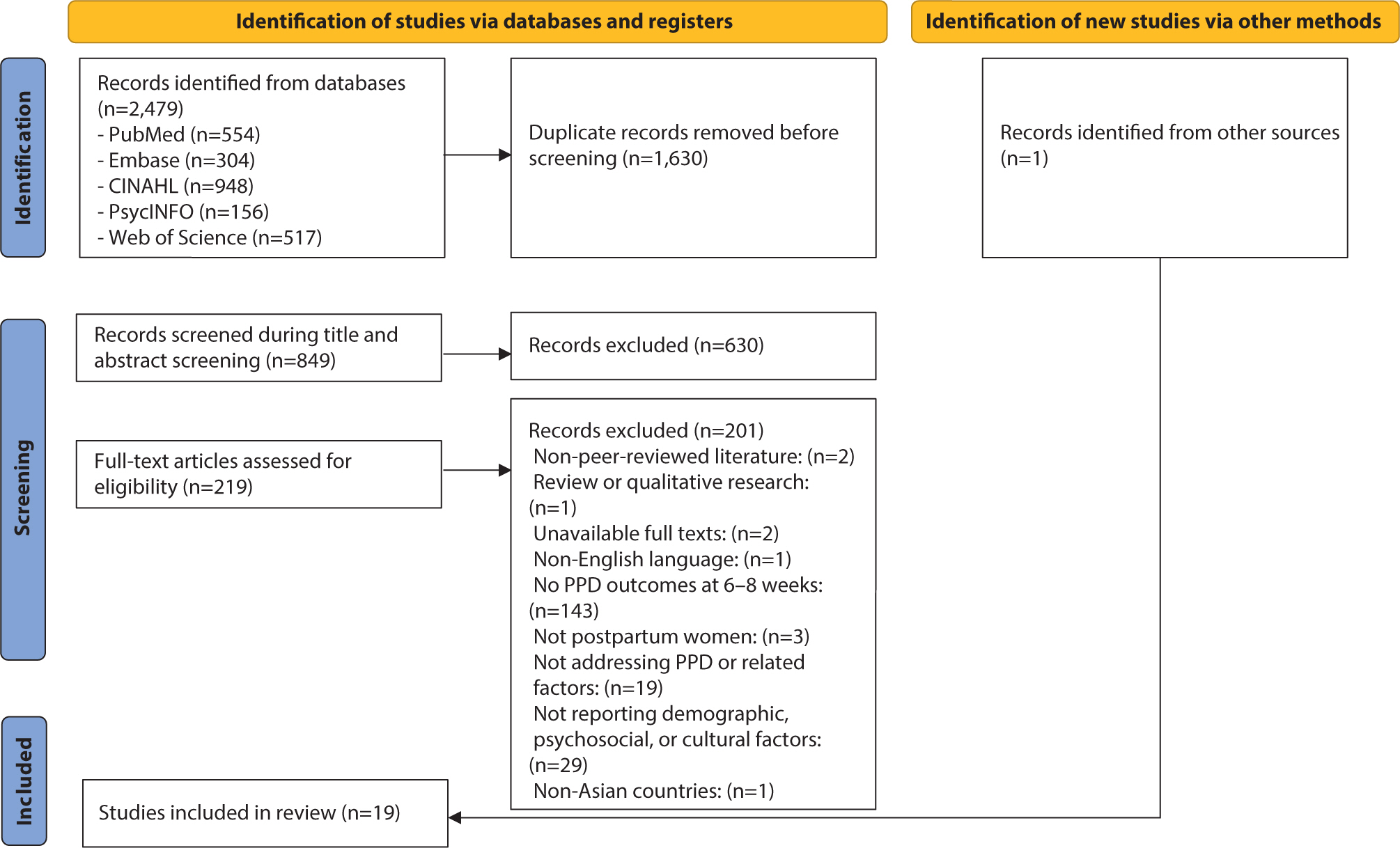
The prevalence of postpartum depression (PPD) in Asia is reported to range from 13.53% to 22.31%. However, there remains a gap in the identification of PPD, particularly regarding cultural cutoff points. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to determine the prevalence and associated factors of PPD in Eastern, South-eastern, Western, and Southern Asian countries and analyze the cutoff points of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) used across these countries. Following Arksey and O'Malley’s five-step scoping review framework, the population was defined as mothers, the concept as the EPDS, and the context as the Asian region. A literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. The data analysis focused on demographic characteristics, EPDS cutoffs and features, PPD prevalence, and its associated factors. Nineteen studies were selected. Most countries used translated versions of the EPDS with demonstrated reliability and validity. The cutoff scores varied, with most using scores of 10 or higher. The prevalence of PPD ranged from 5.1% to 78.7%. Key associated factors for PPD included cultural factors such as relationships with in-laws and preferences for the newborn’s sex. To improve the accuracy of PPD screening in Asia, the EPDS should be used consistently, and appropriate cutoff criteria must be established. In addition, prevention strategies and programs that reflect the cultural characteristics and social context of Asia need to be developed for the early detection and prevention of PPD.
