 , Jitendra Singh Nigam
, Jitendra Singh Nigam , Immanuel Pradeep
, Immanuel Pradeep , Ashutosh Rath
, Ashutosh Rath , Seetu Palo
, Seetu Palo , Naina Kumar
, Naina Kumar


Citations

 , Joonil Hwang
, Joonil Hwang , Hai-Jeon Yoon
, Hai-Jeon Yoon , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn


Citations

 , Minsung Kim
, Minsung Kim
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols are designed to minimize surgical stress, preserve physiological function, and expedite recovery through standardized perioperative care for primary colorectal surgery patients. This narrative review explores the benefits of current ERAS protocols in improving outcomes for these patients and provides insights into future advancements. Numerous studies have shown that ERAS protocols significantly reduce the length of hospital stays by several days compared to conventional care. Additionally, the implementation of ERAS is linked to a reduction in postoperative complications, including lower incidences of surgical site infections, anastomotic leaks, and postoperative ileus. Patients adhering to ERAS protocols also benefit from quicker gastrointestinal recovery, marked by an earlier return of bowel function. Some research indicates that colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery with ERAS protocols may experience improved overall survival rates. High compliance with ERAS protocols leads to better outcomes, yet achieving full adherence continues to be a challenge. Despite these advantages, implementation challenges persist, with compliance rates affected by varying clinical practices and resource availability. However, the future of ERAS looks promising with the incorporation of prehabilitation strategies and technologies such as wearable devices and telemedicine. These innovations provide real-time monitoring, enhance patient engagement, and improve postoperative follow-up, potentially transforming perioperative care in colorectal surgery and offering new avenues for enhanced patient outcomes.
Citations

 , Jieun Jang
, Jieun Jang , Nayoung Kim
, Nayoung Kim
Citations

 , Zekeriya Temircan
, Zekeriya Temircan
The present study aims to examine the frequency of sleep disorders and the level of sleep quality, as well as their relationship with health-related quality of life in cancer patients.
This multi-center cross-sectional survey included 333 cancer patients ranging in age from 16 to 72 years, between June 15, 2017, and August 30, 2018 at the Ankara Oncology Hospital and Erciyes University Kemal Dedeman Oncology Hospital Polyclinic. Data were collected via various surveys conducted through face-to-face interviews, including following measurement tools: Short Form 36 Health Questionnaire, the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, the Epworth Sleepiness, and the Berlin Sleep Questionnaire for obstructive sleep apnea. Face-to-face interviews were carried out with patients who presented for an initial examination or follow-up and were awaiting their appointments.
The most commonly reported sleep disorders were daytime sleepiness (36.9%), sleep respiratory disorders (34.8%), insomnia (29.4%), and parasomnias (28.8%). Good sleepers were found to have significantly higher physical (40.20±10.08 vs. 33.21±8.06; P<0.001) and mental component scores (43.54±8.25 vs. 38.20±7.52; P<0.001) than poor sleepers. Conversely, individuals with insomnia (P<0.01), daytime sleepiness (P<0.001), sleep-respiratory disorders (P<0.05), and bruxism (P<0.001) showed significantly lower scores in both physical and mental components. Additionally, those with restless legs syndrome had a significantly lower physical component score (P<0.001), and those with parasomnias had significantly lower mental component scores.
Cancer patients exhibited moderate average sleep quality scores, with over half of them demonstrating low quality sleep patterns. Sleep disorders significantly impacted their health-related quality of life.
Citations


Endocrine tumor syndromes constitute a group of disorders characterized by tumors in hormone-producing tissues. These conditions predominantly affect younger patients and often have a familial inheritance. Advances in molecular genetics in recent decades have facilitated the identification of several genes associated with these tumors. The recent World Health Organization classification of adrenocortical tumors integrates the latest developments in pathology, oncology, and molecular biology. In addition, this updated classification includes adrenal cortical diseases based on an understanding of germline susceptibility to these conditions and their clonal-neoplastic nature. Catecholamine-secreting tumors, including pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma, have been found to have a genetic predisposition in as many as 80% of cases. Compared to sporadic cases, endocrine tumor syndromes are more likely to present bilaterally and show synchronous or metachronous disease. This highlights the critical need for early diagnosis, intervention, and ongoing surveillance. This review focuses on the clinical manifestations and genetic basis of endocrine tumor syndromes originating from the adrenal glands.
Citations

Over the past 3 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has posed significant challenges to the healthcare system, leading to delays in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases due to the need for social distancing measures. Colorectal cancer has not been immune to these disruptions, and research in various countries has explored the impact of COVID-19 on the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. One notable consequence has been the postponement of colorectal cancer screenings, potentially resulting in disease progression, which can adversely affect surgical and oncological outcomes. Furthermore, the treatment approach for colorectal cancer may vary depending on the extent of disease progression and the healthcare policies implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this systematic review, we examine treatment strategies, surgical outcomes, and oncological variables across multiple studies focusing on colorectal cancer treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this analysis was to assess how medical policies enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have influenced the outcomes of colorectal cancer treatment. We hope that this review will provide valuable insights and serve as a foundational resource for developing guidelines to address potential medical crises in the future.
 , Eun Jung Park
, Eun Jung Park
In stage IV colorectal cancer (CRC), peritoneal metastasis is associated with a poor prognosis. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) after cytoreductive surgery (CRS) is an effective treatment option that offers survival benefits in patients with peritoneal metastatic CRC. For over the past several decades, a multitude of studies have been conducted on CRS and HIPEC for peritoneal metastatic diseases, and research in this area is ongoing. Proper patient selection and a meticulous preoperative assessment are crucial for achieving successful postoperative outcomes. The completeness of cytoreduction and the surgical techniques employed are key factors in improving oncologic outcomes following CRS and HIPEC. The role of HIPEC for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes is currently being evaluated in recent clinical trials. This article reviews the fundamental principles of CRS combined with HIPEC and discusses recent clinical trials concerning the treatment of CRS and HIPEC in CRC patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis.

