 , So Young Lee
, So Young Lee
 , Gyeongmin Im
, Gyeongmin Im
 , Sohyun Ahn
, Sohyun Ahn , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
Citations

 , Jooyoung Choi
, Jooyoung Choi

Citations

 , Seoyoung Kim
, Seoyoung Kim , Dohyoung Rim
, Dohyoung Rim
Citations


Citations


Citations



Citations

Shoulder diseases pose a significant health challenge for older adults, often causing pain, functional decline, and decreased independence. This narrative review explores how deep learning (DL) can address diagnostic challenges by automating tasks such as image segmentation, disease detection, and motion analysis. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of DL-based convolutional neural networks and machine learning frameworks in diagnosing various shoulder pathologies. Automated image analysis facilitates the accurate assessment of rotator cuff tear size, muscle degeneration, and fatty infiltration in MRI or CT scans, frequently matching or surpassing the accuracy of human experts. Convolutional neural network-based systems are also adept at classifying fractures and joint conditions, enabling the rapid identification of common causes of shoulder pain from plain radiographs. Furthermore, advanced techniques like pose estimation provide precise measurements of the shoulder joint's range of motion and support personalized rehabilitation plans. These automated approaches have also been successful in quantifying local osteoporosis, utilizing machine learning-derived indices to classify bone density status. DL has demonstrated significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in the management of shoulder diseases in older patients. Machine learning-based assessments of imaging data and motion parameters can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, to ensure their generalizability, reproducibility, and effective integration into routine clinical workflows, large-scale, prospective validation studies are necessary. As data availability and computational resources increase, the ongoing development of DL-driven applications is expected to further advance and personalize musculoskeletal care, benefiting both healthcare providers and the aging population.
 , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn , Rena Lee
, Rena Lee
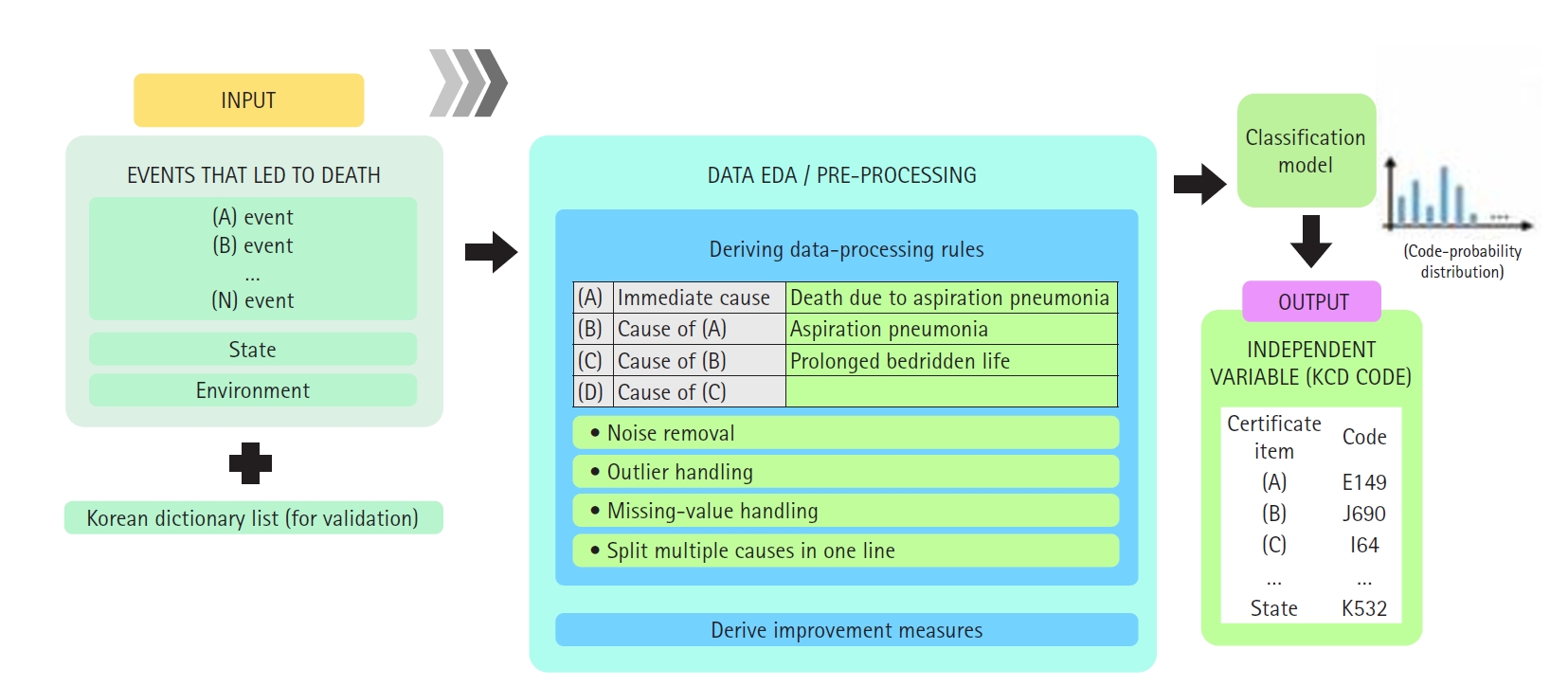
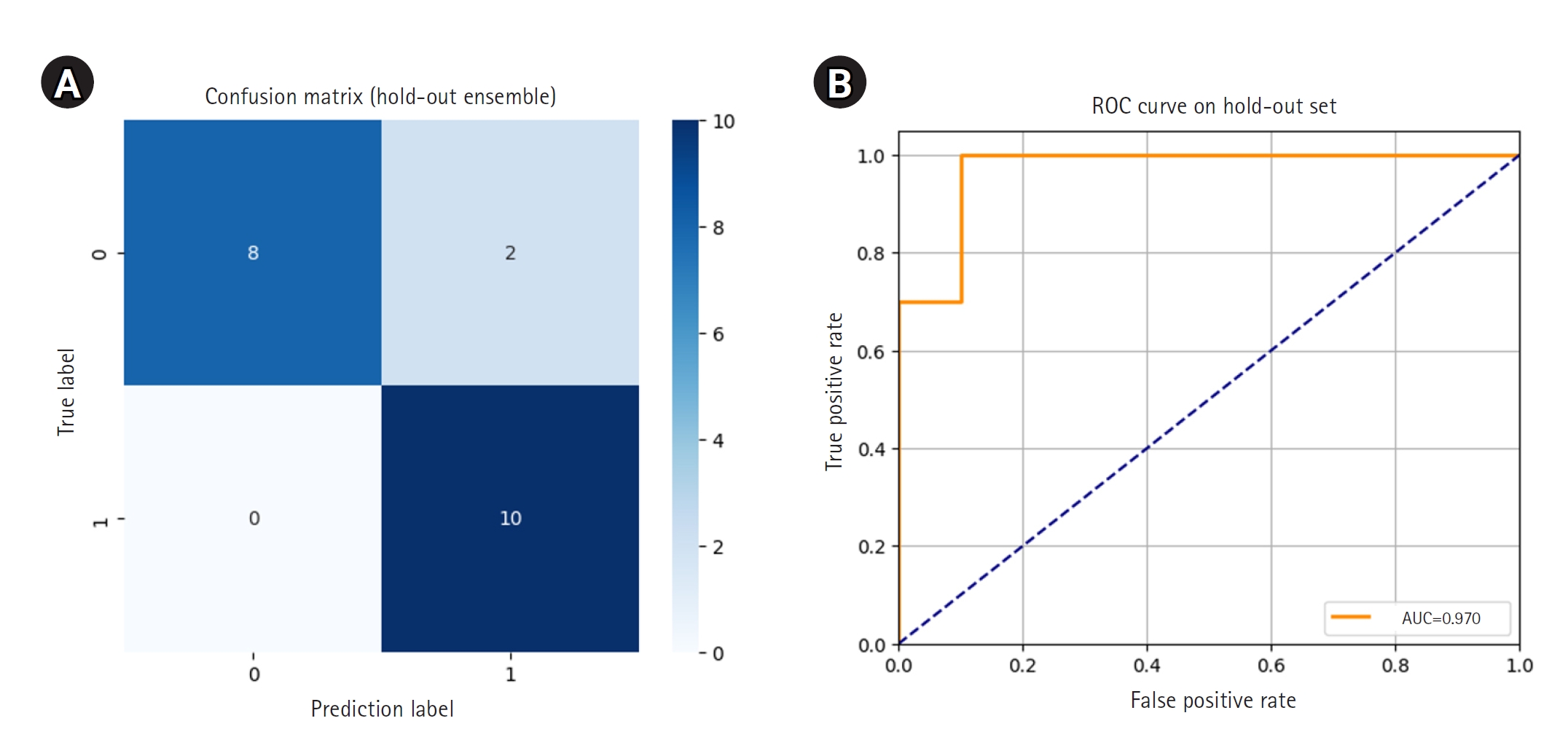
This study aimed to develop an accurate pediatric bone age prediction model by utilizing deep learning models and contrast conversion techniques, in order to improve growth assessment and clinical decision-making in clinical practice.
The study employed a variety of deep learning models and contrast conversion techniques to predict bone age. The training dataset consisted of pediatric left-hand X-ray images, each annotated with bone age and sex information. Deep learning models, including a convolutional neural network , Residual Network 50 , Visual Geometry Group 19, Inception V3, and Xception were trained and assessed using the mean absolute error (MAE). For the test data, contrast conversion techniques including fuzzy contrast enhancement, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (HE) , and HE were implemented. The quality of the images was evaluated using peak signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), mean squared error, SNR, coefficient of variation, and contrast-to-noise ratio metrics. The bone age prediction results using the test data were evaluated based on the MAE and root mean square error, and the t-test was performed.
The Xception model showed the best performance (MAE=41.12). HE exhibited superior image quality, with higher SNR and coefficient of variation values than other methods. Additionally, HE demonstrated the highest contrast among the techniques assessed, with a contrast-to-noise ratio value of 1.29. Improvements in bone age prediction resulted in a decline in MAE from 2.11 to 0.24, along with a decrease in root mean square error from 0.21 to 0.02.
This study demonstrates that preprocessing the data before model training does not significantly affect the performance of bone age prediction when comparing contrast-converted images with original images.
Citations

 , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
The capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) have recently surged, largely due to advancements in deep learning inspired by the structure and function of the neural networks of the human brain. In the medical field, the impact of AI spans from diagnostics and treatment recommendations to patient engagement and monitoring, considerably improving efficiency and outcomes. The clinical integration of AI has also been examined in specialties, including pathology, radiology, and oncology. General surgery primarily involves manual manipulation and includes preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care, all of which are critical for saving lives. Other fields have strived to utilize and adopt AI; nonetheless, general surgery appears to have retrogressed. In this review, we analyzed the published research, to understand how the application of AI in general surgery differs from that in other medical fields. Based on previous research in other fields, the application of AI in the preoperative stage is nearing feasibility. Ongoing research efforts aim to utilize AI to improve and predict operative outcomes, enhance performance, and improve patient care. However, the use of AI in the operating room remains significantly understudied. Moreover, ethical responsibilities are associated with such research, necessitating extensive work to gather evidence. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and leveraging lessons from AI success stories in other fields, AI tools could be specifically tailored for general surgery. Surgeons should be prepared for the integration of AI into clinical practice to achieve better outcomes; therefore, the time has come to consider ethical and legal implications.
Citations

 , Heisook Lee
, Heisook Lee
This review aims to highlight the importance of research on structural, functional, molecular-biological, and disease-specific sex differences in the brain, and to examine current bibliometric indicators related to research on sex differences. The Web of Science Core Collection was searched for related articles from 2010 to 2023. Structural and functional brain differences according to sex, including variations in communication patterns between hemispheres, may play a role in mental disorders. Sex differences in neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and γ-aminobutyric acid contribute to disparities in mental health, addiction, and neurodevelopmental conditions. Neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia exhibit sex-based differences in prevalence, symptoms, brain changes, and neurotransmitter disruptions under hormonal influence. There is a growing body of research on depression, adolescence, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and cognition, highlighting the importance of considering sex/gender factors. Recent studies on sex differences in brain diseases have identified variations in brain structure, function, and neurophysiological substances, as well as in hormones and genes between the sexes. The incidence of psychiatric disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer’s disease is increasingly being linked to sex differences, and the need for research into the mechanisms underlying these differences is gaining recognition. However, there remains a significant gap in sex-specific neuroscience research related to the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and management of these conditions. Advancing inclusive research will require comprehensive training, a consensus on methodology, diverse perspectives through collaborative frameworks, governmental/institutional support, and dedicated funding to create suitable research environments and implementation strategies.
Citations


Heart failure (HF) represents a serious public health concern, characterized by substantial morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in pharmacological management, a gap persists in understanding and accounting for sex-related differences in HF treatment. This review was performed to clarify the impact of sex on the clinical outcomes of HF medications. Insights from various clinical trials and studies have highlighted differences between men and women in drug responses and adverse effects, indicating the need for a more nuanced approach to HF management. Promoting greater representation of women in clinical trials and the development of research methodologies that consider sex differences are crucial steps in advancing precision medicine. Such efforts ensure that therapeutic strategies are optimally tailored to the unique biological and genetic profiles of each person. Ultimately, this review emphasizes the vital need for a more inclusive and personalized approach to HF pharmacotherapy, underscoring the critical role of sex-related differences in shaping effective and individualized treatment pathways.
Citations