 , Jong Kil Nam
, Jong Kil Nam , Bon Jin Koo
, Bon Jin Koo , Hyun Jung Lee
, Hyun Jung Lee , Tae Un Kim
, Tae Un Kim , Hwaseong Ryu
, Hwaseong Ryu , Yun Jeong Hong
, Yun Jeong Hong , Seungsoo Lee
, Seungsoo Lee , Dong Hoon Lee
, Dong Hoon Lee , Sung Woo Park
, Sung Woo Park
The aim of this study was to examine the clinical presentation, treatment delivery, and cisplatin eligibility of Korean patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC) in a real-world setting.
We performed a retrospective cohort study of patients initially diagnosed with UC from March 2013 to June 2018. Creatinine clearance >60 mL/min and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (0-1) were adopted as cisplatin eligibility criteria.
This study included 557 eligible patients. Median age was 71.0 years (range, 33-94 years), and males were dominant (80%). Primary tumor sites were: upper genitourinary tract, 18%; bladder, 81%; and urethra, 0.4%. Initial disease status was non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (313, 56%), diffuse infiltrating non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (19, 3%), cTanyN0 upper tract UC (75, 13%), cT2-4N0 bladder UC (82, 15%), TanyN1-3 UC (36, 7%), or initially metastatic UC (32, 6%). At the time of analysis (June 2019), following treatments were delivered to 134 patients with localized UC: radical operation with or without perioperative treatment (89, 67%), definitive chemoradiation (7, 5%), and palliative surgery or supportive care only (36, 28%). In total, 89 patients had metastatic UC, including those with recurrent disease (n=57), and 34 (38%) of the 89 were eligible for cisplatin.
Clinical presentations in East Asian UC patients were consistent with those of previous studies in other countries, except for a relatively high incidence of upper genitourinary tract. Our results can serve as a benchmark for further advances and future research for treatments of UC in East Asian patients.
Citations

 , Ji Hyen Lee
, Ji Hyen Lee , Hyun-Hae Cho
, Hyun-Hae Cho , Hae Soon Kim
, Hae Soon Kim
To investigate brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with central precocious puberty (CPP) by age at onset and sex.
We included 130 CPP patients with brain MRI findings of the pituitary gland treated at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between February 2007 and October 2013 and divided them by age and sex: boys, girls aged ≤6 years, and girls aged >6 years. The control group comprised 224 patients who underwent brain MRIs, and we compared their incidental brain findings with those of the CPP group.
In the CPP subgroups who underwent pituitary MRIs, the frequency of incidental brain lesions was 31.6% in boys, 47.1% in girls ≤6 years and 29.8% in girls >6 years. The incidence of pituitary abnormalities was 42.1% in boys, 64.7% in girls ≤6 years and 47.9% in girls >6 years. Among pituitary abnormalities, pituitary hypoplasia had a significantly higher incidence rate in girls ≤6 years (41.2%) than in boys (15.8%) or girls >6 years (13.8%, P=0.027). Hypothalamic hamartomas were detected in one girl aged ≤6 years and in one boy, but not in girls aged 6 years (P=0.075). The incidence of pineal cysts was higher in the CPP groups and significantly higher in girls ≤6 years (47.1%) than in the control group (11.2%, P=0.001).
