 , Abdulraheem Almokhtar
, Abdulraheem Almokhtar , Hashem Bukhary
, Hashem Bukhary , Raed Sharaf
, Raed Sharaf , Khalid Alhomayani
, Khalid Alhomayani
 , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
 , Oh Haeng Lee
, Oh Haeng Lee , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
Citations

Shoulder pain is a common complaint in primary care settings. The prevalence of shoulder pain is on the rise, especially in societies with aging populations. Like other joint-related conditions, shoulder pain is predominantly caused by degenerative diseases. These degenerative changes typically affect bones, tendons, and cartilage, with common conditions including degenerative rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Diagnosing these degenerative diseases in older adults requires a thorough understanding of basic anatomy, general physical examination techniques, and specific diagnostic tests. This review aims to outline the fundamental physical examination methods for diagnosing shoulder pain in older adult patients in primary care. The shoulder's complex anatomy and its broad range of motion underscore the need for a systematic approach to evaluation. Routine inspection and palpation can identify signs such as muscle atrophy, bony protrusions, or indications of degenerative changes. Assessing range of motion, and distinguishing between active and passive deficits, is crucial for differentiating conditions like frozen shoulder from rotator cuff tears. Targeted strength tests, such as the empty can, external rotation lag, liftoff, and belly press tests, are instrumental in isolating specific rotator cuff muscles. Additionally, impingement tests, including Neer’s and Hawkins’ signs, are useful for detecting subacromial impingement. A comprehensive understanding of shoulder anatomy and a systematic physical examination are vital for accurately diagnosing shoulder pain in older adults. When properly executed and interpreted in the clinical context, these maneuvers help differentiate between various conditions, ranging from degenerative changes to rotator cuff pathology.
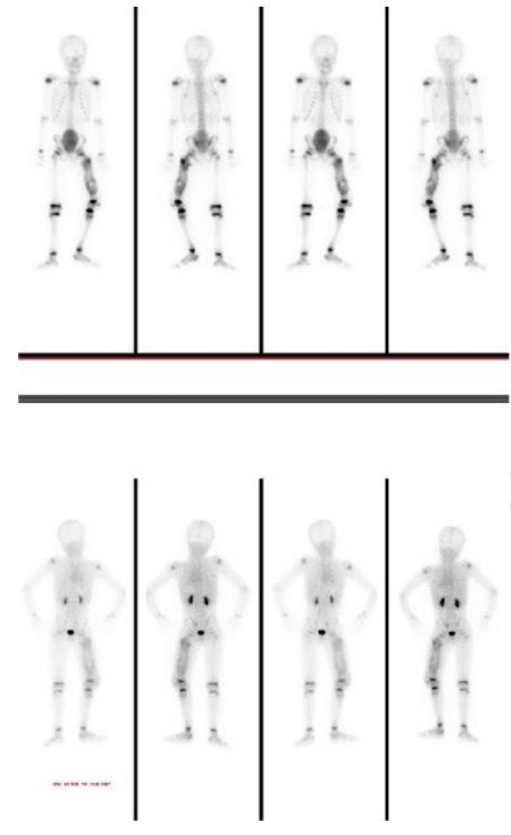
Shoulder diseases pose a significant health challenge for older adults, often causing pain, functional decline, and decreased independence. This narrative review explores how deep learning (DL) can address diagnostic challenges by automating tasks such as image segmentation, disease detection, and motion analysis. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of DL-based convolutional neural networks and machine learning frameworks in diagnosing various shoulder pathologies. Automated image analysis facilitates the accurate assessment of rotator cuff tear size, muscle degeneration, and fatty infiltration in MRI or CT scans, frequently matching or surpassing the accuracy of human experts. Convolutional neural network-based systems are also adept at classifying fractures and joint conditions, enabling the rapid identification of common causes of shoulder pain from plain radiographs. Furthermore, advanced techniques like pose estimation provide precise measurements of the shoulder joint's range of motion and support personalized rehabilitation plans. These automated approaches have also been successful in quantifying local osteoporosis, utilizing machine learning-derived indices to classify bone density status. DL has demonstrated significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in the management of shoulder diseases in older patients. Machine learning-based assessments of imaging data and motion parameters can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, to ensure their generalizability, reproducibility, and effective integration into routine clinical workflows, large-scale, prospective validation studies are necessary. As data availability and computational resources increase, the ongoing development of DL-driven applications is expected to further advance and personalize musculoskeletal care, benefiting both healthcare providers and the aging population.
