
 , Sohyun Ahn
, Sohyun Ahn , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
Citations

 , Yoon Jin Choi
, Yoon Jin Choi , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Joo Young Roh
, Joo Young Roh , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
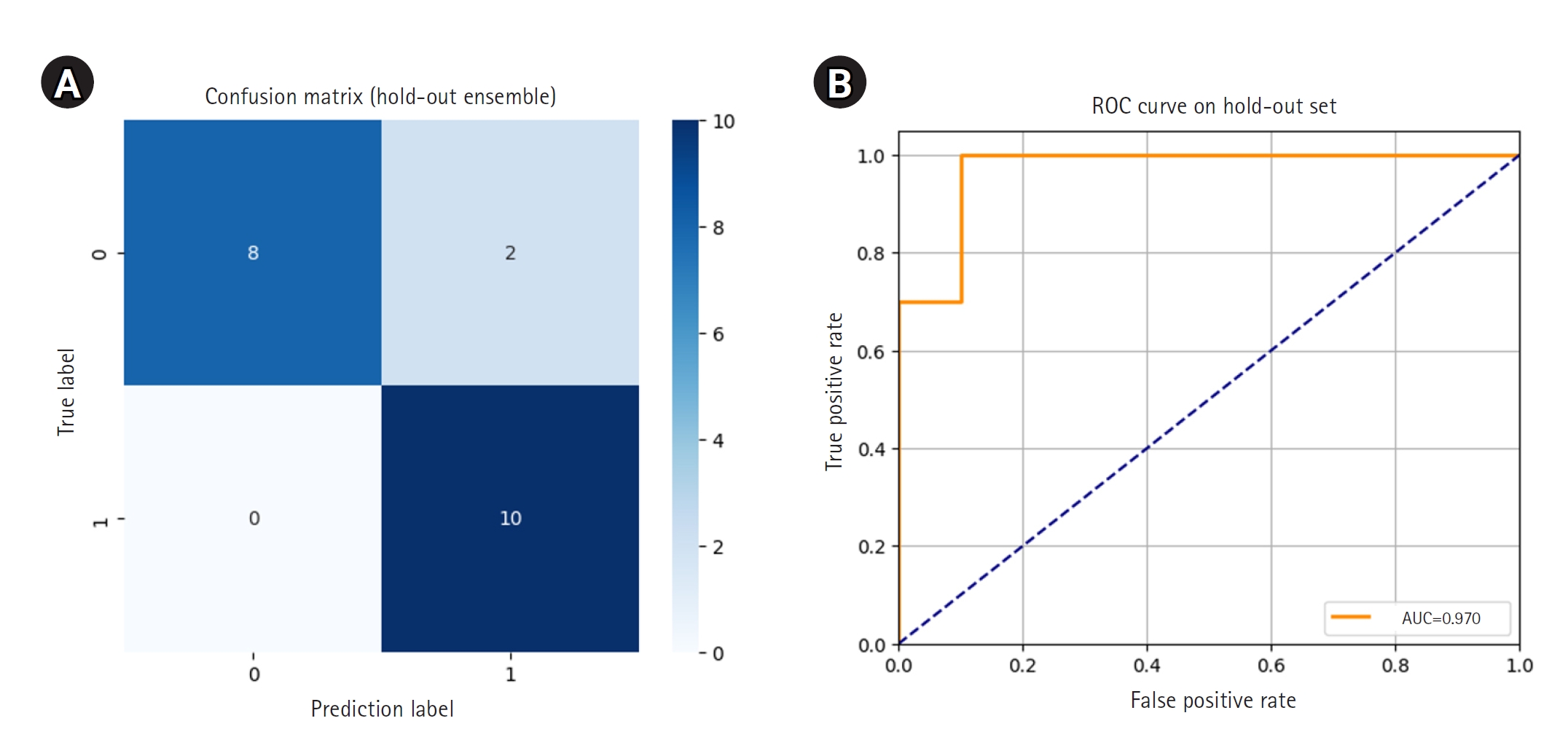
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which are often acquired from environmental sources such as water and soil, exhibit a variety of cutaneous manifestations that frequently lead to misdiagnoses and delays in treatment. A 77-year-old woman presented with multiple skin lesions in a sporotricoid distribution on her right leg, which persisted despite standard antibiotic treatments. Based on the skin biopsy, revealing granulomatous inflammation with acid-fast bacilli, and PCR testing, a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection was diagnosed. Antimycobacterial drug combinations, including clarithromycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin for 4 months, complete the skin lesion's clearance. This case underscores the need for heightened suspicion and the use of appropriate diagnostic techniques, including tissue biopsies and molecular methods such as PCR.