The primary objective in the treatment of early rectal cancer is to achieve optimal oncological control while minimizing the long-term impact of therapeutic interventions on patients' quality of life. The current standard of care for most stage I and II rectal cancers involves radical surgery, specifically total mesorectal excision. Although total mesorectal excision is generally curative for early rectal cancers, it can significantly affect patients' quality of life by potentially necessitating a permanent colostomy and causing bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction. Given the morbidity associated with radical surgery, alternative approaches to managing early rectal cancer, such as local excision through transanal excision, transanal endoscopic microsurgery, and transanal minimally invasive surgery, have been investigated. If these surgical approaches are applied cautiously to carefully selected cases of early rectal cancer, it is anticipated that these local procedures will achieve comparable oncological outcomes to the established standard of radical surgery, potentially offering superior results regarding morbidity, mortality, and overall quality of life.

Preoperative chemoradiotherapy (pCRT) followed by total mesorectal excision is the accepted standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. The purpose of pCRT is to prevent the spread of viable tumor cells within the local area during surgical procedures. Additionally, pCRT can facilitate the resection of locally advanced tumors that are otherwise challenging to remove, thereby enabling a radical resection. Although a pathologic complete response is observed in fewer than 20% of patients, the reasons for the variability in tumor response to pCRT are not fully understood. Several techniques have been researched with the aim of improving the tumor response to pCRT. These techniques include intensifying or combining chemotherapy, either simultaneously or sequentially, increasing radiation dose, modifying radiation mode or schedule, adjusting the interval between radiation and surgery, and incorporating multiple agents to increase the efficacy of pCRT. This review discusses various strategies that may improve tumor response outcomes following pCRT.
 , Il Tae Son
, Il Tae Son , Bo Young Oh
, Bo Young Oh
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a globally prevalent and challenging malignancy. Accurate prognosis prediction is essential for optimizing patient care. This comprehensive review discusses the intricate relationships between inflammatory response markers and CRC prognosis. Inflammatory response markers have gained prominence as a prognostic tool. Elevations in the preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein-albumin ratio predict a poor prognosis for patients with CRC. A decreased lymphocyte-monocyte ratio is also a poor prognostic factor. A high Glasgow prognostic score and a high modified Glasgow prognostic score are associated with adverse outcomes, including reduced survival. While significant progress has been made, challenges remain in standardizing the clinical application of these inflammatory response markers. Prospective research and further investigations are warranted to refine the prognostic models. Enhanced understanding and utilization of these inflammatory response markers will help advance personalized treatment strategies, refine surveillance protocols, and improve the management of CRC.
Citations


The rate of colorectal cancer (CRC) has altered. Early-onset CRC patients are increasing, and it is one of the main causes of cancer-related death. Based on epidemiologic change, the CRC screening program needs to be changed. To increase compliance, non-invasive screening techniques are developed. Although CRC survival has increased, the oncologic prognosis of metastatic CRC is remains poor. Even in metastatic CRC, which is the most difficult to treat, attempts are being made to increase the survival rate by active surgical therapy with the creation of chemotherapeutic regimens and targeted treatment based on genomic information. Due to the introduction of aggressive chemotherapy regimens, targeted therapy based on genomic features, and improvements in surgical technique, the role of surgical treatment in metastatic CRC has expanded. Metastatic CRC surgery was indicated for liver, lung, and even peritoneal seeding. Local ablation therapy was also effectively used for liver and lung metastasis. Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy were tried for peritoneal seeding and demonstrated good results in a subgroup of patients, although the right indication was carefully assessed. At the same time, one of the key goals of treatment for CRC was to maintain functional outcomes. Neoadjuvant treatment, in particular, helped rectal cancer patients preserve functional results while maintaining oncologic safety. Rectal cancer organ preservation techniques are now being researched heavily in a variety of neoadjuvant treatment settings, including immunotherapy and whole neoadjuvant therapy. Precision medicine based on patient and disease characteristics is currently being used for the diagnosis and treatment of CRC.
Citations


Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a condition of anorectal dysfunction that occurs frequently following anal sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer and can reduce the quality of life. In this review, we summarize the main symptoms and pathophysiology of this syndrome and discuss the treatment approaches. Early evaluation and initiation of appropriate treatment postoperatively are crucial. The most frequently used tool to evaluate the severity of LARS is the LARS score, and an anorectal manometer is used for objective evaluation. LARS is believed to be caused by multiple factors, and some of its causes include direct structural damage to the anal sphincter, damage to the innervation, loss of rectoanal inhibitory reflex, and decreased rectal volume and compliance. Diet modifications, medications, pelvic floor muscle training and biofeedback are the primary treatments, and rectal irrigation can be added as a secondary treatment. If LARS symptoms persist even after 1 to 2 years and significantly reduce the quality of life, antegrade irrigation, sacral nerve stimulation or definitive stoma may be considered. High-quality evidence-based studies on LARS treatment are lacking, and randomized controlled trials aimed at developing severity-based treatment algorithms are needed.
Citations

Minimally invasive surgery for colorectal disease has now become the standard treatment in Republic of Korea. However, there are limitations to the laparoscopic approach, such as an unstable camera support, a limited range of motion, and poor ergonomics. Recent advances in technology have led to the introduction of robotic surgical systems in colorectal surgery to overcome these shortcomings. Robot-assisted colorectal surgery has clear advantages in many aspects. Surgery involving the rectum benefits the most among colorectal diseases owing to technical difficulties in rectum dissection. The concept of robotic surgery is not different from laparoscopic surgery in that it is a minimally invasive surgery, and abundant research demonstrates comparable results from both modalities for postoperative complications, oncological outcomes, and functional outcomes. However, the cost of robot-assisted surgery limits surgeons to performing robotic surgeries in only selected cases. Improvements regarding cost-effectiveness and more convincing studies that support benefits of robotic surgery are needed to popularize robot-assisted colorectal surgery.
Citations


