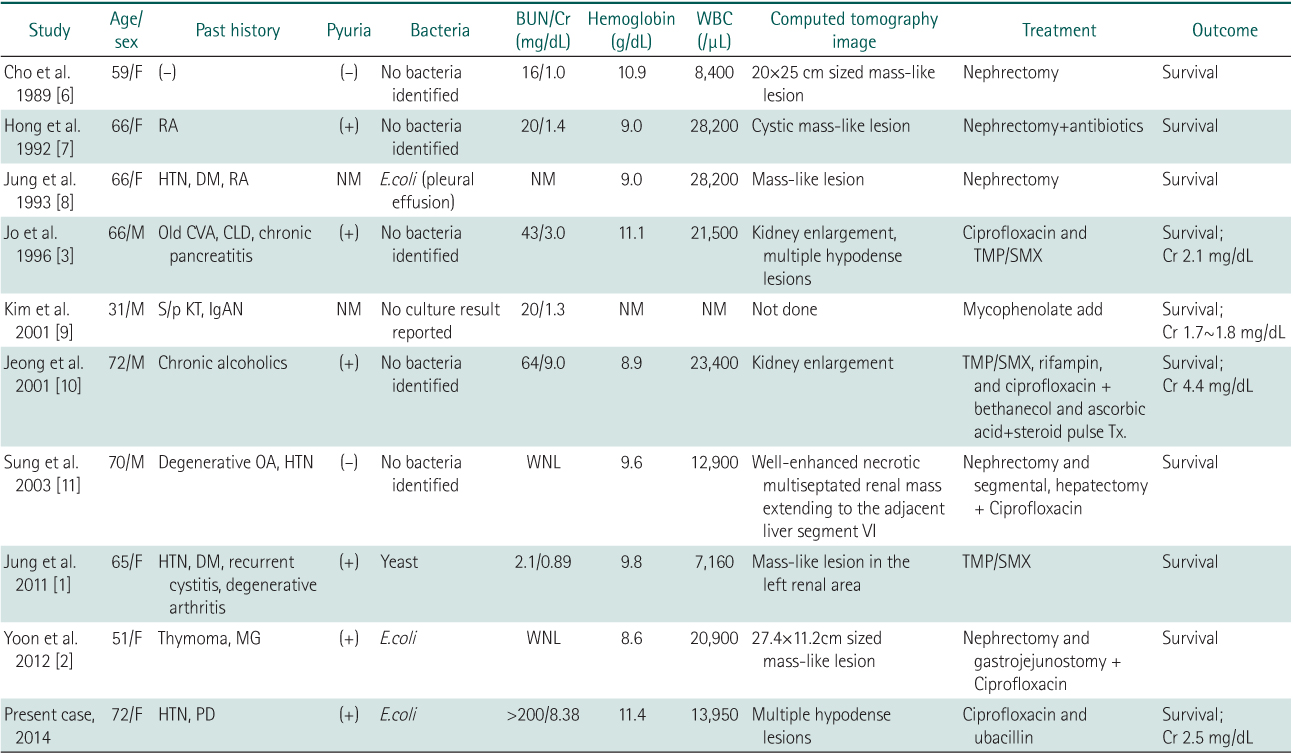

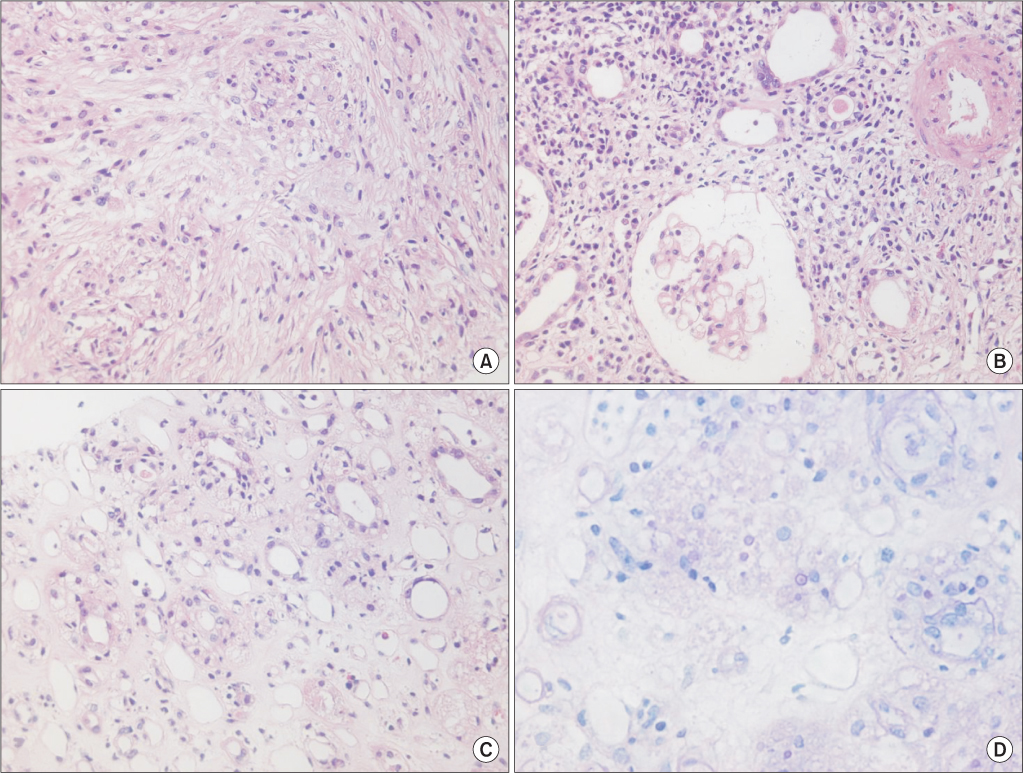
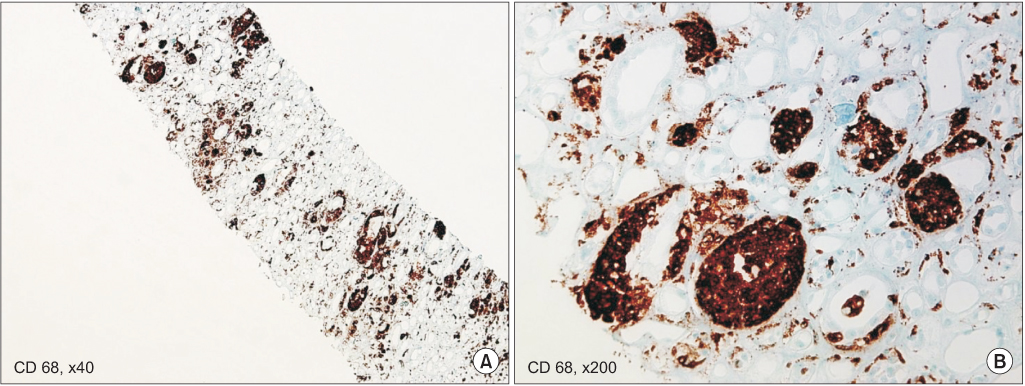
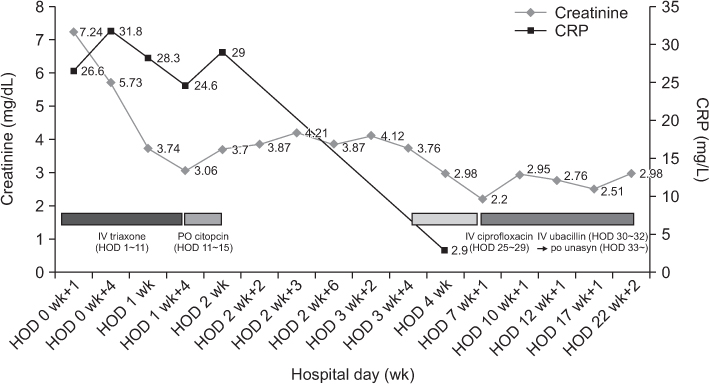
BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cr, serum creatinine level; WBC, white blood cell count; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; NM, not mentioned; E.coli, Escherichia coli; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; CLD, chronic liver disease; TMP/SMX, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole; CP, chronic pancreatitis; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; Tx, treatment; OA, osteoarthritis; WNL, within normal limits; MG, Myasthenia gravis; PD, Parkinson' s disease.
BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cr, serum creatinine level; WBC, white blood cell count; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; NM, not mentioned;