This review classifies and summarizes the major shoulder diseases affecting older adults, focusing on rotator cuff disease, frozen shoulder, osteoarthritis, and shoulder instability. It explores each condition's pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnostic approaches, and treatment strategies to guide clinicians in optimizing patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life. Age-related degenerative changes, comorbidities, and distinct etiological factors contribute to the presentation of shoulder disorders in older adults. Rotator cuff disease ranges from tendinopathy to full-thickness tears and is influenced by genetic predispositions, inflammatory cytokines, and muscle quality. Frozen shoulder results from fibroproliferative changes in the capsule, leading to significant pain and restricted motion. Osteoarthritis involves cartilage degeneration and bony remodeling, often necessitating surgical interventions such as arthroplasty. Shoulder instability, though less frequent, is complicated by associated injuries like rotator cuff tears and fractures, requiring tailored management strategies. Advances in imaging techniques, biologic treatments, and surgical procedures, particularly arthroscopic and arthroplasty options, have improved diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic outcomes. A thorough classification of shoulder diseases in older adult patients highlights the complexity of managing these conditions. Effective treatment requires individualized approaches that integrate conservative measures with emerging biologic or surgical therapies. Future research should focus on targeted interventions, standardized diagnostic criteria, and multidisciplinary collaboration to minimize disability, optimize function, and improve overall quality of life in this growing patient population. Multimodal strategies, including patient education, structured rehabilitation, and psychosocial support, further enhance long-term adherence and outcomes. Ongoing vigilance for comorbidities, such as osteoporosis or metabolic disorders, is necessary for comprehensive care.
 , Kyoung Hwan Koh
, Kyoung Hwan Koh , In-Ho Jeon
, In-Ho Jeon
The elbow joint, with its intricate anatomy, plays a pivotal role in the upper limb's functional movements. Common surgical indications include epicondylitis, osteoarthritis, tendon tears, and neuropathies. Irrespective of the nature of surgery, appropriate postoperative rehabilitation is essential to enhance recovery, optimize functional outcomes, and minimize complications. Protective measures for the elbow vary based on the surgical procedure is performed. Extended postoperative immobilization is generally not advised. Temporary splints may be utilized to protect the soft tissues in the immediate aftermath of surgery, with patients advised to intermittently remove them to facilitate elbow movement. To increase mobility while ensuring the safety of repaired tendons or ligaments, articulated dynamic braces are recommended. This review delivers clinically useful recommendations specific to various surgical procedures, designed to be user-friendly even for non-specialists in orthopaedic surgery.
 , Young Dae Jeon
, Young Dae Jeon
Pain originating from the elbow can be due to issues affecting the joint itself or the structures surrounding it. These structures include the medial and lateral epicondyles, associated ligaments, the origins of wrist flexor and extensor muscles, the olecranon bursa, the distal biceps tendon, and the radial and ulnar nerves. Pain that appears to originate from a different location may actually be referred pain, potentially stemming from the neck (cervical radiculopathy) or the shoulder. Among complaints related to the elbow, lateral elbow pain is the most frequently reported. This pain could originate from the lateral epicondyle, the radiohumeral joint, or it could be referred pain from other areas. Medial elbow pain is the second most common complaint, often resulting from issues with the medial epicondyle or the ulnar nerve as it travels through the cubital tunnel. The biceps tendon is frequently the cause of anterior elbow pain. Patients who report swelling in the elbow are often experiencing olecranon bursitis. These conditions can often be effectively managed through conservative treatment. The aim of this article is to provide a structured approach to addressing patients with elbow pain, by detailing the common causes of such discomfort and exploring effective nonsurgical treatment options.
 , Yong-Bum Joo
, Yong-Bum Joo , Jae-Young Park
, Jae-Young Park , Woo-Yong Lee
, Woo-Yong Lee
Elbow pain is a common symptom encountered in clinical practice. Pathology can arise from any component of the joint, including the bone, tendons, ligament, bursa, or nerves. This paper discusses how elbow pain can be differentiated according to its anatomic location and presents the corresponding causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
 , Jong In Han
, Jong In Han , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Chi Hyo Kim
, Chi Hyo Kim , Guei Yong Lee
, Guei Yong Lee , Choon Hi Lee
, Choon Hi Lee , Yeon Jin Cho
, Yeon Jin Cho
There are controversies about the analgesic effects of intraaarticular morphine and local anethetics bupivacaine. This study sought to compare the effects of saline with mor-phine, bupivacaine with or without epinephrine, administrated intraarticularly upon pos-toperative pan following arthroscopic knee surgery under general anesthesia.