Local recurrence was reduced considerably due to the introduction of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy as treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer. However, certain proportions of patients would experience local recurrence inevitably; the lateral pelvic lymph node is the primary site of rectal cancer recurrence even after administering neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. It remains unknown whether lateral pelvic lymph node metastasis is considered as a locoregional disease or a distant metastasis. Although the oncologic stance of lateral pelvic lymph node metastasis is controversial, there is increasing research interest in evaluating the conditional benefit of lateral pelvic lymph node dissection in a subgroup of patients. Researchers reported an improvement in local control in patients with clinically suspected lateral pelvic lymph node metastasis before/or after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy who underwent lateral pelvic lymph node dissection. However, there is no clear consensus regarding the indication, diagnostic method, and extent of lateral pelvic lymph node dissection.
Citations

Brain metastases are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with systemic cancer and are among the most common intracranial tumors in adults. Its incidence increases as cancer therapies improve, and patients live longer, providing new challenges to the multidisciplinary teams that manage these patients. The contemporary neurosurgical treatment of intracranial metastases has become gradually more complex as the available therapeutic options increase. For the past 50 years, whole brain radiotherapy and systemic corticosteroids have been considered as the standard of care for patients with brain metastases. However, in recent years, stereotactic radiosurgery is spotlighted as an alternative therapeutic modality for these patients because of its relatively short, convenient, and non-invasive treatment course. Stereotactic radiosurgery is a radiation therapy technique in which multiple focused radiation beams intersect over a target, which results in the delivery of highly conformal, high-dose of radiation to the target and minimal radiation to surrounding normal parenchyma. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of stereotactic radiosurgery as a treatment modality for patients with brain metastases.
Citations

 , Juhui Kim
, Juhui Kim , Mi-Kyung Kim
, Mi-Kyung Kim , Yun Hwan Kim
, Yun Hwan Kim , Seung Cheol Kim
, Seung Cheol Kim
Lymphomas that originate from the female genital tract are very rare. Primary cervical lymphoma only accounts for less than 1% of all extra-nodal lymphomas. Clinical manifestations of primary cervical lymphoma can be nonspecific, vaginal bleeding being the most common symptom, and this makes timely diagnosis often difficult. Prognosis and optimal treatment have yet been established due to the rarity of the disease. In this article, a rare case of primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of cervix is reported with a review of the available literature.
Citations

 , Hyungju Kwon
, Hyungju Kwon , Woosung Lim
, Woosung Lim , Byung-In Moon
, Byung-In Moon , Nam Sun Paik
, Nam Sun Paik
Active surveillance (AS) of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma was first suggested by Dr. Akira Miyauchi at Kuma Hospital in 1993. Based on several subsequent evidences, AS was approved by the American Thyroid Association in 2015. AS is no longer an experimental treatment but has become an acceptable standard of care for patients with low-risk thyroid cancers. No molecular markers, such as BRAF mutations, have been identified to predict the prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer. However, future molecular studies may reveal the relationship between genetic mutations and thyroid cancer prognosis. AS involves closely monitoring thyroid cancer over time, instead of immediately treating it with surgery. Patients and medical doctors should consider these two options: observation or surgery.
Over the past decade, substantial advances have been made in the individualization of therapeutic strategies for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Treatment strategies have been developed and classified according to their molecular and genetic characteristics based on predictive biomarkers such as microsatellite instability,
Citations

 , Geon Woo Lee
, Geon Woo Lee , Jae-Joon Kim
, Jae-Joon Kim , Sang-Bo Oh
, Sang-Bo Oh , So Yeon Oh
, So Yeon Oh , Eun-Ju Park
, Eun-Ju Park , Jin Hyeok Kim
, Jin Hyeok Kim , Joo Yeon Jang
, Joo Yeon Jang , Ung-Bae Jeon
, Ung-Bae Jeon
Terminally ill cancer patients in hospice palliative care unit are reluctant to undergo repetitive invasive procedures due to coagulopathies and poor performance or condition, while catheter management such as regular irrigation during hospitalization is easy. The purpose of this study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of indwelling intraperitoneal (IP) catheter in hospitalized terminally ill cancer patients with recurrent ascites.
A retrospective review was conducted in patients who underwent IP catheter at the hospice palliative care unit of Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital between August 2016 and June 2018. All catheters were inserted by interventional radiologists with radiological guidance. The primary end-points were functional IP catheter maintenance rate, which is catheter maintained with patency for drainage until the intended time.
A total of 25 terminally ill cancer patients underwent IP catheters placements during the study period. All catheters were successfully inserted without major complications, but one patient had trivial bleeding and one other patient had temporary pain. The median time from admission to catheter insertion was 5 days (range, 1 to 49 days). Twenty-one catheters were maintained with function until the intended time, three cases were maintained without function, and the last one was removed early due to obstruction and pain. Finally, the functional IP maintenance rate was 84% (21/25) and the median functional catheter life span was 15 days (95% confidence interval, 10.8 to 17.2).
Our study showed relatively favorable results for IP catheter maintenance and safety in hospitalized terminally ill cancer patients with malignant ascites.
 , Yun Ha Hwang
, Yun Ha Hwang , Joong Gyu Ha
, Joong Gyu Ha , In Taek Hwang
, In Taek Hwang , Seung Hyun Kim
, Seung Hyun Kim
Uterine tumors resembling ovarian sex-cord tumors (UTROSCT) are very rare tumors that occur mainly in the uterine fundus of women in reproductive age. These tumors can be classified into group 1 and group 2 by histological results. In group 1, epithelial-like differentiation is partially observed in the tumors. In group 2, sex-cord elements are predominant in uterine mural mass. We experienced UTROSCT group 1 in a 29-year-old woman who complained of severe abdominal pain that started one week after delivery and UTROSCT group 2 case in a 49-year-old woman who complained of dysfunctional uterine bleeding. We report two different types of UTROSCT cases that we experienced.
Citations

