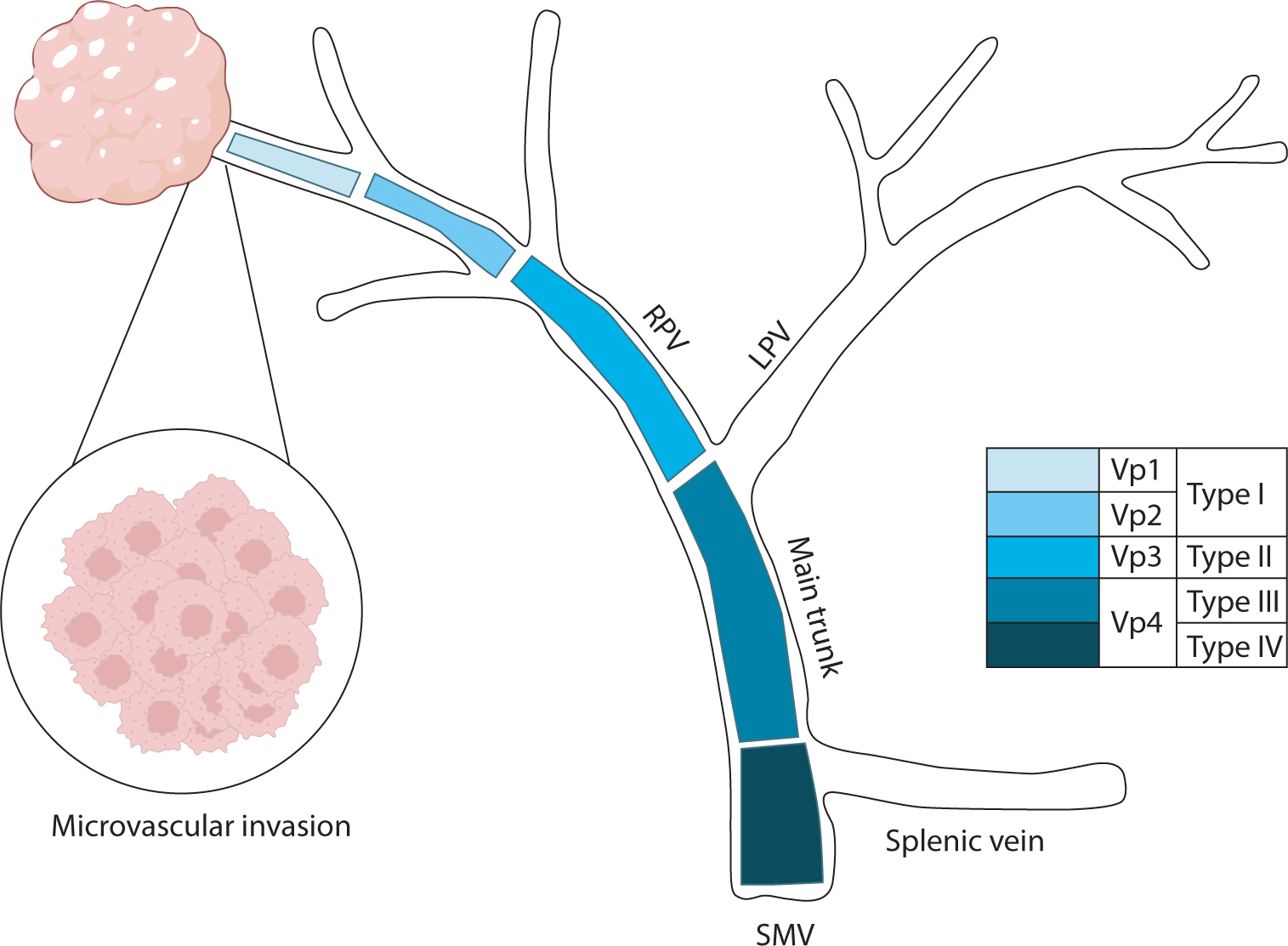
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.

Small-for-size syndrome (SFSS) is a critical complication of partial liver
transplantation, particularly in adult-to-adult living donor liver
transplantation (ALDLT) using a small graft. Minimally required liver graft size
for a successful ALDLT is classically 40% of a standard recipient’s liver
volume or 0.8% of recipient body weight. Recent progress in perioperative care
and technical improvement push the lower limit of safe graft size to 25% of the
recipient’s standard liver volume or 0.6% of the graft versus recipient
weight ratio although this is an ongoing debate. The clinical manifestations of
SFSS include various symptoms and signs related to graft dysfunction and portal
hypertension in patients with small grafts. The risk factors for SFSS include
poor preoperative patient condition, including portal pressure, surgical
techniques to reduce portal pressure, and graft quality and size. Hence, various
approaches have been explored to modulate inflow and pressure to a small graft
and to decrease the outflow block to alleviate this SFSS as well as the
selection of a patient and graft. Additionally, recent research and efforts to
prevent and treat SFSS are reviewed.
 , Rack Kyung Chung
, Rack Kyung Chung , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Geun Hong
, Geun Hong
Liver transplantation (LT) is the only treatment for end stage of liver failure. In Korea, annually it has been performed 1,300 cases. Most of LTs are performed in large volumes centers. More than half of centers performing LT in Korea are low volume hospital and started a LT program recently. We present our four-year experiences and outcomes of anesthesia for LT since 2013.
Anesthetic and surgical outcomes of 49 consecutive patients who received LT (living donor LT, 21 cases; deceased donor LT, 28 cases) between April 2013 and April 2017 were analyzed retrospectively.
All patients were adult, with the mean age of 53.5±9.2 years. The most common cause of original liver diseases was hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis (40.8%). The mean MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score was 18.8±10.7. Postreperfusion syndrome was observed in 34.7%, which were all controlled by calcium, norepinephrine, ephedrine and epinephrine. The mean postoperative intensive care unit stay of deceased donor LT recipients (13.6±9.0 days) was significantly longer than that of living donor LT recipients (8.0±3.3 days). There was no intraoperative mortality in patients receiving LT. Thirty-day post-transplant survival rate was 93.8% and 3-year survival rate was 88.6 %. The most common postoperative complication was pneumonia.
We have started LT successfully with multidisciplinary team's steady effort. Adaptation and setting up LT protocol, adequate equipment, proper training at established transplant centers are essential to begin a successful LT program.
 , Joo Ho Lee
, Joo Ho Lee , Yun Bin Lee
, Yun Bin Lee , Hana Park
, Hana Park , Seong Gyu Hwang
, Seong Gyu Hwang , Kyu Sung Rim
, Kyu Sung Rim
Acute clinical deterioration in patients with chronic liver disease is called acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF). Principles of management of ACLF consist of early identifying etiology of liver disease, rapid intervention of precipitating event and discreet intensive cares. Despite medical intensive cares, if liver failure progresses, liver transplantation could be the other option. Also, liver transplantation is the only treatment that offers a chance of cure for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the underlying liver cirrhosis simultaneously. Emergent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) can be performed for patients with acute liver failure and improves survival rate, especially in circumstances which liver graft is often not available because of deceased donors are not affordable. Here, we describe a chronic hepatitis B patient who developed ACLF accompanying early HCC. Because he did not improved with medical care, he received emergent LDLT. After LDLT, he showed great improvement without critical complications.
Citations


