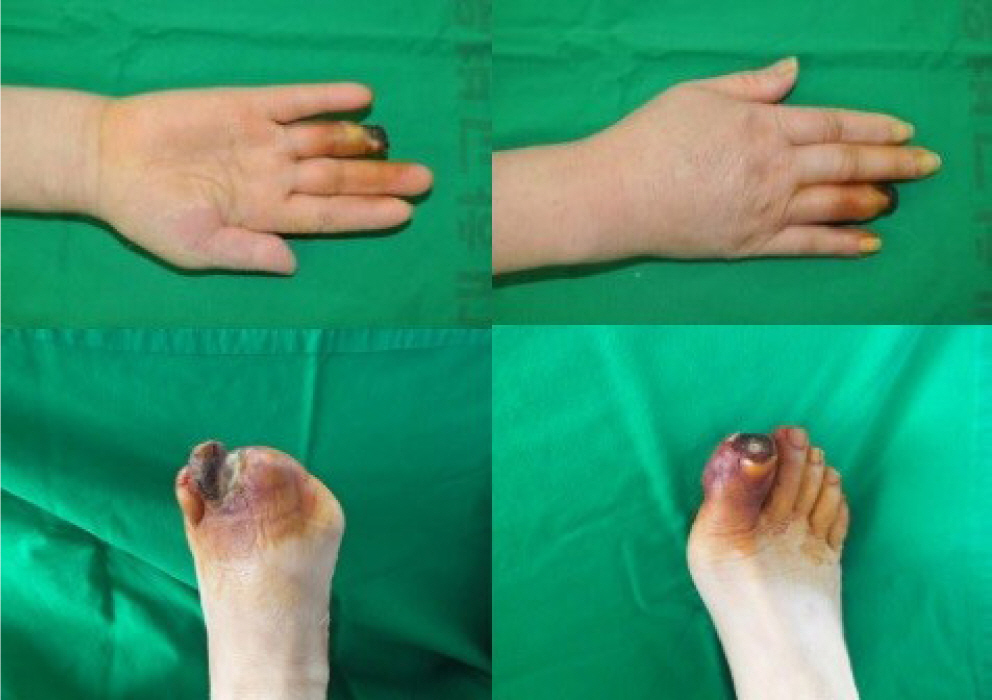
Symmetrical peripheral gangrene is a severe condition marked by symmetric acral necrosis without obstruction of the major blood vessels. This case report examines the critical decisions involved in choosing between early and delayed amputation, as well as determining the extent of the necessary amputation. We present three cases: one involving antiphospholipid syndrome, another with disseminated intravascular coagulation, and a third associated with diabetes mellitus. All three cases ultimately required amputation due to symmetrical peripheral gangrene. In the first two cases, amputation was delayed, which is typically advantageous as it allows for the clear demarcation of necrotic tissue. However, in the third case, where infection was evident, immediate amputation was necessary despite the patient's overall poor health.
 , Claudia Santosa
, Claudia Santosa , Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne
, Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne , Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara
, Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara  , Hee-June Kim
, Hee-June Kim , Sung Hun Kim
, Sung Hun Kim , Suk-Joong Lee
, Suk-Joong Lee
Citations


