
Citations


Citations


Citations


Citations

 , Woong Sub Koom
, Woong Sub Koom , Hong In Yoon
, Hong In Yoon , Kyung Hwan Kim
, Kyung Hwan Kim , Chan Woo Wee
, Chan Woo Wee , Jaeho Cho
, Jaeho Cho , Yong Bae Kim
, Yong Bae Kim , Ki Chang Keum
, Ki Chang Keum , Ik Jae Lee
, Ik Jae Lee
Carbon-ion radiotherapy (CIRT) offers superior dose distributions and greater biological effectiveness than conventional photon-based radiotherapy (RT). Due to its higher linear energy transfer and relative biological effectiveness, CIRT is particularly effective against radioresistant tumors and those located near critical organs. Since the first dedicated CIRT facility was established in Japan in 1994, CIRT has demonstrated remarkable efficacy against various malignancies, including head and neck tumors, skull base and upper cervical spine tumors, non-small-cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and bone and soft tissue sarcomas. This narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of the current status of CIRT, highlighting its clinical indications and future directions. According to clinical studies, CIRT achieves high local control rates with manageable toxicity across multiple cancer types. For instance, in head and neck tumors (e.g., adenoid cystic carcinoma and mucosal melanoma), CIRT has achieved local control rates exceeding 80%. In early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer, CIRT has resulted in local control rates over 90% with minimal toxicity. Moreover, CIRT has shown promise in treating challenging cases of hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic cancer, where conventional therapies are limited. Nonetheless, the global adoption of CIRT remains limited due to high costs and complexity. Future directions include conducting randomized controlled trials to establish high-level evidence, integrating new technologies such as ultrahigh-dose-rate (FLASH) therapy, and expanding CIRT facilities globally with strategic planning and cost-effectiveness analyses. If these challenges are addressed, CIRT is poised to play a transformative role in cancer treatment, improving survival rates and the quality of life.
Citations


FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) is an innovative approach that delivers ultra-high dose rates exceeding 40 Gy in less than a second, aiming to widen the therapeutic window by minimizing damage to normal tissue while maintaining tumor control. This review explores the advancements, mechanisms, and clinical applications of FLASH-RT across various radiation sources. Electrons have been predominantly used due to technical feasibility, but their limited penetration depth restricts clinical application. Protons, offering deeper tissue penetration, are considered promising for treating deep-seated tumors despite challenges in beam delivery. Preclinical studies demonstrate that FLASH-RT reduces normal tissue toxicity in the lung, brain, skin, intestine, and heart without compromising antitumor efficacy. The mechanisms underlying the FLASH effect may involve oxygen depletion leading to transient hypoxia, reduced DNA damage in normal tissues, and modulation of immune and inflammatory responses. However, these mechanisms are incompletely understood, and inconsistent results across studies highlight the need for further research. Initial clinical studies, including treatment of cutaneous lymphoma and bone metastases, indicate the feasibility and potential benefits of FLASH-RT in patients. Challenges for clinical implementation include technical issues in dosimetry accuracy at ultra-high dose rates, adaptations in treatment planning systems, beam delivery methods, and economic considerations due to specialized equipment requirements. Future directions will involve comprehensive preclinical studies to optimize irradiation parameters, large-scale clinical trials to establish standardized protocols, and technological advancements to overcome limitations. FLASH-RT holds the potential to revolutionize radiotherapy by reducing normal tissue toxicity and improving therapeutic outcomes, but significant research is required for real-world clinical applications.
Citations