 , Ahyoung Cho
, Ahyoung Cho , Hae Kyung Yoo
, Hae Kyung Yoo , Hye-Sung Moon
, Hye-Sung Moon
The aim of our study is to compare the findings of investigative modalities and second look laparoscopy in ovarian cancer and establish the safety and accuracy of second look laparoscopy for detecting ovarian cancer.
We retrospectively reviewed 11 patients with ovarian cancer treated by a single surgeon from 2006 to 2013. These patients were diagnosed at the time of primary cytoreductive surgery and received six cycles of combination chemotherapy. Then, they underwent second look laparoscopy. They were followed up with tumor markers monthly and PET-CT and/or CT scans.
All 11 patients had undergone primary surgery followed by six cycles of consolidation chemotherapy. Eight patients had positive pathologic findings on second look laparoscopy (72.7 %). The CA 125 level was higher in one patient (12.5%). In seven patients who had positive results on second look laparoscopy, the value was well below normal limits (87.5%). Three patients had recorded increases in fluorodeoxyglucose uptake (37.5%). The increase in standardized uptake values in specific regions in the scans corresponded to positive biopsies from those regions. Seven patients who had positive findings on second look laparoscopy were treated with consolidation chemotherapy. The 5-year survival rate was 66.67%, and the 5-year recurrence rate was 33.33%.
There are limitations to the accuracy of current investigative techniques, and we must rely on clinical correlation with these modalities for each case of second look laparoscopy. It is feasible to safely perform second look laparoscopy to detect remnant ovarian cancer.
 , Hee Jung Park
, Hee Jung Park , Chang Mo Moon
, Chang Mo Moon , Seong-Eun Kim
, Seong-Eun Kim , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung , Min Sun Cho
, Min Sun Cho
Cancer stem cells are defined as focal cluster of cells within a tumor that possess the capacity for self-renewal and differentiation into phenotypically heterogeneous cells. Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) is considered one of the gastric cancer stem cell markers. We aimed to investigate how the expression of CD44 varies according to the clinicopathologic characteristics in gastric cancer.
For this study, 157 patients who received an operation due to gastric cancer between May 1998 and December 2009 were selected. CD44 immunohistochemistry was reviewed using the semi-quantitative scoring of intensity and proportion. The sum of the intensity and proportion scores was calculated, and a score of 2 or less was deemed ‘CD44-negative’ and 3 or more as ‘CD44-positive.’
Among the final 143 subjects, 69 (48.3%) were CD44 positive. Older age, intestinal type gastric cancer, lymphatic invasion, and lymph node metastasis were significantly correlated with expression of CD44. In the multivariate analysis, older age was the only independent factor associated with CD44 expression (P=0.028). CD44 expression was correlated with overall survival, 5-year survival, and disease-free survival. In the multivariate analysis, older age, male gender, and lymphatic invasion were independent predictors of poor overall survival. Also, older age and lymphatic invasion were significant factors in 5-year survival, and lymphatic invasion was an independent factor of poor disease-free survival.
Older age (≥60 years) was independently associated with CD44 expression in gastric cancer patients. Also, CD44 expression was correlated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Citations

 , Jun Seop Lee
, Jun Seop Lee , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Jeong Jeong
, Jeong Jeong
The phase of the menstrual cycle was demonstrated to have an influence on the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery, but little was known for breast surgery, which was shown to have relatively higher incidence of PONV, >60%. We performed this study to investigate the influence of the phase of menstrual cycle on PONV after breast cancer surgery.
A total of 103 patients, who were scheduled for breast cancer surgery under general anesthesia, were recruited, and patients with irregular menstrual cycles, history of previous history of PONV were excluded. Groups were divided in two ways as follows: 1) gynecologic classification: premenstrual and menstrual (days 25 to 6), follicular (days 8 to 12), ovulation (days 13 to 15), and luteal phase (days 20 to 24); 2) menstrual classification: menstrual (days 1 to 8) and non-menstrual (days 9 to 28). PONV were recorded using Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching at postoperative 6 and 24 hours.
The overall incidence of PONV during postoperative 24 hours was 35.4%. At the menstrual classification, the incidence of PONV at postoperative 24 hours was higher in the menstrual group than that in the non-menstrual group (16.7% vs. 4.2%, P=0.057). The severity of PONV, measured with Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching was significantly different between menstrual and non-menstrual groups (P=0.034).
The duration and severity of the PONV after breast cancer surgery were demonstrated to be prolonged and aggravated during menstruation, respectively. Therefore, consideration of menstrual cycle for scheduling breast cancer surgery could effectively prevent the PONV and reduce medical cost.
Citations

 , Hyung Jun Park
, Hyung Jun Park , Kyoung-Gyu Choi
, Kyoung-Gyu Choi , Key Hwan Lim
, Key Hwan Lim , Kee Duk Park
, Kee Duk Park
Orbital metastases are rare and predominantly unilateral occurrences. Bilateral metastases affecting the extraocular muscles are extremely rare. A few case reports of bilateral metastases to extraocular muscles described binocular diplopia with conspicuous bilateral external ophthalmoplegia as an initial symptom. We report a case in which unilateral ptosis was an initial symptom and bilateral incomplete ophthalmoplegia was found on initial neurologic examination in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. The patient had hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, and so was treated by hormonal therapies and closely monitored. The presence of a secondary orbital lesion presents many difficulties of differential diagnosis and treatment. A thorough neurologic examination to detect ocular manifestations is most important for localization and broad differential diagnosis including mechanical orbital metastatic lesion.
Citations