 , Yaiza Del Pozo Martín, Joan Marsh
, Yaiza Del Pozo Martín, Joan Marsh 성별(sex)과 젠더(gender)의 차이를 이해하는 것은 질병 관련 병태생리학 연구, 사회인구학적 건강결정요인, 의학적 또는 사회적 중재의
긍정적 영향 및 위해성 등을 막론하고 엄밀하고 포용적연구에 있어 필수적이다. 다양한 젠더를 포함한 연구가 활발해졌지만 성별과 젠더를 변수로
명시하는 연구는 여전히 부족하다. 2016년에 발표된 성별과 젠더 형평성(Sex and Gender Equity in Research,
SAGER) 지침은 널리 지지되고 있지만, 소수의 과학 학술지와 기관들에서만 이를 공식적인 편집 및 출판 정책에 반영하고 있다.
 , Paola De Castro, Sera Tort, Mirjam Curno
, Paola De Castro, Sera Tort, Mirjam Curno Citations

 , Hwa Young Lee
, Hwa Young Lee , Young Mi Park
, Young Mi Park , Hee Jung Yi
, Hee Jung Yi
A Womans University College of Medicine faces curriculum reform in 2020. To determine what reforms are needed in the premedical curriculum, a needs assessment was conducted.
This study utilizes qualitative study method. A focus group interview was conducted with four students who completed premedical courses from November to December 2018. Interviews were conducted in two groups by grade level, and each interview was recorded. After transcribing the recorded contents, four researchers analyzed the data using conventional content analysis.
Students chose A Womans University College of Medicine considering their future careers as female medical professionals and other considerations such as scholarships. The students expected diverse experiences, exchanges with students in different departments, and fusion of medicine with other fields during their premedical years. Overall, these expectations were met during the course, but individual needs for customized education, such as liberal arts, were unmet. In general, students' attitudes toward premedical courses were very motivated and they actively used resources provided by the university.
Qualitative research can provide a better understanding of quantitative data, such as a student survey performed to prepare for curriculum reform. Based on this understanding, the curriculum will be reformed to reflect the educational needs of students, to motivate students and to provide satisfactory education.
Citations

 , Angela Cho
, Angela Cho , Chul Min Park
, Chul Min Park
A 66-year-old postmenopausal woman received routine gynecologic check-up. Transvaginal ultrasonography and abdominal and pelvic computed tomography showed about 5-cm cystic mass in uterus with solid component and the patient had thin endometrium and the serum level of CA 125 was normal. We performed a total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and found tumor which had brownish cystic fluid and about 2 cm sized and colored in light yellowish, polypoid protruding solid mass, located within the myometrial wall. Histopathological examination of frozen section revealed malignancy. The tumor was confined within the myometrium and its histologic type was clear cell adenocarcinoma. Finally we identified that the myometrial mass was clear cell adenocarcinoma originated from adenomyosis pathologically. The malignant transformation of adenomyosis is very rare. When we find a cystic change with solid component in adenomyosis patients, clear cell adenocarcinoma should be suspected as a differential diagnosis and magnetic resonance imaging should be considered for further evaluation.

All Korean citizens should join the National Health Security System by law. The National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) are one of major components to support this system, and all data about medical expenses for the medical claims are stored and managed in the institutions. Recently, medical research using administrative claims databases has dramatically progressed in Korea and worldwide, and the methods how to use them are briefly reviewed in this article. Research using these databases have several strengths. Researchers can perform the complete enumeration survey in a real world. They can get new valuable findings because the number in the database is usually large enough to detect the minute difference with a big statistical power. They can obtain more detailed and reproducible results. Moreover, they can investigate a very rare disease or infrequent side effects of drugs. However, we must recognize that research using administrative claims database also has several incoherent limitations. These databases have not been constructed originally for research, but for reimbursement. Therefore, there are no important data including medical history and laboratory findings of each patient, which are crucial to adjust baseline characteristics. In addition, it is hard to discover causal relationship and direct association with the included information. In spite of limitations, researchers can easily use these databases for their research now than ever, and the results may be utilized not only to expand the academic knowledge but also to influence the determination of national healthcare policy.
Citations

 , Eun Sook Kang
, Eun Sook Kang , Ki Sook Hong
, Ki Sook Hong , Gyoung Hee Kim
, Gyoung Hee Kim
Congenital Pelger-Huët anomaly is an autosomal dominant disorder affection leukocyte differentiation manifested by the presence of unsegmented of bilobed nuclei with increased condensation, but it is generally assumed that it has no clinical effects. We observed a case of congenital Pelger-Huët anomaly in 9 year-old boy. He was admitted to Ewha Womans University Hospital due to fever and diagnosed as viral infection of upper respiratory tract. On routine peripheral blood examination, we found majority of the neutrophils had uni-or bilobed nuclei. In familial examination, his mother & brother have had Pelger-Huët anomaly without any significant symptoms. On neutrophil function test, moderate defect of chemotaxis was noted.

Recently Computers are more and more widely used in many aspects of medicine, including education, and using computers to assist in traditional learning has many advantages. This study was carried out to provide modeling of computer learning program in health statistics.
The author analysed the present program and then surveyed the student's need by self administrated questionnaires. By one student modeling, the computer learning program has been developed and then the program was remodeled into the whole(80-90) students program.
The students thought that the current health statistical experiment was useful but laborius. And they wanted to try to new program with computer statistical package. In the aspect of trial on new educational method, the model of computer learning program in Health Statistics has been developed.
The computer learning program will be implemented in this second semester(1996) but the teacher and the students will be devoted to the program. And then it will be succeeded.
 , Gyu Ryong Choi
, Gyu Ryong Choi , Soo Seung Choi
, Soo Seung Choi
There are several types of research methodology in the medical research papers. Each of these research methodologies establish their proper purposes in the medical resarches. This study was performed to examine the frequencies and types of research methodologiy for the purpose of providing the prospective aspects.
We reviewed 765 research papers in the Ewha Medical Journal, from 1978 to 1995. The research paper were included all kinds of papers in the Ewha Medical Journal such as review articles, oiginal articles, case reviews and so on. And we classified the research metho-dologies into case study, clinical trial, observational study, experimetal study and study for di-agnostic methods.
Case study was most commonly used study design(332 papers,43.4%), followed by experimental study(185 papers, 24.2%). In the 1970s, case report(44.1%) was the most com-monly used study design and enxt was experimental study(17.7%). In the 1980s, also the most commonly used study design was case report(48.7%) and experimental study(24.9%) was mark-edly increased than 1970s. Not only the experimental study(24.8%)but also clinical trial(16.1%)was outstandingly increased in the 1990s. Especially experimental study and clinical trial in the clinical research papers were increased more and more to the 1990s. The most common paper volume was December(35.9%)in the Ewha Medical Journal. The differences of research metho-dology among basic science, medical part and surgical part were significant(p<0.01).
The authors suggested that the Ewha Medical Journal have been changed in the aspects of methodology, but have more qualitative arguementations on research metho-dology which are indispensable activities of prospective the Ewha Medical Journal.

Estrogen receptor-related protein was examined on gastrectomy specime from 16 cases of advaced gastric adenocarcinoma and 7 cases of early gastric carcinoma(EGC) by using peroxidase-anti-peroxidase method on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. Positive reaction was seen in 7 out of 16 cases of advanced carcinoma and in 4 out of 8 cases of EGC(50%). Among advanced carcinoma, 3 cases of mucinous carcinoma were negative and 2 cases of signet ring cell carcinoma(SRC) showed focal positive reaction only in combined poorly differentiated(PD) area(10% of tumor cells). PD advanced carcinoma consisted of 4 cases of medullary type and 3 cases of individual cell type. Two out of 4 medullary type showed positive reaction in 20 and 80% of tumor cells and 2 out of 3 individual cell type showed positive reaction in 50 and 70% of tumor cells. Gland-forming type of advanced carcinoma consisted of 1 each case of intestinal and cardiac type and 1 mixed intestinal and cardiac type. Only 1 case of intestinal type showed positive reaction in 50% of tumor cells Among EGC, 2 cases of SRC were negative and 2 cases of PD carcinoma showed 5 and 10% positivity in PD area and 20 and 40% positivity in admixed gland-forming area. Gland-forming EGC consisted of 3 cased of intestinal type and 1 case of cardiac type. One case from each group showed positive reaction in 50 and 20% of tumor cells, respectively. In summary, positive reaction to antibody to estrogen receptor-related protein(P29) was expressed in PD(66.7%), gland-forming(50%), SRC, and mucinous type in order in both early and advanced carcinoma. The difference between age, sex, and other factors was not clear due to limitation of specimen.