 , YoungMoon Goh
, YoungMoon Goh , Jungwon Kwak
, Jungwon Kwak
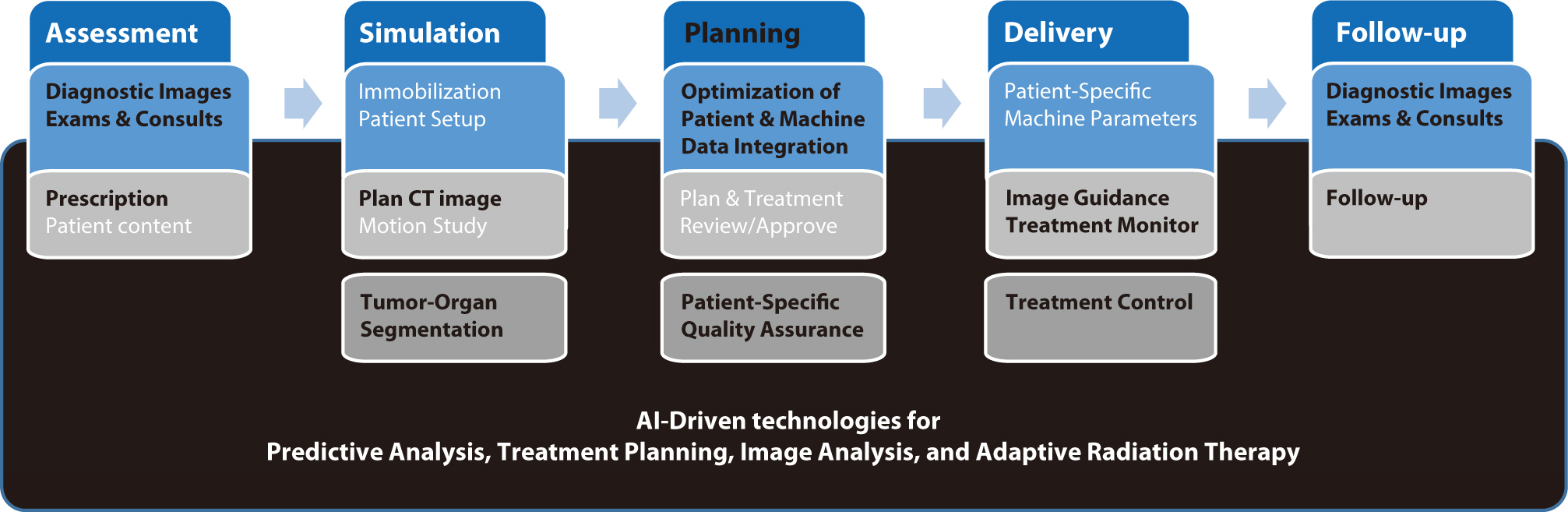
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various medical fields, including radiation oncology. This review explores the integration of AI into radiation oncology, highlighting both challenges and opportunities. AI can improve the precision, efficiency, and outcomes of radiation therapy by optimizing treatment planning, enhancing image analysis, facilitating adaptive radiation therapy, and enabling predictive analytics. Through the analysis of large datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters, AI can automate complex tasks, reduce planning time, and improve accuracy. In image analysis, AI-driven techniques enhance tumor detection and segmentation by processing data from CT, MRI, and PET scans to enable precise tumor delineation. In adaptive radiation therapy, AI is beneficial because it allows real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on changes in patient anatomy and tumor size, thereby improving treatment accuracy and effectiveness. Predictive analytics using historical patient data can predict treatment outcomes and potential complications, guiding clinical decision-making and enabling more personalized treatment strategies. Challenges to AI adoption in radiation oncology include ensuring data quality and quantity, achieving interoperability and standardization, addressing regulatory and ethical considerations, and overcoming resistance to clinical implementation. Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is crucial to overcoming these obstacles. By addressing these challenges, AI can drive advancements in radiation therapy, improving patient care and operational efficiencies. This review presents an overview of the current state of AI integration in radiation oncology and insights into future directions for research and clinical practice.
Citations

