Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2018. Ewha Womans University School of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Values are presented as number of cases (%) or mean±SD (range) unless otherwise indicated.
*Not recorded in 13 cases.
†Accompanied by cervical lymphadenopathy except only one case of axillary lymphadenopathy.
‡The mesenteric lymph node involvement was examined by imaging studies (computed tomography or sonography) on 14 patients, five of them were detected.
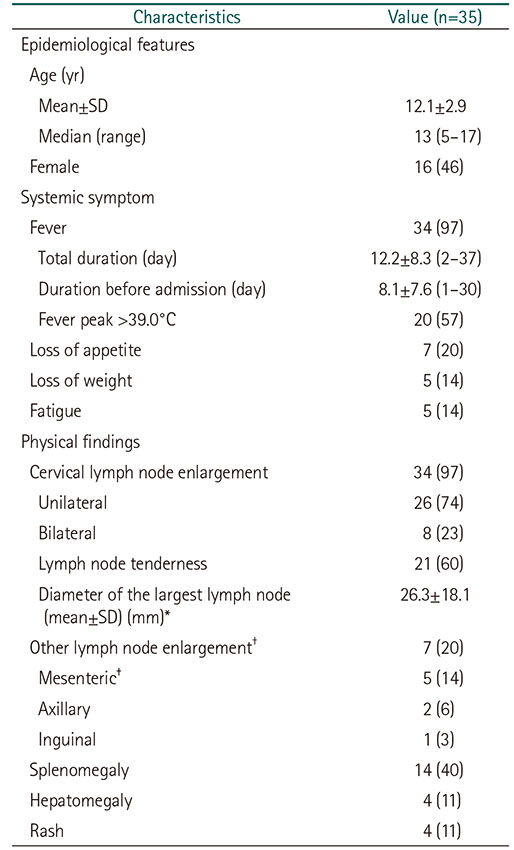

Values are presented as number of cases (%) or mean±SD (range) unless otherwise indicated.
*Not recorded in 13 cases.
†Accompanied by cervical lymphadenopathy except only one case of axillary lymphadenopathy.
‡The mesenteric lymph node involvement was examined by imaging studies (computed tomography or sonography) on 14 patients, five of them were detected.
ANA, antinuclear antibody; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; CMV, cytomegalovirus; MTBC, mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.
Values are presented as number of cases (%) or mean±SD (range) unless otherwise indicated. *Not recorded in 13 cases. †Accompanied by cervical lymphadenopathy except only one case of axillary lymphadenopathy. ‡The mesenteric lymph node involvement was examined by imaging studies (computed tomography or sonography) on 14 patients, five of them were detected.
ANA, antinuclear antibody; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; CMV, cytomegalovirus; MTBC, mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.