 , Joohyun Woo
, Joohyun Woo , Hyang Suk Choi
, Hyang Suk Choi , Seok Joon Lee
, Seok Joon Lee , Jihye Choi
, Jihye Choi , Chan Sub Park
, Chan Sub Park , Min-Ki Seong
, Min-Ki Seong , Woo Chul Noh
, Woo Chul Noh
The evaluation of menopausal status is an important subject in the field of treatment of hormone receptor positive breast cancer. According to the menopausal status, endocrine therapy should be categorized by individual patient. However, the gonadal injury caused by various therapeutic drugs and its recovery would confuse the interpretation of clinical and biological markers for ovarian reserve. There are some methods to examine the functional ovarian reserve indirectly. Ultrasonography for counting follicles is a relatively reliable procedure, although it is not feasible because of time-labor consumption and high cost. Biological marker from blood samples such as serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), serum estradiol (E2), serum inhibin, or anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) would be a better choice. The examination of serum FSH and E2 is already recommended as biomarkers for measuring functional ovarian reserve in many guidelines. However, there are limitation of serum FSH and E2 in patients with chemotherapy-induced amenorrhea and treated by tamoxifen. AMH is promising biomarker in the field of infertility treatment even in the patients treated by chemotherapy. It might be a possible biomarker to determine the menopausal status for decision-making whether aromatase inhibitor could be applicable or not in hormone positive breast cancer patients with chemotherapy induced amenorrhea or treated by tamoxifen.
 , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Soon Sup Chung
, Soon Sup Chung , Kyoung Sook Hong
, Kyoung Sook Hong , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
In the metastatic process, interactions between circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and the extracellular matrix or surrounding cells are required. β1-integrin may mediate these interactions. The aim of this study was to investigate whether β1-integrin is associated with the detection of CTCs in colorectal cancer.
We enrolled 30 patients with colorectal cancer (experimental group) and 30 patients with benign diseases (control group). Blood samples were obtained from each group, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) mRNA for CTCs marker and β1-integrin mRNA levels were estimated by using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, and the results were compared between the two groups.
CEA mRNA was detected more frequently in colorectal cancer patients than in control patients (P=0.008). CEA mRNA was significantly reduced after surgery in the colorectal cancer patients (P=0.032). β1-integrin mRNA was detected more in colorectal cancer patients than in the patients with benign diseases (P<0.001). In colorectal cancer patients, expression of β1-integrin mRNA was detected more for advanced-stage cancer than for early-stage cancer (P=0.033) and was significantly decreased after surgery (P<0.001). In addition, expression of β1-integrin mRNA was significantly associated with that of CEA mRNA in colorectal cancer patients (P=0.001).
In conclusion, β1-integrin is a potential prognostic factor following surgical resection in colorectal cancer patients. β1-integrin may be a candidate for use as a marker for early detection of micrometastatic tumor cells and for monitoring the therapeutic response in colorectal cancer patients.

Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) is the most common hereditary colorectal cancer syndrome and accounts for about 5% of colorectal cancer. It is inherited as autosomal dominant type and is caused by germline mutations in mismatch repair genes such as
 , Woosung Lim
, Woosung Lim
Selenium is an essential microelement in animals including human. Selenium plays an important role in cellular functions such as deoxygenation and detoxification. Also, it can be used in treatment of cardiac disease, hepatic disease, AIDS and various cancers. Recent meta-analysis showed that high selenium exposure was associated with decreased risk of several cancers. Selenium has an effect on anticarcinogesis through several mechanisms, which are regulation of cell cycles, apoptosis, DNA damage and repair, inhibition of cellular adhesion and migration, anti-angiogenesis and immune modulation. Even though many laboratory studies have provided convincing evidence of these mechanisms, results from epidemiologic and clinical studies of selenium does not coincide with each other. Well-designed trials considering dosage and chemical form of selenium supplement as well as confounding factors and long-term follow-up of them would be needed to use selenium in chemoprevention and therapy of cancers.
Citations