 , Haeryoung Kim
, Haeryoung Kim
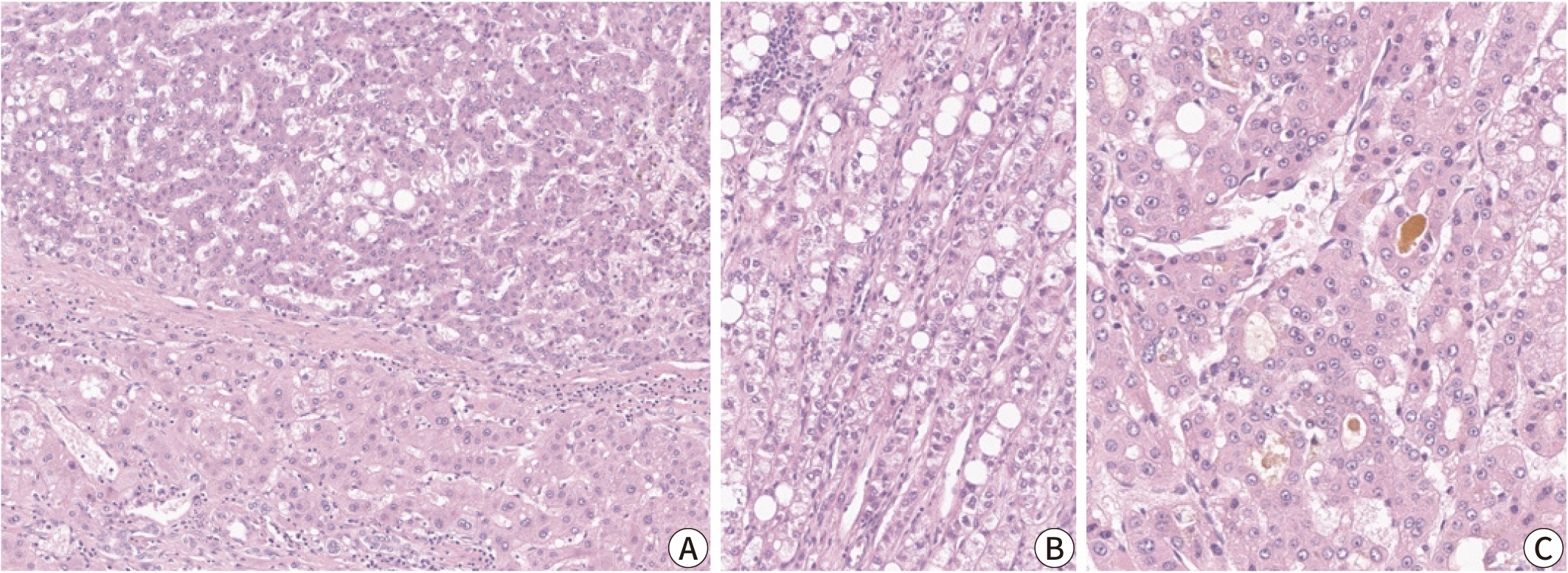
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths
worldwide, with poor clinical outcomes due to challenges in early detection and
limited efficacy of current treatments such as receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors and immunotherapy. HCC exhibits significant heterogeneity at both
histopathological and molecular levels, complicating its management but offering
potential for personalized therapeutic approaches. This review outlines the
morpho-molecular heterogeneity of HCC and summarizes various histological
subtypes, including steatohepatitic, clear cell, macrotrabecular-massive,
scirrhous, lymphocyte-rich, and fibrolamellar HCCs. Each subtype possesses
distinct clinical, histological, and molecular features; for instance,
steatohepatitic HCC is associated with metabolic dysfunction and shows
IL-6/JAK/STAT activation, while clear cell HCCs often have
Citations


Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is increasingly recognized as a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, driven by the global obesity epidemic. Projected to become the primary cause of HCC by 2030, MASH-HCC presents unique clinical challenges. This review examines its clinical management, including surveillance strategies and treatment advances, and discusses prospects to overcome existing challenges. MASH-HCC accounts for 10%–20% of HCC cases, particularly in Western countries, with a rising incidence due to obesity. Risk factors include cirrhosis, diabetes, obesity, alcohol, smoking, genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3), and microbiome alterations. The pathogenesis involves fibrosis, immune dysfunction (e.g., T-cell impairment), and molecular changes. Prevention focuses on lifestyle modifications. Surveillance in patients with MASH cirrhosis is crucial but is hindered by poor ultrasound sensitivity in obese patients, necessitating alternative methods. Treatment mirrors that of other HCC types, but comorbidities and potentially reduced efficacy of immunotherapy necessitate tailored approaches. MASH is becoming the leading cause of HCC, necessitating lifestyle interventions for prevention. Improved surveillance and early detection are critical but challenging due to obesity-related factors. Treatments align with those for other HCC types, but comorbidities and potential differences in immunotherapy efficacy due to T-cell dysfunction require careful consideration. Key needs include identifying molecular drivers in non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, developing preventive therapies, refining surveillance methods, and tailoring treatments. Trials should specifically report MASH-HCC outcomes to enable personalized therapies. Further research is needed to understand T-cell dysfunction, optimize immunotherapies, and identify predictive biomarkers.
 , Taek Chung
, Taek Chung , Dong Kyu Kim
, Dong Kyu Kim , Hyungjin Rhee
, Hyungjin Rhee
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is a heterogeneous bile duct adenocarcinoma with a rising global incidence and a poor prognosis. This review aims to present a comprehensive overview of the most recent radiological research on iCCA, focusing on its histopathologic subclassification and the use of imaging findings to predict prognosis and inform treatment decisions. Histologically, iCCA is subclassified into small duct (SD-iCCA) and large duct (LD-iCCA) types. SD-iCCA typically arises in the peripheral small bile ducts and is often associated with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis. It presents as a mass-forming lesion with a relatively favorable prognosis. LD-iCCA originates near the hepatic hilum, is linked to chronic bile duct diseases, and exhibits more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes. Imaging is essential for differentiating these subtypes and assessing prognostic factors like tumor size, multiplicity, vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, enhancement patterns, and intratumoral fibrosis. Imaging-based prognostic models