In a double-blined, randommized manner, 40 patients received one of saline(20ml, n=10), morphine(1mg in 20ml NaCl, n=10), bupivacaine(0.25%, 20ml, n=10), bu-pivacaine with epinephrine(0.25%, 20ml, 200ug of epinephrine, n=10) intaarticularly at the completion of surgery. The pain scores by VAS were determined after 1,2,3,4 and 24 hours after intraarticular administration.
There were no significant statistical differences between four groups in the pain score. The maximal pain scores were 37.5 in control group, 48.0 in morphine group, 33.6 in bupivacaine group postoperative 1 hour and 32.9 in bupivacaine with epinephrine group pos-toperative 2 hours. The pain scores were decreased as the time went by and were minimin as 21.4 in control group, 17.6 in morphine group, 11.2 in bupivacaine group and 12.3 in bu-pivacaine with epinephrine group 24 hour postoperatively.
Though there were no significant statistical significances with those doses, there were tendencies that the bupivacaine group with or without epinephrine had the postoperative analgesic effect rather than control group, and morphine group had a slow onset of analgesic ef-fect. So, we should study to decide the dose or volume of the drugs and appropriate time to evaluate for the anagesic effects after knee arthroscopy further.

There have been many recent advances in the clinical and basic sciences concerring the causeand cure of back pain and sciatica.
Pain drawings has improved our diagnostic acumen and clinical evaluation in same speed ofmodern diagnositic equipment such as magnetic resonance imaging(MRI). Adequate pain drawings obtained from 100 patients who was treated for a low back disorder from October 1993 to September 1994.
An initial dignostic impression was made at a glance over the pain drawing into five diagnostic group and the results were compared with the final diagnosis after treatment with magnetic resonance image(MRI).
One helpful strategy in diagnosing cause of back and leg pain syndrome is to assign patientsto one of five diagnostic groups. These are (1) benign etiologies (2) radicalopathy from herniated disk (3) radicalopathy seconday to spinal stenosis (4) serious underlying disorders and (5)behavioral disorders.
The initial impressions were 7 benign back pains, 55 disc herniation, 20 spinal stenosis, 15significant underlying disorder and 3 psycogenic back pain. The final diagnosis were 61 disc herniation, 17 spinal stenosis, 12 underlying disease, 7 degenertative disease, 3 psychogenic disorder.
Concerning the disc herniation, spinal stenosis, psychogenic disorder there were significant relationship between the initial impression and the final diagnosis. Pain drawings afford an important clue to disc herniation, psycogenic disorder in the assessment of back pain.

The treatment of herniated lumbar disc has been a challenging problem in spite of various methods of treatments such as conservative, chymopapain injection, percutaneous automated nucleotome method and surgical removeal of discs. Among the above listed treatment, Smith and Brown reported the clinical experience by way of intradiscal injection of chymopapain with beneficial result and clinical reports followed thereafter.
On the other hand, the serious neural adverse effects were reported by Smith laboratories since the clinical application of chymopapain such as transverse myelitis, paralysis, seizures and hemiplegia which is not fully clarified but may be due to chymopapain itself and improper technique. This study was carried out to clarify the effect of chymopapain on the spinal cord and peripheral nerves by way of application topically in rabbits.
The results were as follows :
1) There were no abnormal gross or histological findings when the chymopapain was spread around the sciatic nerve and spinal cord extradurally.
2) In the group of the chymopapain injected into the sciatic nerve sheath, there was immediate nerve paralysis and severe necrosis of the axon. But the schwann's sheath was intact and no hemorrhage was observed.
3) In the group of intradural chymopapain injection, there was massive hemorrhage, perivascular neutrophil infiltration and necrosis of the gray mater of spinal cord.
In conclusion with this experimental study, the chymopapain induced peripheral neuropathy followed by axonal necrosis when injected into peripheral nerve. The central neuropathy was developed with hemorrhage and necrosis of the gray mater of the cord when the chymopapain injected intradurally.

