| Ji Yeon Byun | 8 Articles |
|
[English]
Purpose
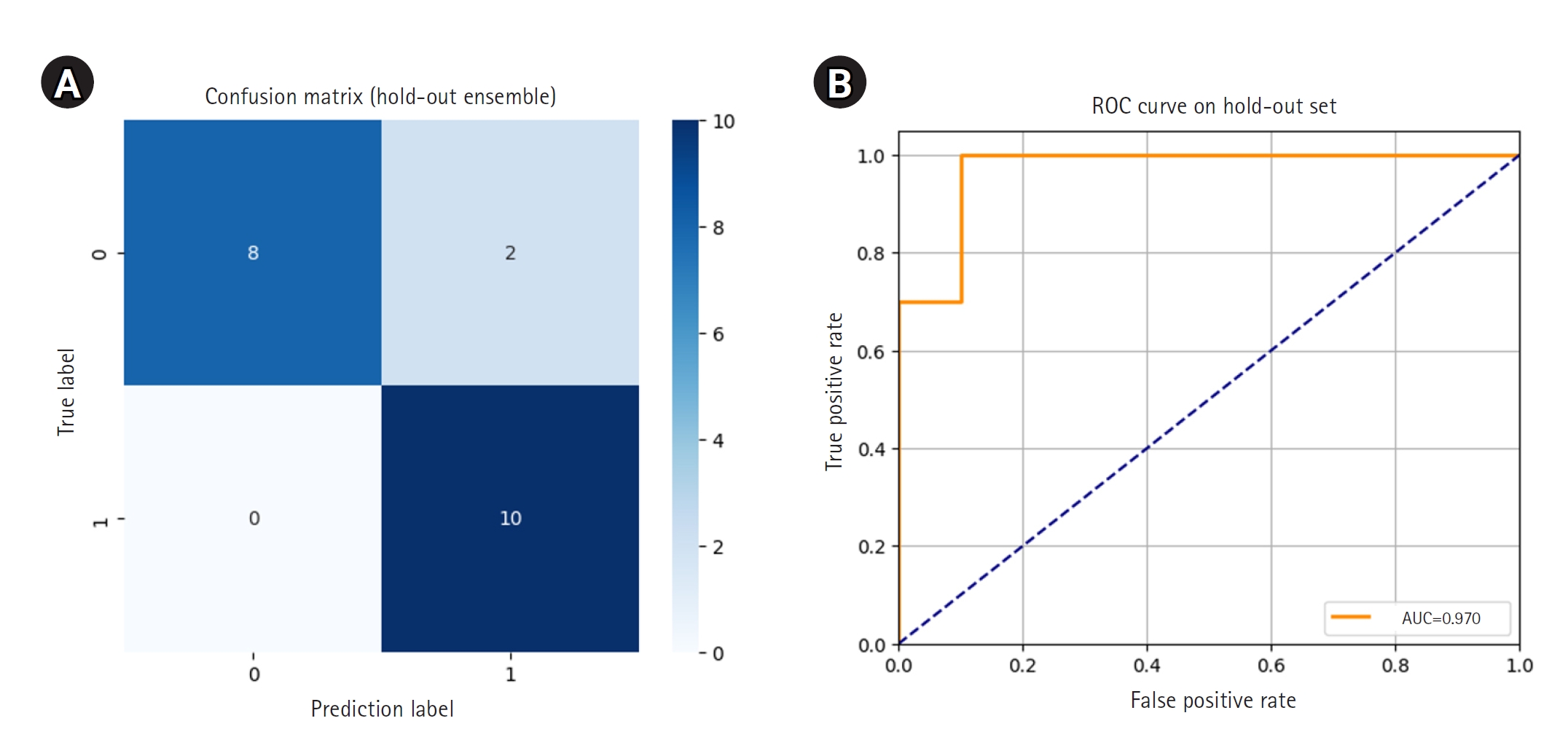
This study developed and validated a deep learning model for the automated early detection of androgenetic alopecia (AGA) using trichoscopic images, and evaluated the model’s diagnostic performance in a Korean clinical cohort. Methods We conducted a retrospective observational study using 318 trichoscopic scalp images labeled by board-certified dermatologists according to the Basic and Specific (BASP) system, collected at Ewha Womans University Medical Center between July 2018 and January 2024. The images were categorized as BASP 0 (no hair loss) or BASP 1–3 (early-stage hair loss). A ResNet-18 convolutional neural network, pretrained on ImageNet, was fine-tuned for binary classification. Internal validation was performed using stratified 5-fold cross-validation, and external validation was conducted through ensemble soft voting on a separate hold-out test set of 20 images. Model performance was measured by accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the curve (AUC), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) calculated for hold-out accuracy. Results Internal validation revealed robust model performance, with 4 out of 5 folds achieving an accuracy above 0.90 and an AUC above 0.93. In external validation on the hold-out test set, the ensemble model achieved an accuracy of 0.90 (95% CI, 0.77–1.03) and an AUC of 0.97, with perfect recall for early-stage hair loss. No missing data were present, and the model demonstrated stable convergence without requiring data augmentation. Conclusion This model demonstrated high accuracy and generalizability for detecting early-stage AGA from trichoscopic images, supporting its potential utility as a screening tool in clinical and teledermatology settings. Citations Citations to this article as recorded by

[English]
[English]
[English]
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which are often acquired from environmental sources such as water and soil, exhibit a variety of cutaneous manifestations that frequently lead to misdiagnoses and delays in treatment. A 77-year-old woman presented with multiple skin lesions in a sporotricoid distribution on her right leg, which persisted despite standard antibiotic treatments. Based on the skin biopsy, revealing granulomatous inflammation with acid-fast bacilli, and PCR testing, a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection was diagnosed. Antimycobacterial drug combinations, including clarithromycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin for 4 months, complete the skin lesion's clearance. This case underscores the need for heightened suspicion and the use of appropriate diagnostic techniques, including tissue biopsies and molecular methods such as PCR. Citations Citations to this article as recorded by

[English]
[English]
Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare skin complication in which subcutaneous fat necrosis occurs in association with pancreatic disorders, most commonly acute or chronic pancreatitis. Erythematous subcutaneous nodules develop on the legs and spontaneously ulcerate or exude an oily substance. A 32-year-old Korean female patient presented with a 2-week-history of tender nodules with erythematous crusts on her left shin. She had a history of alcoholic liver cirrhosis and, 5 weeks earlier, had been diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. The histopathologic findings from a skin biopsy were consistent with lobular panniculitis, without signs of vasculitis, and diffuse fat necrosis. Basophilic calcium deposits were present in the dermis and subcutaneous fat. These findings were suggestive of pancreatic panniculitis. The skin lesion had a chronic course corresponding to repeated exacerbations of the patient’s pancreatitis. Thus, in the differential diagnosis of subcutaneous nodules, clinicians should consider pancreatic panniculitis as a cutaneous manifestation of pancreatic disease.
[English]
[English]
|
|