 , Sun Young Kim
, Sun Young Kim , Min Ju Kim
, Min Ju Kim , Eun Kyung Hong
, Eun Kyung Hong , Sang Ho Lee
, Sang Ho Lee , Chang Woo Shim
, Chang Woo Shim
A 56-year-old man was diagnosed with cancer of the ascending colon along with retroperitoneal lymph node and peritoneal metastases. After six cycles of palliative chemotherapy, he presented with acute-onset jaundice. Imaging examinations did not show abnormal liver findings other than a periportal linear hypoattenuating area, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiography revealed a tight stricture of the proximal common bile duct. Total bilirubin continued to increase after endoscopic sphincterotomy and biliary stent insertion. Blind liver biopsy revealed tumor infiltration along liver lymphatics, but ruled out tumor involvement of hepatic parenchyma and sinusoids. Tumor cells were predominantly confined to within the lymphatic vessels and were not observed in the arteries or veins. Although one loading dose of cetuximab and two fractions of palliative radiotherapy were administered, the patient succumbed to acute liver injury 30 days after the development of jaundice.
 , Im Il Na
, Im Il Na , Min Woo Jung
, Min Woo Jung , Su Heui Lee
, Su Heui Lee , Jae Woon An
, Jae Woon An , Jae Soo Koh
, Jae Soo Koh
Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare form of soft tissue sarcoma, and frequently, metastases are found at diagnosis. In patients with metastatic or unresected ASPS, systemic treatment is extremely limited, because conventional chemotherapeutic agents have not been effective in most cases. A novel agent inhibiting angiogenesis, pazopanib, has been proven to be effective for metastatic soft tissue sarcoma in a second-line setting. However, the efficacy of pazopanib in ASPS has not yet been reported. A 22-year-old man presented with right calf ASPS and multiple lung metastases. Pazopanib as a second-line treatment showed significant tumor response. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the effectiveness of pazopanib in ASPS.
 , Hyun Joo Song
, Hyun Joo Song , Min Jung Kim
, Min Jung Kim , Weon Young Chang
, Weon Young Chang , Bong Soo Kim
, Bong Soo Kim , Chang Lim Hyun
, Chang Lim Hyun
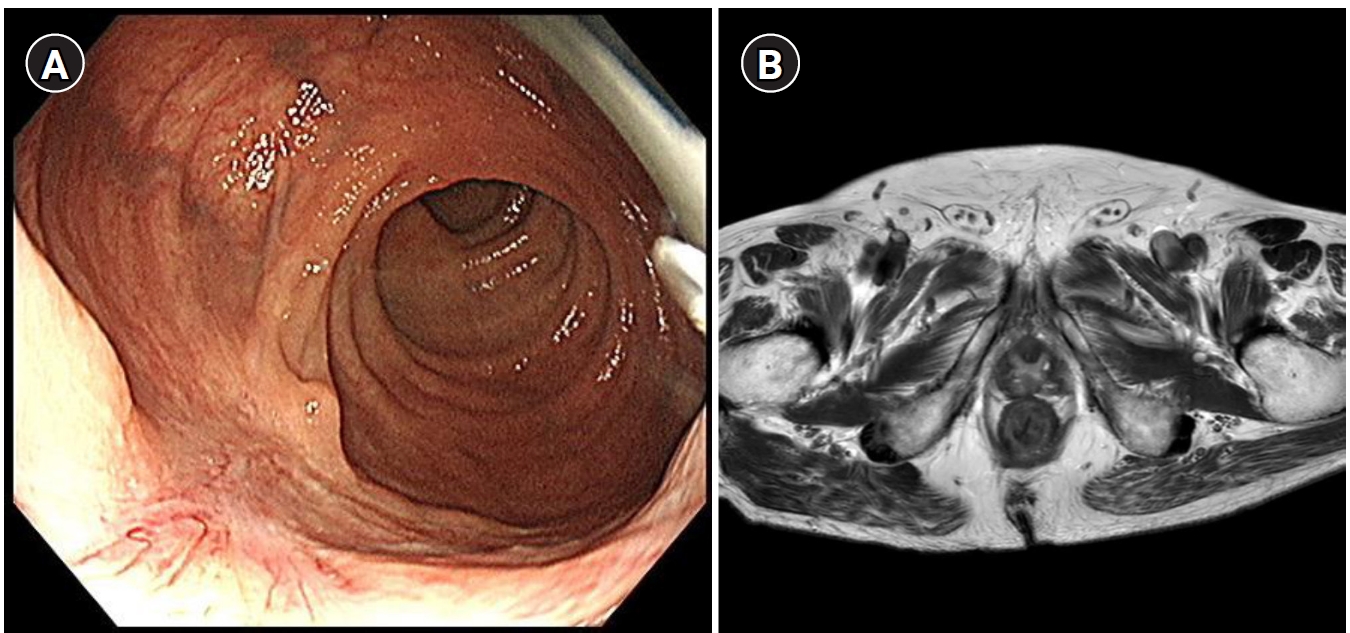
Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome (SRUS) is a rare benign and chronic rectal disease that has a wide spectrum of clinical presentations and variable endoscopic findings. It is usually diagnosed by histopathological examination through biopsy. A 68-year-old man was referred to our hospital with anal pain and difficulty on bowel movement. Colonoscopy showed a hemorrhagic ulcerated mass in the rectum. All radiologic findings such as abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography-CT and magnetic resonance imaging were suspicious of rectal cancer. Although the patient underwent repeat endoscopic biopsy and one surgical biopsy, the results were not indicative of malignancy. Two months after conservative management, clinical symptoms and colonoscopic findings were markedly improved. Thus, we report this rare case of a 68-year-old man who had a central ulcerated mass that mimicked rectal cancer on gross colonoscopic and radiologic findings, representing an SRUS variant.
Citations

 , Jinsu Kim
, Jinsu Kim , Seokyoung Yoon
, Seokyoung Yoon , Eung-Ho Cho
, Eung-Ho Cho , Changwon Jung
, Changwon Jung , Hye Jin Kang
, Hye Jin Kang
A 37-year-old woman underwent a total mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer (pT1N0M), and then recurred in the right lung followed by the pancreas. Lung lobectomy and pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy were performed, and systemic chemotherapies including trastuzumab were sequentially administered. However, metastasis to the pancreatic tail was detected. She underwent image-guided radiation therapy, but this was not effective. Lapatinib plus capecitabine combination was administered as forth-line treatment and the metastatic lesion was disappeared. She is continuing this regimen with a complete response for 48 months until now.
Citations

 , Hyun Soo Park
, Hyun Soo Park , Myung Hwa Lee
, Myung Hwa Lee , Sung Hee Kim
, Sung Hee Kim , Jung Hwan Shin
, Jung Hwan Shin
Ectopic pregnancy is an implantation of the fertilized ovum outside the uterine cavity. Most of ectopic pregnancies are located within the fallopian tube. We describe a rare case of 34-year-old woman complaining of lower abdominal pain and positive urinary pregnancy test. Pelvic ultrasound exam suggested tubal pregnancy with hemoperitoneum. However, pelviscopy revealed the bleeding point was subserosal myoma located just next to the right ovary. Uterus and both fallopian tubes were grossly free. Laparoscopic myomectomy with ectopic mass excision was performed and we observed the serial decrease of β-hCG level. Patient was well recovered and postoperative finding was not remarkable. Hereby, we report a rare case of ectopic pregnancy on uterine myoma with subserosal type with a brief review of literatures.
 , Seok Ho Seo
, Seok Ho Seo , Seung Hyun Lee
, Seung Hyun Lee , Dae Won Park
, Dae Won Park , Dong Goo Kang
, Dong Goo Kang , Seung Uk Lee
, Seung Uk Lee
Stress-induced cardiomyopathy, so-called Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, has recently been reported in Japan. Stress-induced cardiomyopathy is characterized by transient left ventricular apical dysfunction and ballooning, with normal coronary angiographic findings. We describe a rare case of stress-induced cardiomyopathy associated with lung adenocarcinoma presenting as hyponatremia.
Citations