have demonstrated predictive accuracy comparable to traditional pathological staging systems. Furthermore, imaging findings are instrumental in guiding treatment decisions, including those regarding surgical planning, lymphadenectomy, neoadjuvant therapy, and the selection of targeted therapies based on molecular profiling. Advancements in radiological research have improved our understanding of iCCA heterogeneity, facilitating prognosis prediction and treatment personalization. Imaging findings assist in subclassifying iCCA, predicting outcomes, and informing treatment decisions, thus optimizing patient management. Incorporating imaging-based approaches into clinical practice is crucial for advancing personalized medicine in the treatment of iCCA. However, further high-level evidence from international multicenter prospective studies is required to validate these findings and increase their clinical applicability.
 , Jeong-Ju Yoo
, Jeong-Ju Yoo , Sang Gyune Kim
, Sang Gyune Kim , Young Seok Kim
, Young Seok Kim
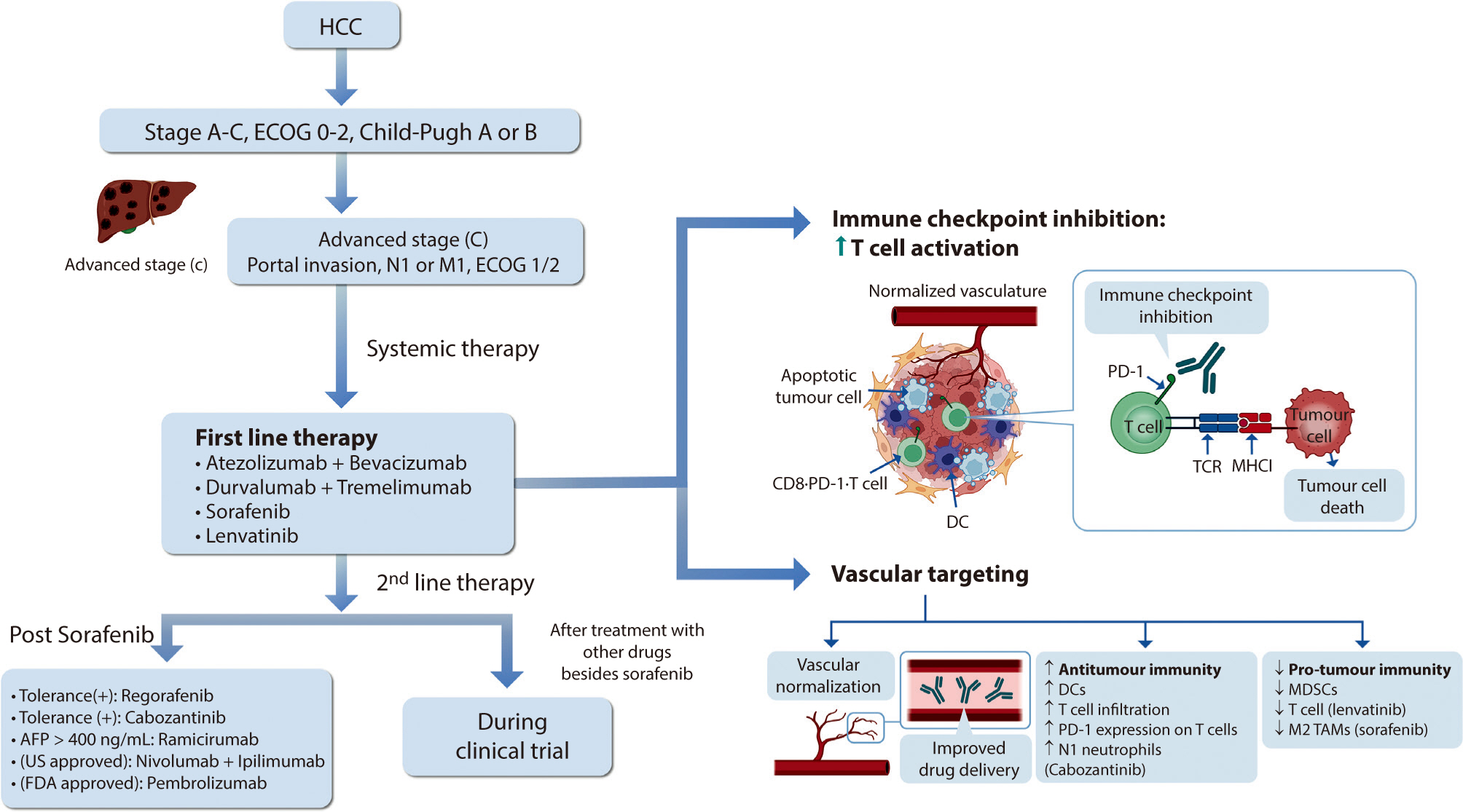
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a critical health concern in Korea, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer mortality and imposing substantial economic burdens, particularly among the working-age population. This review examines recent advancements in treating advanced HCC, referencing the updated 2022 HCC guidelines and the Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer system. Historically, first-line systemic therapies included sorafenib and lenvatinib, with regorafenib, cabozantinib, or ramucirumab serving as second-line options. Since 2020, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown superior overall survival than sorafenib, leading to the adoption of combination therapies such as atezolizumab with bevacizumab and durvalumab with tremelimumab as first-line treatments. The IMbrave150 study demonstrated that atezolizumab–bevacizumab significantly extended median overall survival and progression-free survival, with the longest survival reported in any phase 3 trial for advanced HCC. Similarly, the HIMALAYA study indicated that durvalumab combined with tremelimumab significantly improved survival rates. Second-line therapies now include regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab, nivolumab with ipilimumab, and pembrolizumab, each offering benefits for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, these therapies are associated with side effects that require careful management. Traditional targeted therapies can lead to hypertension, cardiovascular events, and hand-foot skin reactions, whereas immune checkpoint inhibitors may cause immune-related adverse events affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. Clinicians must be well-versed in these treatments and their potential side effects to provide optimal patient care. The emergence of combination therapies targeting complex biological pathways signifies a new paradigm in HCC treatment, emphasizing the importance of continuous education and vigilant monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Citations