Citations

 , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
 , Min Young Lee
, Min Young Lee , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
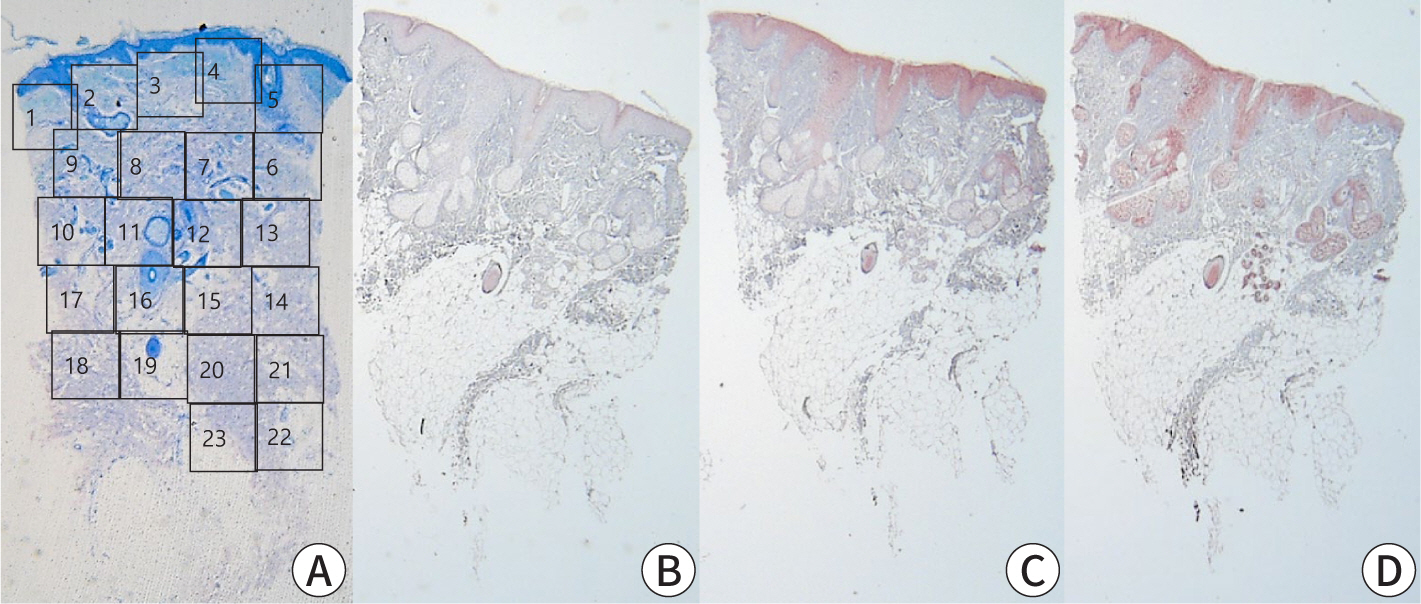
Pancreatic panniculitis is a rare skin complication in which subcutaneous fat necrosis occurs in association with pancreatic disorders, most commonly acute or chronic pancreatitis. Erythematous subcutaneous nodules develop on the legs and spontaneously ulcerate or exude an oily substance. A 32-year-old Korean female patient presented with a 2-week-history of tender nodules with erythematous crusts on her left shin. She had a history of alcoholic liver cirrhosis and, 5 weeks earlier, had been diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. The histopathologic findings from a skin biopsy were consistent with lobular panniculitis, without signs of vasculitis, and diffuse fat necrosis. Basophilic calcium deposits were present in the dermis and subcutaneous fat. These findings were suggestive of pancreatic panniculitis. The skin lesion had a chronic course corresponding to repeated exacerbations of the patient’s pancreatitis. Thus, in the differential diagnosis of subcutaneous nodules, clinicians should consider pancreatic panniculitis as a cutaneous manifestation of pancreatic disease.
 , Rosa Kim
, Rosa Kim , Min Young Lee
, Min Young Lee , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
 , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee

