 , Sohyun Ahn
, Sohyun Ahn , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
Citations


Citations

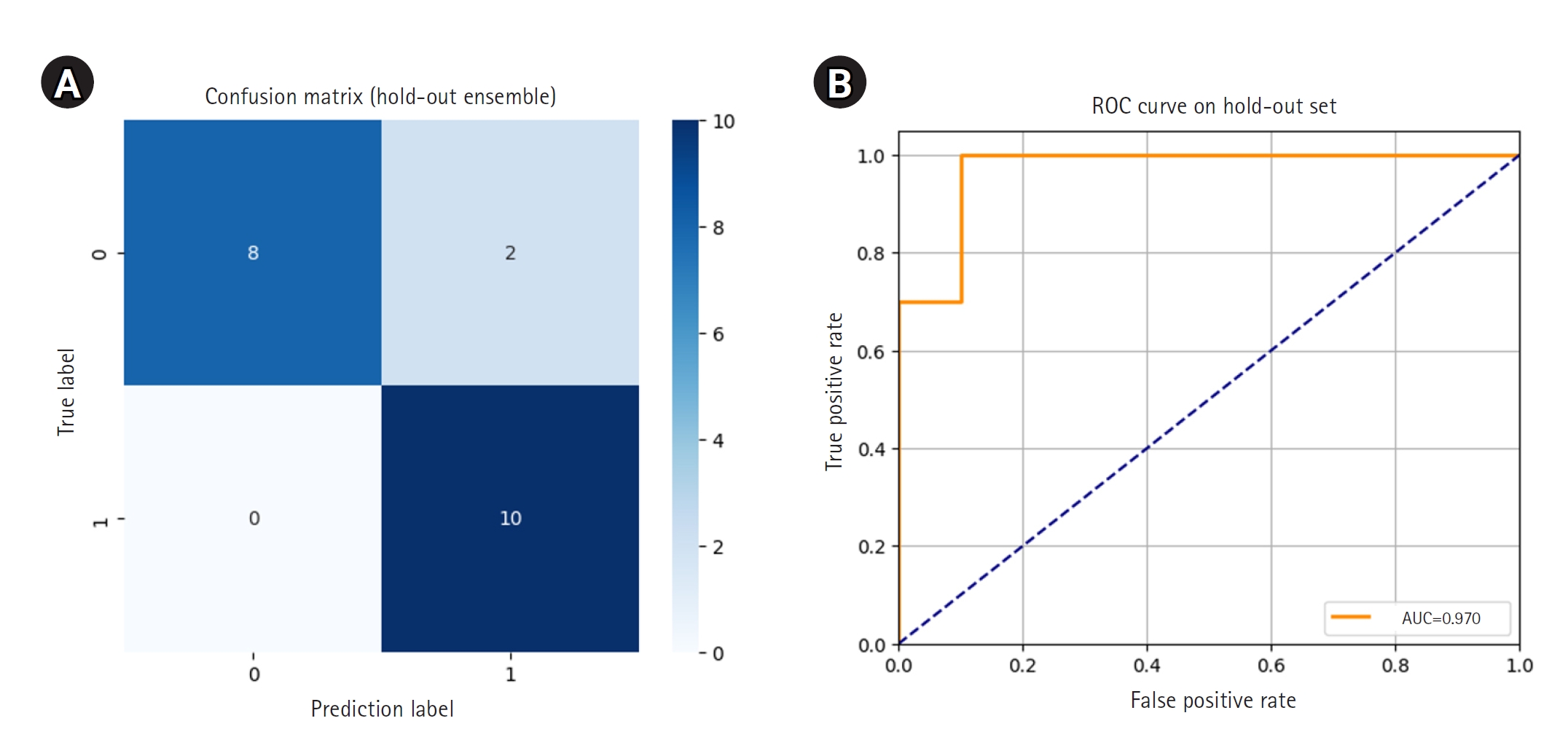
Shoulder diseases pose a significant health challenge for older adults, often causing pain, functional decline, and decreased independence. This narrative review explores how deep learning (DL) can address diagnostic challenges by automating tasks such as image segmentation, disease detection, and motion analysis. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of DL-based convolutional neural networks and machine learning frameworks in diagnosing various shoulder pathologies. Automated image analysis facilitates the accurate assessment of rotator cuff tear size, muscle degeneration, and fatty infiltration in MRI or CT scans, frequently matching or surpassing the accuracy of human experts. Convolutional neural network-based systems are also adept at classifying fractures and joint conditions, enabling the rapid identification of common causes of shoulder pain from plain radiographs. Furthermore, advanced techniques like pose estimation provide precise measurements of the shoulder joint's range of motion and support personalized rehabilitation plans. These automated approaches have also been successful in quantifying local osteoporosis, utilizing machine learning-derived indices to classify bone density status. DL has demonstrated significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in the management of shoulder diseases in older patients. Machine learning-based assessments of imaging data and motion parameters can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, to ensure their generalizability, reproducibility, and effective integration into routine clinical workflows, large-scale, prospective validation studies are necessary. As data availability and computational resources increase, the ongoing development of DL-driven applications is expected to further advance and personalize musculoskeletal care, benefiting both healthcare providers and the aging population.