The author reports a case of surgery-proved hypertrophic interstitial neuritis of cauda equina. The pathogenesis of the unique myelographic findings is described and illustrated. SUMMARY A case of surgery-proved hypertrophic interstitial neuritis of cauda equina is reported. The unique myelographic findings are illustrated. To the author's knowledge, no other condition produces these abnormalities.
 , Hyo-Ju Ham
, Hyo-Ju Ham , Kwan-Yong Lee
, Kwan-Yong Lee , Ji-Woong Roh
, Ji-Woong Roh , Jin-Sok Yu
, Jin-Sok Yu , Woo-Baek Chung
, Woo-Baek Chung
Early repolarization is a common electrocardiographic (ECG) feature found in young adults, men and athletes, and has been considered to be a benign feature for the last several decades. But recent studies suggest that early repolarization may be related to idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death. We report a young man, 35 years old, who had life threatening ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac arrest. He was evaluated for cardiac causes of ventricular fibrillation. There was no explanation other than that his ECG showed an early repolarization pattern so we treated him with implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Thus, we suggest that early repolarization may be related with life threatening ventricular arrhythmia.
 , Sun Wook Kim
, Sun Wook Kim , Young Ju Kim
, Young Ju Kim , Hyun Ju Kim
, Hyun Ju Kim , Jung-Hee Lee
, Jung-Hee Lee , Myeong-Ki Hong
, Myeong-Ki Hong , Byung-Chul Chang
, Byung-Chul Chang
With the aging population, more patients who have undergone previous coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) are surviving long enough to require subsequent aortic valve replacement (AVR). Conventional redo AVR after prior CABG involves resternotomy, dissection and clamping of the patent bypass graft vessel. Favorable results have been reported for AVR following previous CABG; however, the problems of this procedure includes that injury to the patent bypass grafts can result in catastrophic complications. Increasing patient age and comorbidities may increase operative mortality, less invasive percutaneous aortic valve intervention has advanced. However, because there are no sufficient data comparing transcatheter aortic valve intervention with surgical AVR, currently, the surgical approach should still be consider as the standard of treatment for AVR following previous CABG. We report a patient in whom successful conventional AVR was underwent after previous CABG with patent left internal mammary artery.
 , Hanna Kang
, Hanna Kang , Dong Eun Song
, Dong Eun Song , Min-Sun Cho
, Min-Sun Cho
 , Soo A Oh
, Soo A Oh , Kyoung-Eun Lee
, Kyoung-Eun Lee , Eun-Sun Yoo
, Eun-Sun Yoo , Moon Young Choi
, Moon Young Choi , Jee-Young Ahn
, Jee-Young Ahn , Chu-Myong Seong
, Chu-Myong Seong
Leukotriene B4(LTB4) is lipid mediator derived from membrane phospholipids during the process of inflammation, having many roles(ie; inducer of chemotaxis, the production of nitric oxide, transepithelial migration of neutrophil). The major activities of LTB4 include the recruitment and activation of leukocytes, suggesting that it may involve the process for transendothelial migration of nuclear cells in bone marrow environment. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) have a cell signaling roles that are involved in signal transduction cascades of numerous growth factor-, cytokine-, and hormone-mediated pathways, and regulate many biological systems. In this present study, we focused on the role of LTB4 and ROS on transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells across endothelial or stromal cell monolayer.
MS-5, murine stromal cell line cells, or bEnd.3, murine microvascular cell line cells, were grown to confluence on microporous transwell membrane. Murine marrow cells were placed on top of the prepared transwell membrane. The transwells were then seated in wells containing media and LTB4 with or without pretreatment of N-acetylcysteine(NAC), an oxygen free radical scavenger, or diphenylene iodonium(DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase-like flavoproteins. Cells that migrated through the stromal or endothelial layer into the wells were assayed for transendothelial migration.
The numbers of migrated bone marrow nuclear cells through the bEnd.3 were increased by treatment of LTB4(control, 12.5±0.2%; 50nM, 22.7±0.9%; 100nM, 44.3±1.4%; 200 nM, 36.3±0.9%; p<0.05). The numbers of migrated bone marrow nuclear cells through the MS-5 were also increased by treatment of LTB4(control, 11.0±0.9%; 50nM, 25.7±0.9%; 100nM, 35.8±1.8%; 200nM, 32.1±0.9%; p<0.05). However, increasing effect of LTB4 to the transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells through the MS-5 or bEnd.3 were inhibited by pretreatment of NAC or DPI.
Through our data, it is suggested that LTB4 could induce the transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells and ROS might be involved on the transendothelial migration of bone marrow nuclear cells by LTB4. It would be very interesting to test the effects of LTB4 and ROS on stem cell mobilization and homing in the future.
 , Kristi J Ferguson
, Kristi J Ferguson
Comparing with the traditional curriculum which provides mainly basic medical science training in the first 2 years, the early exposure to clinical medicine is a major trend of medical education through recent decades. However the timing, extent, content and methods of the 'early clinical education' are not defined clearly and the application is various. Preparing the transformation of the curriculum from undergraduate to graduate entry at Ewha medical school, the concepts of 'early clinical exposure' into our new curriculum needs to be clear. We want to decide how early and how deep and what contents of clinical knowledge and skills are to be introduced in the new curriculum.
Literature review. Interview with a developer and the participants of the 'early clinical education' curricula which has been applied in the Carver College of Medicine, University of lowa since 1998.
The early exposure of clinical knowledge and skills has been introduced world widely and many curricula have it as early as the very week of entrance. Problem based learning, standardized patient program, clinical skill labs and clinical mentoring, etc. are being used with various modification. Early clinical education enhanced the loaming interest and professional minds to the medical students as well as their achievements.
The early clinical education will be applied to the new curriculum of the graduate school of medicine starting 2007 in Ewha Medical School.
 , Se Yong Choi
, Se Yong Choi , In Suk Yang
, In Suk Yang
The advances in surgical techniques and stabilizing devices have made the off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB) popular, and good results have been published. We analyzed the early results of OPCAB performed in our hospital.
Between January 2004 and December 2004, 23 patients underwent OPCAB. There were 14males and 9 females with mean age of 62.6±10.3years. Preoperative diagnoses were unstable angina in 13(57%), acute myocardial infarction in 9(39%), and stable angina in 1(4%). Preoperative angiographic diagnoses were three-vessel disease in 12 (52%), two-vessel disease in 8(35%), one-vessel disease in 1(4%), and left main disease in 2(9%).