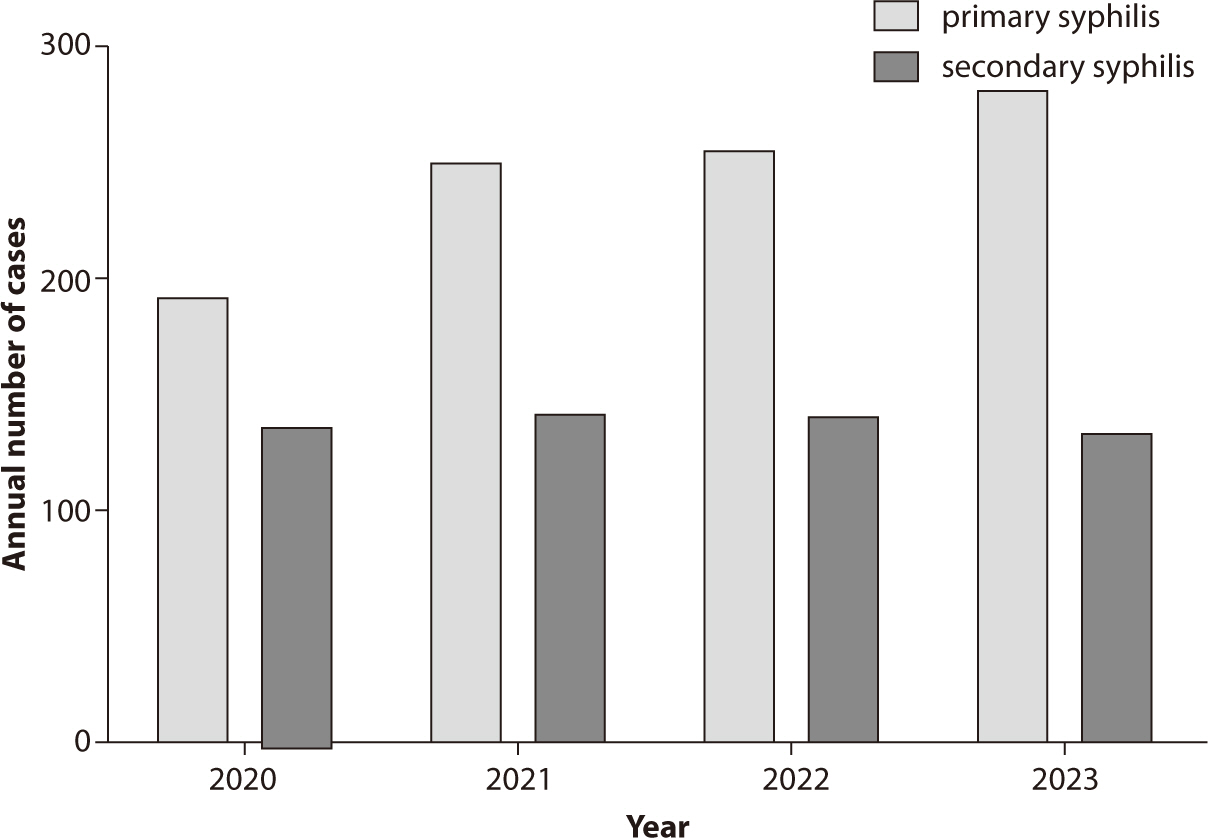

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) continue to pose significant public health
challenges in Korea, with syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia,
Citations