There was a higher incidence of brain abnormalities on pituitary MRIs and a higher incidence of pineal cysts, possibly associated with CPP pathogenesis, in younger CPP patients than in other patients.
Citations


We retrospectively analyzed the clinical and radiologic findings of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia.
We retrospectively studied the chest radiographs of 10 infants, who were clinically diagnosed as bronchopulmonary dysplasia from January, 1994 to December, 1995.
The underlying disease of the cases that has BPD were, there were hyaline membrane disease in 4 cases, repeating apnea in 4 cases, septicemia, peneumonia in 2 cases.
The most common radiological findings were coarse nodular & streaky densities in perihilar region(7/10),emphysematous overdistention(6/10), and other findings such as bubbly pattern (3/10), lace-like pattern with strands of density(2/10) appeared.
Premature and infants with thigh oxygen and intermittent positive pressure ventilation therapy, the chronic persistent pulmonary abnormality in chest X-ray films highly suggests the possibility of bronchopulmonar dysplasia.
 , Eun Mi Nam
, Eun Mi Nam , Si Hoon Park
, Si Hoon Park , Gil Ja Shin
, Gil Ja Shin , Woo Hyung Lee
, Woo Hyung Lee , Bong Suk Shim
, Bong Suk Shim
We describe an unusual 30-year-old female patient with a history of refractory hypertension and hypokalemia. She was diagnosed as primary aldosteronoism with bilateral adrenal hyperplasia 8 years age and blood pressure has been controlled with spironolactone 200mg/day, nifedipine 40mg/day, Cardura 4mg/day and oral potassium supplement till these days.
Recently refractory high blood pressure was developed and about 5×4×4.5cm sized left a-drenal mass was observed by abdominal CT. The hypertension and hypokalemia was controlled by left adrenalectomy.
 , Young Sik Park
, Young Sik Park , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Hea Soo Koo
, Hea Soo Koo
Castleman's disease, giant lymph node hyperplasia, is a rare benign tumor which was originally reported by Castleman in 1956. It has two types of pathological characteristics of hyaline-vascular and plasma cell. Surgery is usually perferred because of the giant mass shadow on the chest roentgenogram rather than symptomes it causes. It is cured completely by resection without recurrence. We have experienced a case of Castleman's disease in the right anterosuperior mediastinum in a 36-year-old female. She was treated by surgical resection with good result She is well one year after surgeny.

Fibrous dysplasia of the bone is a relatively rare condition characterized by fibrous tissue replacement of skeleton, it may be monostotic with confined to one bone, or polyostotic with situated in many bones. Favored locations are long bones of the lower extremities and fibrous dysplasis may produce defective growth and deformity, pathologic fracture, and pain in any bone, basically the bone structure is replaced to variable degree by avascular fibrous tissue, and formed thin trabeculae of bone. The author experienced 3 cases of fibrous dysplasia that are 2 cases tomonostotic and 1 case of polyostotic lesions and a brief review was done with literatures.
 , Hyeon Hui Kang
, Hyeon Hui Kang , Ji Hyun Kim
, Ji Hyun Kim , Hwa Young Lee
, Hwa Young Lee , Kyung Yoon Chang
, Kyung Yoon Chang , Hae Kyung Yang
, Hae Kyung Yang , Sang Haak Lee
, Sang Haak Lee , Hwa Sik Moon
, Hwa Sik Moon , Bae Young Lee
, Bae Young Lee
A 60-year-old man visited our hospital because of the incidentally found mass of the rib on chest radiography. Chest X-ray showed expansile bony hypertrophy on left 5th rib and bone setting of the computed tomography scan of chest revealed 4.2×2.5 cm sized, elongated bony expansion with geographic radiolucent lesion in the medullary cavity and cortical thinning. Technetium-99m bone scintigraphy showed diffusely increased radioactivity along the left 5th rib. We present this case to discuss about a possible differential diagnosis in this type of lesion.
 , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Jung-Hwa Chung
, Jung-Hwa Chung , Seok-Hyung Kang
, Seok-Hyung Kang , Do-Kyeung Song
, Do-Kyeung Song , Seung-Jung Jun
, Seung-Jung Jun , Hye-In Kim
, Hye-In Kim
Until recently, colorectal polyps were classified predominantly as hyperplastic or adenomatous. While adenomatous polyps are well-characterized precursor lesions of adenocarcinomas, hyperplastic polyps have been considered as benign lesion. However, some hyperplastic polyps with serrated morphology of the crypts have been recognized to have distinctive features and these polyps were termed 'serrated adenomas'. Recent data show that sessile serrated adenomas (SSA) might be the precursors of serrated colonic cancers, underlining the necessity of identifying them. SSA is approximately 3% of all polyps, commonly appears as flat or sessile and yellowish due to mucus production. In the pathogenesis of SSA, progression to high grade dysplasia or early invasive carcinoma may be associated with serrated neoplasia pathway different from adenoma-carcinoma sequence. We report a case with a colon polyp diagnosed as sessile serrated adenoma with high grade dysplasia after endoscopic submucosal dissection.

I investigated the relationships among International prostate symptom score(IPSS), prostatic size and other factors, and look into the possibility of the expert system for benign prostatic hyperplasia in symptomatic prostatism.
Through the prostate awareness program, 349 men had undergone IPSS questionnaire, uroflownetry and transrectal ultrasonography. I analyzed the correlation coefficient to revel the relationship among age, maximal flow rate(MFR), and prostatic size, according to the several parameters.
The relationships among the age, MFR and prostatic size were statistically significant. When the all men were classified according to the height, weight, educational course and resident place, the relationships were not significant different.
 , So Yun Cho
, So Yun Cho , Mi Ae Lee
, Mi Ae Lee , Kyu Kwang Whang
, Kyu Kwang Whang , Jeong Hee Hahm
, Jeong Hee Hahm
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia(ALHE) is a benign, uncommon disorder of unknown etiology and usually appears as intradermal or subcutaneous, red to brown papules and/or nodules, usually located on the head and neck region, and occurring in young adults.
Histopathologically ALHE is an angiolymphoproliferative lesion which shows characteristically plump epitheloid or histioid endothelial cells, accompanied by an inflammatory infiltrate that mainly consists of lymphocytes and eosinophils.
We reported a case of angiolymphoid hypreplasia with eosinophilia occurring on the scalp in a 52-year-old female and review the literature.

Endometrial hyperplasia(EH) and endometrial carcinoma(EC) very in their biologic potential, which may be correlated with the histologic grade. Evaluation of cellular kinetics, which may prove to be another measure of predicting biologic behavior. Accessments of AgNORs and PCNA(proliferative cell nuclear antigen) indeces in 33 cases of EH including 16 cases of simple hyperplasia(SH), 8 of complex hyperplasia(CH), and 9 of atypical hyperplasia(AH), and 28 of EC including 7 of grade I, 12 of grade II, and 6 of grade III were performed. The results were as follows :I, 12 of grade II, and 6 of grade III were performed. The results were as follows : 1. AgNOR counts per glandular cells(Mean SD) were 2.7±0.2 in normal proliferative and 2.3±0.2 in secretory endometrium, and increased to 3.2±0.3 in SH, 3.5±0.3 in CH, to 5.4±0.4 in AH, and finally 6.9±0.5 in endometrioid carcinoma(grade I: 5.8±0.7, grade II: 6.7±0.6, grade III: 8.4±0.9). 2. PCNA indeces(percentages of nuclear positive cells of total cells of glands) were 16±14.2 in normal proliferative endometrium and 12±8.1 in secretory endometrium, and increased to 18.4±14.7 in SH, 21.6±17.8 in CH, 36.4±27.4 in AH, and finally 42.1±31.3 in EC(grade I: 38.3±23.2,grade II: 39.4±25.4, and grade III: 58.4±35.3). 3. DNA aneuploidy was detected in 4 cases of EC(40%), and tended to be more frequently found in poorer histologic grade. This data suggest that cell kinetic evaluation of EH and EC using AgNORs and PCNA is well correlated with histologic grade. And with the aspect of biologic potential, AH could be regarded as well differentiated EC.