 , Seon Bin Yoon
, Seon Bin Yoon , Mi Ju Cheon
, Mi Ju Cheon , Young Min Koh
, Young Min Koh , Hyeon Sik Oh
, Hyeon Sik Oh , Se Joong Kim
, Se Joong Kim , Seung Hyeun Lee
, Seung Hyeun Lee
Pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is a rare form of lung cancer that originates from submucosal glands of tracheobronchial tree. Unlike low-grade tumor with benign nature, high-grade case is even rarer and has aggressive clinical features with no definite treatment option. Here, we report a case of high-grade pulmonary MEC with fulminant clinical course. A 74-year-old man presented with cough, sputum and mental change. Chest imaging showed massive mediastinal lymphadenopathy with obstructive pneumonia, and multiple metastases in lung and adrenal gland. Bronchoscopy showed polypoid masses obstructing right main bronchus and bronchus intermedius. Histopathology revealed a mixture of glandular structure lined with mucussecreting cells and nests of squamoid cells with nuclear atypia and pleomorphism, which is compatible with high-grade MEC. We intensively treated the patient with combination antibiotics and ventilator care. However, the patient did not respond to the treatment and rapidly deteriorated, and finally expired a month after diagnosis.
 , Jae Myung Cha
, Jae Myung Cha , Joung Il Lee
, Joung Il Lee , Kwang Ro Joo
, Kwang Ro Joo , In Taik Hong
, In Taik Hong , Hye Jin Ki
, Hye Jin Ki
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is the most common mesenchymal neoplasm of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. These tumors are frequently small, asymptomatic and found incidentally. GI bleeding is a common complication of these tumors, but small sized, very low risk GIST rarely complicated with fatal bleeding. In this report, we describe a 42-year-old woman with a jejunal GIST accompanied by severe GI bleeding. She presented with melena and an angiographic embolization was performed for a jejunal mass with bleeding. However, rebleeding was suspected after an angiographic embolization and an emergent segmental resection for the bleeding mass was performed. She was finally diagnosed as a 1.8 cm sized very low risk GIST in jejunum. In conclusion, physician should consider that even very low risk GIST can be the cause of GI bleeding when there is severe bleeding.

To find out differential points between benign and malignant pleural disease.
We retrospectively analyzed the CT scans of 33 patients(20 men and 13 women ; mean age, 56) with pleural diseases including 12 malignant diseases(lung cancer(n=10), metastasis(n=2)) and 21 benign diseases(tuberculous empyema(n=12), bacterial empyema(n=7), hemothorax related exudate(n=2)).
In malignant diseases, irregular(n=3) or nodular(n=3), and mediastinal pleural thickening(n=6) were observed but extrapleural fat accumulation or pleural calcification were not.
In benign diseases, irregular pleural thickening was not observed in bacterial empyema but in tuberculous empyema(n=3) and hemothorax related exudate(n=1). Mediastinal pleural thickening and extrapleural fat accumulation were observed in tuberculous(n=5, 5) and bacterial(n=2, 2) empyema and hemothorax related exudate(n=1, 2) and pleura calcification was observed in tuberculous(n=3) and bacterial(n=2) empyema.
Findings of irregular or nodular pleural thickening were observed only in malignant disease with exception of tuberculous empyma and hemothorax related exudate. Extrapleural fat accumulation and pleural calcification were observed only in benign disease.
 , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Guie Yong Lee
, Guie Yong Lee , Chi Hyo Kim
, Chi Hyo Kim
Vasovagal syncope is one of the most common causes of transient syncope during anesthesia for elective surgery in patients with a history of syncope and requires special attention and management of anesthetics. The causes and pathophysiological mechanism of this condition are poorly understood, but it has a benign clinical course and recovers spontaneously. However, in some cases, this condition may cause cardiovascular collapse resulting in major ischemic organ injury and be life threatening. Herein we report a case and review literature, regarding completing anesthesia safely during an elective surgery of a 59-year-old female patient with history of loss of consciousness due to suspected vasovagal syncope followed by cardiovascular collapse and cardiac arrest, which required cardiopulmonary resuscitation and insertion of a temporary pacemaker and intra-aortic balloon pump immediately after a fine-needle aspiration biopsy of a lung nodule located in the right middle lobe.
 , Eun Young Kim
, Eun Young Kim , Min-Ji Seo
, Min-Ji Seo , Eun Chung
, Eun Chung , Min-Jung Cho
, Min-Jung Cho , Hyun-Jin Oh
, Hyun-Jin Oh , Ji-Hye Jang
, Ji-Hye Jang , Ji-Chan Park
, Ji-Chan Park , Jung-Uee Lee
, Jung-Uee Lee , Suk-Young Park
, Suk-Young Park
Gastric metastasis from breast cancer is rare and only six cases have been reported in Korea. Colon metastasis is more rare than gastric metastasis. We report a 63-year-old woman with gastric and colon metastases of invasive lobular carcinoma of breast. She was diagnosed as right breast cancer, received right modified radical mastectomy 10 years ago and has been treated with chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Investigating for melena and a small caliber of stool, we found gastric and colon metastases. The diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer was made through gross pathologic and immunohistochemistry staining. We report a case with gastric and colon metastases from breast cancer and a review of the associated six case reports in Korea.
Citations