The mean number of grafts was 2.6±0.9 per patient. Vessels accessed were left anterior descending artery in 23, diagonal branch in 14, obtuse marginal branch in 9, right coronary artery in 12, and posterior descending artery in 1. Left internal mammary artery were used in 22 patients and bilateral internal mammary arteries were used in 1 patient. There was no operative mortality. Postoperative complications were cerebral vascular accident in 1, postoperative bleeding which required operative management in 2, arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation in 5, and minor operative wound problem in 1. Pre-discharge graft patency was evaluated in 11 patients. One internal mammary artery graft was occluded in 11 internal mammary artery graft evaluated. The patency rate was 91%. Seventeen saphenous vein grafts were patent in 19 saphenous vein grafts and the patency rate was 89%.
Our result of OPCAB is promising and OPCAB is suggested to be the ideal technique with less morbidity and mortality.
 , So-Youn Woo
, So-Youn Woo
To investigate the time of rearrangement of the TCR gene in the process of NKT cell differentiation from CD34+ human cord blood cells in vitro.
We isolated the CD34+ human cord blood cells and induced the differentiation of NKT cells by liquid culture including IL-15, FL and SCF for 30 days. In order to detect the time of TCR gene rearrangement in differentiated NKT cell, we performed PCR for TCR-rearrangement excision circles (TRECs) with isolated DNA.
Signal joint TREC first appeared on day 4 or day 8 and continuously existed until day 30. Between day 9 and day 21, cells showed high output of coding joint TRECs after signal joint rearrangement.
In differentiated NKT cells, TCR gene rearrangement started within a week after culture started and mostly occurred in 2 to 3 weeks after culture started.
 , Woon-Sub Han
, Woon-Sub Han , Kyong-Gyu Choi
, Kyong-Gyu Choi
EEG is a record of electronic signals of brain. If there are effective methods for analysis of EEG signal it can be used as a diagnostic tool for diseases related to brain function. We developed a new diagnostic system for analysis of EEG by using nonlinear dynamic theory.
We made a basic computer program which was designed to analysis of pattern of EEG. For analysis of pattern, EEG signal was processed by variable experimental analytical methods and grouped by common pattern.
Program was composed of multiple systems. Signal generating system was composed of Lorenz signal generation and Rossler signal generation parts. EEG processing system was composed of Normalization, Band pass filtering, First Second difference, Add random noise and Sur-rogate making parts. EEG analyses system was composed of Spectral analyses, Phase space analyses, Correlation analyses and Mode analyses parts. Pattern recognition and grouping system was com-posed of data format, Power spectrum, Neural network process and Classification parts.
We developed a basic computer program for systemic analysis of EEG by Nonlinear analysis methods.
 , Hye-Young Choi
, Hye-Young Choi , Mi-Hye Paeng
, Mi-Hye Paeng , Sung Wan Byun
, Sung Wan Byun , Mi Sung Kim
, Mi Sung Kim
To evaluate the CT findings of ossicular disruption and fracture utilizing high resolution computed tomography(HRCT) of the temporal bone.
The authors retrospectively reviewed the HRCT scans of 11 patients with ossicular injuries between January 1998 and June 2002 using films in 8 patients, PACS in 3 patients. The type of ossicular injuries, temporal bone fracture, and associated adjacent injuries were evaluated.
Among the 11 patients of ossicular injuries, there were 10 cases of incudomalleal disruption, 4 cases of incudostapedial disruption, and 1 case of fracture of malleus, fracture of incus, disruption of long and lenticular process of incus, nonvisualization of processes of incus. The temporal bone fractures were longitudinal in 7 cases, transverse in l case. Other injuries were fracture of the carotid canal, caroticocavemous fistula, fracture of sphenoid and occipital bones.
Incudomalleal disruption was the most frequent tupe of ossicular injuries and associated temporal bone fracture was longitudinal type. HRCT using PACS was useful in evaluation of ossicular injuries than films.
 , Jae Jin Han
, Jae Jin Han
There have been many parameters that determined the results of radiocephalic ffisutla. However, few reliable intraoperative parameters have been suggested until now. The purpose of this study was to find the correlation between intra-operative blood flow and early patency of radiocephalic fistula.
Between March 1998 and October 1999, 45 radiocephalic arteriovenous fistulas were constructed in 38 patients. Intra-operative blood flow measurements were made 10 minutes after complection of the vascular anastomoses with 3-4mm handheld flow probes. Patients were followed until failure of fistula or 3months after first hemodialysis with these fistulas. Intraoperative blood flow as well as age, sex, presence of diabetes, size of cephalic vein, thrill on the fistula and flow of radial artery were correlated with early patency.
The mean intraoperative blood flow was 195.9±16.7 mL/min ranged from 50 to 500 mL/min, and it was the only significant parameter that determined early patency of radiocephalic fistula. Fistulas with flow less than 150 ml/min(10 of 18) revealed higher failure rate than those of flow more than 150 ml/min(1 of 27), which was statistically significant(p<0.01). All of the patients with flow less than 70 ml/min(5 of 5) failed in maintaining patency within a month. However, the other variables were not correlated with early patency.
In conclusion intra-operative blood flow measurements can be performed with ease and intraoperative blood flow in radiocephalic fistula is well correlated with early patency of the fistula. And we rocommend that radio-cephalic fistula of flow less than 150mL/min should be observed carefully and that of flow less than 70mL/min must be abandoned intraoperatively.
 , Joon Sim
, Joon Sim , Yang-Hee Lim
, Yang-Hee Lim , Jin-Hwa Lee
, Jin-Hwa Lee , Gil-Ja Shin
, Gil-Ja Shin
Most pulmonary thromboemboli arise from the deep vein thrombosis, which have complete clinical and at least near complete roentgenographic and angiographic resolution within four to six week of the acute event.
But chronic pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale from unresolved pulmonary embolism complicate acute embolic episode with a frequency of less than 1 percent. Rarely pulmonary thromboemboli can result from right atrial thrombi.
We experienced a case of chronic thromoboembolic pulmonary hypertension, which wrose from right atrial thrombi in the patient with rheumatic valvaular heart disease and thoracic aorta atherosclerotics stenosis.
 , Jin Hyung Kim
, Jin Hyung Kim , Hee Soo Lee
, Hee Soo Lee , Seung Lee Soe
, Seung Lee Soe , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi , Ki Bum Myung
, Ki Bum Myung
Granuloma annulare is a chronic, benigh, degenerative dermatosis, usually developes on the dorsum of hand or foot. A case is reported of localized granuloma annulare on the both ear helices of a 21-year-old male with no history of precipitating causes, including trauma, insect bite, diabetes mellitus, or rheumatoid arthritis. The histology was typical palisading granulomas. Auricular granuloma annulare is rare. A brief review of the pathogenesis and literature is presented.