 , Minsung Kim
, Minsung Kim
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols are designed to minimize surgical stress, preserve physiological function, and expedite recovery through standardized perioperative care for primary colorectal surgery patients. This narrative review explores the benefits of current ERAS protocols in improving outcomes for these patients and provides insights into future advancements. Numerous studies have shown that ERAS protocols significantly reduce the length of hospital stays by several days compared to conventional care. Additionally, the implementation of ERAS is linked to a reduction in postoperative complications, including lower incidences of surgical site infections, anastomotic leaks, and postoperative ileus. Patients adhering to ERAS protocols also benefit from quicker gastrointestinal recovery, marked by an earlier return of bowel function. Some research indicates that colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery with ERAS protocols may experience improved overall survival rates. High compliance with ERAS protocols leads to better outcomes, yet achieving full adherence continues to be a challenge. Despite these advantages, implementation challenges persist, with compliance rates affected by varying clinical practices and resource availability. However, the future of ERAS looks promising with the incorporation of prehabilitation strategies and technologies such as wearable devices and telemedicine. These innovations provide real-time monitoring, enhance patient engagement, and improve postoperative follow-up, potentially transforming perioperative care in colorectal surgery and offering new avenues for enhanced patient outcomes.
Citations


This paper discusses the implications of South Korea's birth notification system and Protected Birth Act, which is set to take effect on July 19, 2024. The legislation aims to prevent infanticide and child abandonment by mandating birth reporting and allowing anonymous births for women in crisis. However, concerns have been raised about the Act's effectiveness in protecting both women and children, particularly regarding issues of disability and migrant families. This paper focuses on gender and healthcare issues, highlighting how the Act perpetuates discrimination against out-of-wedlock pregnancies and upholds normal family ideologies. It notes the absence of critical discussions on women's autonomy, safe pregnancy termination, and paternal responsibility. The importance of healthcare providers understanding and preparing for the Act's implementation is emphasized. The paper calls for strengthening social safety nets to improve healthcare access for vulnerable populations and eliminate discrimination against non-traditional families. Additionally, it addresses the need for comprehensive support systems for crisis pregnancies, including financial assistance, psychological support, parenting education, housing solutions, and expanded healthcare services. This paper acknowledges the Act's significance in providing a systematic state-level approach to protecting pregnant women in crisis, replacing the previous reliance on private organizations. Nonetheless, it also emphasizes the importance of continually reviewing and supplementing the system to address potential rights infringements and ensure its effectiveness. In conclusion, this paper advocates for ongoing discussions on gender and healthcare issues, and for future amendments to the law that reflect real-world circumstances and provide genuine protection for crisis pregnancies and infants.
Citations

 , Sooyoung Cho
, Sooyoung Cho , Yoonsun Won
, Yoonsun Won , Jong Wha Lee
, Jong Wha Lee
Citations

 , Kye Hwa Lee
, Kye Hwa Lee
 , Shinjeong Song
, Shinjeong Song , Chang Mo Moon
, Chang Mo Moon , Hye Ah Lee
, Hye Ah Lee , Junbeom Park
, Junbeom Park
 , Claudia Santosa
, Claudia Santosa , Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne
, Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne , Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara
, Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara Citations


Citations

 , Brandon E. Gavett
, Brandon E. Gavett , Michael Weinborn
, Michael Weinborn , Craig P. Speelman
, Craig P. Speelman , Romola S. Bucks
, Romola S. Bucks , Ralph N. Martins
, Ralph N. Martins
Citations