 , Woosung Lim
, Woosung Lim
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in Korean women and its mortality rate has increased steadily. Although breast cancer is heterogeneous tumor, hormone receptor-positive tumors comprise about 75 percent of all breast cancers. Therefore endocrine therapy that works by targeting estrogen receptor is a pivotal treatment for breast cancers. There are selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as tamoxifen and raloxifene, aromatase inhibitors, such as anastrozole, letrozole and exemestane, fulvestrant and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists used in endocrine therapy. Endocrine therapy is effective in treating early breast cancer as an adjuvant therapy and metastatic breast cancer as a palliative therapy. Also in women who are at high risk for breast cancer, tamoxifen or raloxifene can prevent breast cancer. Studies for neoadjuvant endocrine therapy are emerging. Considering side effects of each drug and overcoming drug resistance are needed to maximize effectiveness of treatment and advance endocrine therapy.
Citations

 , Byung-In Moon
, Byung-In Moon
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in Korean women and its incidence has increased. Among the various treatment methods for breast cancer, chemotherapy plays an important role. The use chemotherapy to treat breast cancer began at the mid 20th century and first combination chemotherapy was conducted in mid 1970s. This chemotherapy reduced breast cancer mortality up to 25~30%, anthracycline and taxane based chemotherapeutic regimens are widely used. Chemotherapy could be classified to neoadjuavnt, adjuvant and palliative setting according to its aim and role. In this review, various drug therapeutic options and their backgrounds are considered based on neoadjuvant, adjuvant and metastatic systemic therapies.
Citations


Malignant neoplasm is the most common cause of death in Korea since 1988. In terms of incidence, still gastric cancer is the most common cancer in male, but breast cancer became the second most common female cancer followed by thyroid cancer. The reasons why incidence of breast cancer is increasing, (1) Westernized food patterns; high fat and high calorie diet, (2) late marriage with lower birth rate, (3) shorter period of breast feeding, (4) longer exposure to estrogen; early menarche with late menopause, hormone replacement therapy, (5) low physical activity with high body mass index, (6) environmental stress, and etc. Still incidence of breast cancer in Korea is relatively low comparing to those of American and European populations, but it is very rapidly increasing with annual increase rate of about 6%. So Korean breast cancer specialists should try to study breast cancer in terms of basic and also clinical aspect and also educate laymen for etiology, symptoms and signs, early detection method including breast self-examination and prevention.
Citations

 , Kwonoh Park
, Kwonoh Park , Ji Yeon Hong
, Ji Yeon Hong , Ji Yeon Kim
, Ji Yeon Kim , Jang Won Park
, Jang Won Park , Yong Won Park
, Yong Won Park , Kyung-Hun Lee
, Kyung-Hun Lee , Kyung-So Jeon
, Kyung-So Jeon
Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy (PTTM) is an uncommon and fatal malignancy-related pulmonary complication characterized by fibrocellular intimal proliferation of small pulmonary arteries and arterioles. It causes marked pulmonary hypertension, right-side heart failure, and sudden death. Diagnosis of PTTM is extremely difficult while the patient is alive. Here, we report a 44-year-old woman who presented with complaining of progressing dyspnea and pulmonary hypertension but with no history of cancer. She was diagnosed with PTTM caused by advanced gastric cancer
Citations

 , Dong Hyeon Lee
, Dong Hyeon Lee
Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy (RARC) for the treatment of muscle invasive bladder cancer is being increasingly applied. Radical cystectomy is complex procedure which should be performed with extensive lymph node dissection and urinary diversion. Currently, the techniques of RARC are well-described, and the feasibility and safety of RARC has been demonstrated. While extracorporeal approach is preferred method for urinary diversion, intracorporeal urinary diversion is gaining popularity. Positive surgical margins are similar to large open series but inferior for locally advanced disease. However, local recurrence and survival rates seem equivalent to open series at short and mid-term follow up. Randomized controlled trial should be conducted to rigorously assess the oncologic outcomes of RARC compared to open radical cystectomy.
 , Young Yo Park
, Young Yo Park
Bladder cancer is the second most common malignancy in urological field. Most new cases are diagnosed as non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), which includes Ta, T1 or carcinoma in situ. Initial management of NMIBC is endoscopic resection, which allows both treatment and pathological staging. Urologist should consider adjuvant intravesical chemotherapy or Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) immunotherapy, depending on the tumor grade or stage to prevent recurrence and progression. Patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) are best treated with radical cystectomy. However, radical cystectomy should be considered even in patients with NMIBC with high risk of progression and BCG refractory tumors. Delay of radical cystectomy in these patients might lead decreased disease specific survival. Patients treated by radical cystectomy should undergo any form of the urinary diversion. Ileal conduit is still most common method for urinary diversion. Orthotopic neobladder is generally performed by experienced hands in high volume center. Patients undergoing orthotopic neobladder should be educated and manually skillful to manipulate their diversion. Neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy is recommended based on level 1 evidence with survival benefit. Recent updated meta-analysis also demonstrated survival benefit in patients with MIBC treated by adjuvant chemotherapy.
Citations

 , Jae Uk Shin
, Jae Uk Shin , Yeon Ho Joo
, Yeon Ho Joo , Jue Yong Lee
, Jue Yong Lee , Ji Hun Kim
, Ji Hun Kim , Yun Jung Park
, Yun Jung Park , Myeng Nam Bae
, Myeng Nam Bae , Sang Mook Bae
, Sang Mook Bae
Intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN) of the pancreas has been recently reported. It is very rare, therefore clinical behavior and prognosis has not yet been characterized. We experienced a case of ITPN of the pancreas which presented with acute pancreatitis and treated with Whipple's operation. Histopathologic finding showed papillary hyperplasia with carcinomatous change. The tumor recurred after 47 month of operation, and she underwent total pancreatectomy. Pathologic finding revealed tubulopapillary growth with high grade dysplasia. Immunohistochemial staining was not performed, however gross and microscopic findings were compatible with ITPN of the pancreas. We report a case of ITPN of the pancreas.