The cleft lip nose deformity is caused by multiple factors that include displa-cement of the lower laterial cartilage, with flattening and false lengthening on the cleft side with shifts of the columella, septum and underlying skeletal base. Many plastic surgeons have felt that early rhinoplasty in cleft lip interferes with the growth of nose, causes increased deformity. Then this study was performed to find the result of the early surgery in the clefe nasal recon-struton.
The alar cartilage was repositioned by freeing it from the skin and nasal lining without its exposure through the incision of cleft lip repair and shifting it to a new position at the time of pirmay cleft lip repair. The repositioned lower lateral cartilage was stabilized in its new position by using through and througn sutures tied over stents. These stent sutures went through the skin, cartilage and nasal lining. The nasal soft tissues were released from the skele-tal base, reshaped.
Improvement in the cleft nasal deformity is noted in most cases. Especially the colu-mella inclination was completely corrected. The nasal dome on the cleft side shows the good contour and projection of the tip, which projects in an equal fashion to the concleft side. The nasal alar symmetry with equal projection of the lobule was observed on the cleft and noncleft side.
Early surgical correction of cleft lip nose deformity doesn't interferes with the growth of nose and promotes more normal grown by early proper contour and position of the lower lateral cartilage. It is more important to take better psychological development and good self-image before the adverse effedct of deformity cause damage.