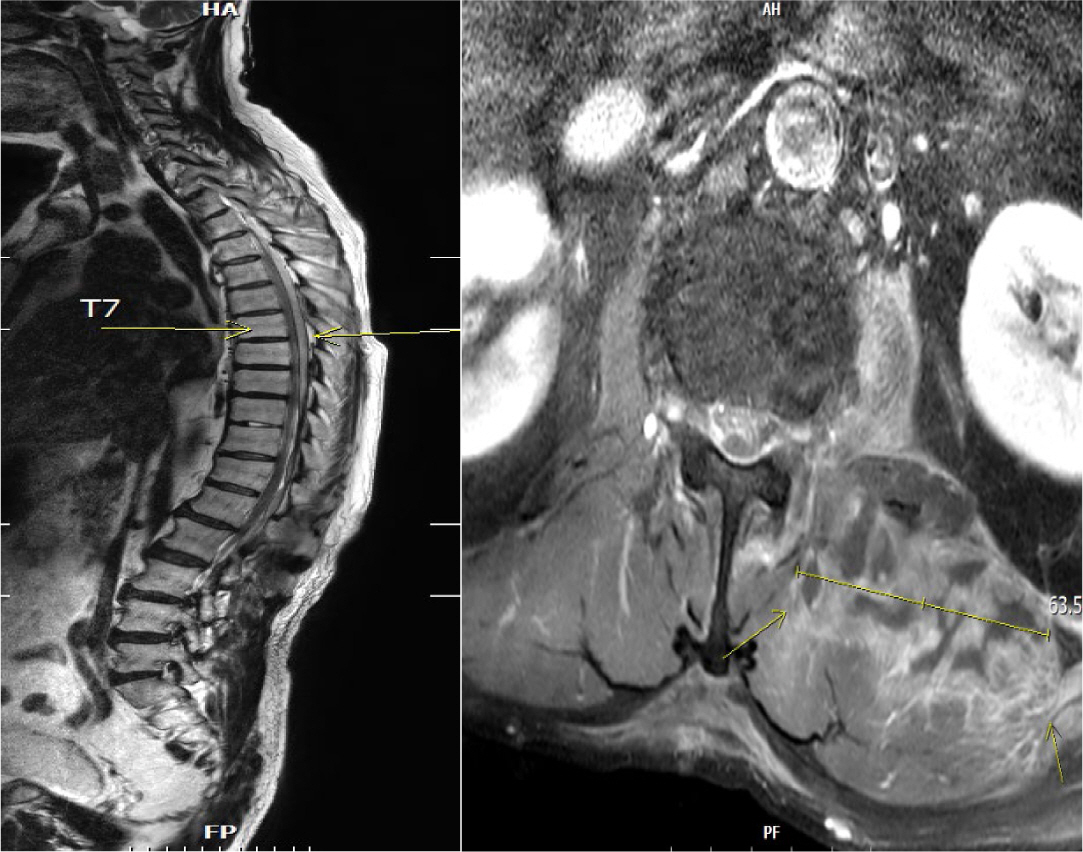

Septic embolism and stroke are serious complications in patients with sepsis and often necessitate urgent surgical intervention to control the source of infection. A 69-year-old man presented with severe pain in his back and left thigh. MRI revealed extensive posterior epidural or subdural abscesses extending from the cervical to the lumbar level, as well as an abscess in the iliopsoas muscle. The patient underwent urgent drainage of the abscesses and decompression of the lumbar spine. Postoperatively, he developed sudden-onset atrial fibrillation and altered mental status. Brain CT showed multiple embolic infarctions. His condition deteriorated due to persistent infection, leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute kidney injury, and septic shock. This case highlights the risk of cerebral embolism and hemorrhagic complications in patients with sepsis who undergo surgery. Early recognition of individuals at high risk and comprehensive perioperative management are critical to reducing the likelihood of such complications.


Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the parasite
Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Treatment should be initiated for all suspected, clinical, or confirmed cases of scabies. Patients affected should be adequately isolated, and high-risk groups with close contact histories should be treated regardless of their symptoms. Optimal treatment strategies can be selected based on age, clinical subtype, and the patient's health status. In Korea, commercially available preparations for scabies treatment include topical 5% permethrin, topical 10% crotamiton, and oral ivermectin. Topical 5% permethrin is the first-line selective treatment for both classic and crusted scabies. Alternative treatments include topical 10% crotamiton and oral ivermectin. After completing treatment, follow-up visits at 2 and 4 weeks are recommended to monitor the therapeutic response. Treatment is considered to have failed if scabies mites or burrows are detected, new clinical characteristics develop, or there is an aggravation of pruritus. Scabies itch should be adequately managed with emollients, oral antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids. Preventive measures, including personal hygiene, patient education, and environmental control, should besd implemented to reduce the transmission of scabies.
Citations


