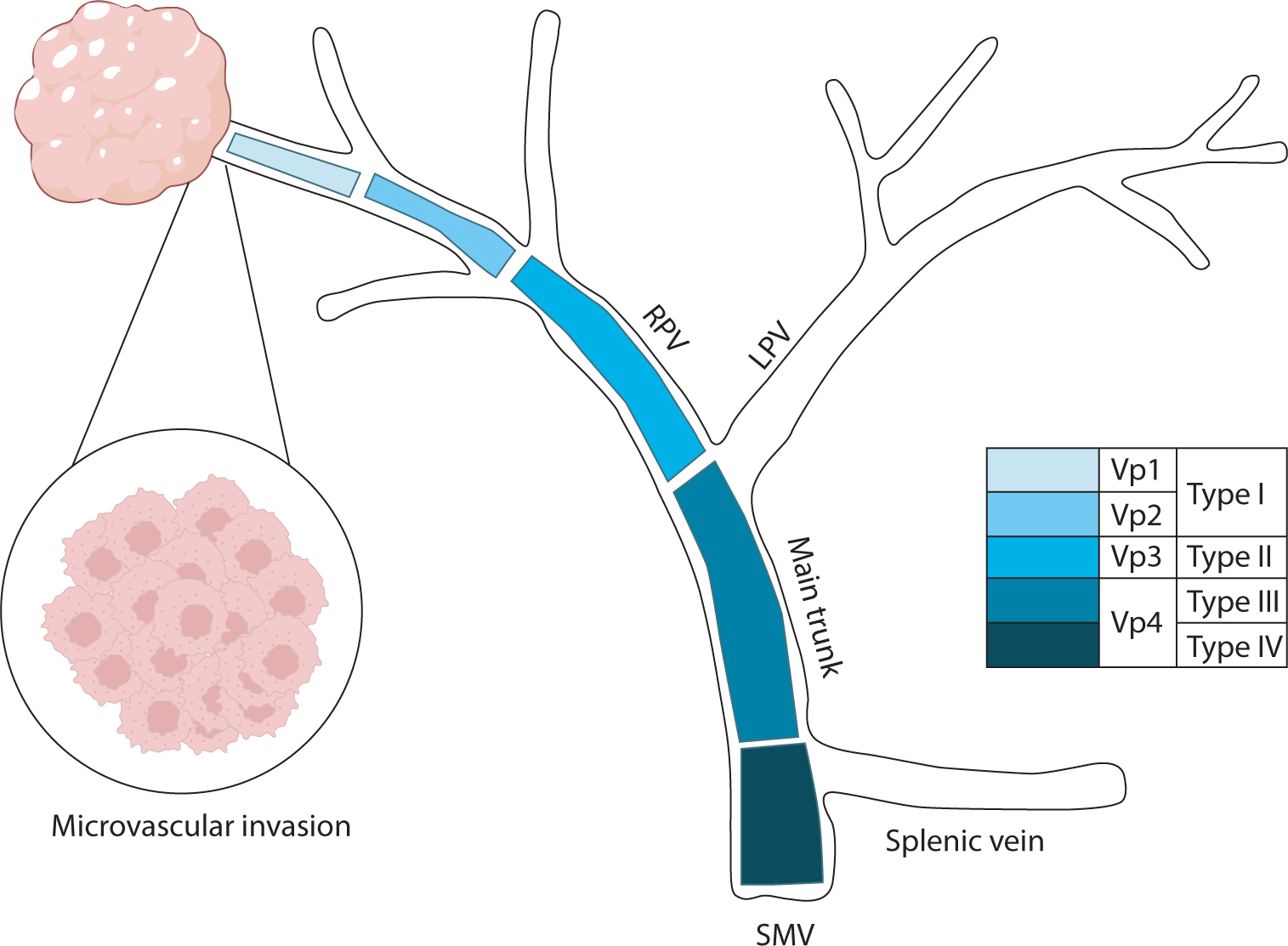
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.
 , Taek Chung
, Taek Chung , Dong Kyu Kim
, Dong Kyu Kim , Hyungjin Rhee
, Hyungjin Rhee
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is a heterogeneous bile duct adenocarcinoma with a rising global incidence and a poor prognosis. This review aims to present a comprehensive overview of the most recent radiological research on iCCA, focusing on its histopathologic subclassification and the use of imaging findings to predict prognosis and inform treatment decisions. Histologically, iCCA is subclassified into small duct (SD-iCCA) and large duct (LD-iCCA) types. SD-iCCA typically arises in the peripheral small bile ducts and is often associated with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis. It presents as a mass-forming lesion with a relatively favorable prognosis. LD-iCCA originates near the hepatic hilum, is linked to chronic bile duct diseases, and exhibits more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes. Imaging is essential for differentiating these subtypes and assessing prognostic factors like tumor size, multiplicity, vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, enhancement patterns, and intratumoral fibrosis. Imaging-based prognostic models have demonstrated predictive accuracy comparable to traditional pathological staging systems. Furthermore, imaging findings are instrumental in guiding treatment decisions, including those regarding surgical planning, lymphadenectomy, neoadjuvant therapy, and the selection of targeted therapies based on molecular profiling. Advancements in radiological research have improved our understanding of iCCA heterogeneity, facilitating prognosis prediction and treatment personalization. Imaging findings assist in subclassifying iCCA, predicting outcomes, and informing treatment decisions, thus optimizing patient management. Incorporating imaging-based approaches into clinical practice is crucial for advancing personalized medicine in the treatment of iCCA. However, further high-level evidence from international multicenter prospective studies is required to validate these findings and increase their clinical applicability.

Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is increasingly recognized as a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, driven by the global obesity epidemic. Projected to become the primary cause of HCC by 2030, MASH-HCC presents unique clinical challenges. This review examines its clinical management, including surveillance strategies and treatment advances, and discusses prospects to overcome existing challenges. MASH-HCC accounts for 10%–20% of HCC cases, particularly in Western countries, with a rising incidence due to obesity. Risk factors include cirrhosis, diabetes, obesity, alcohol, smoking, genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3), and microbiome alterations. The pathogenesis involves fibrosis, immune dysfunction (e.g., T-cell impairment), and molecular changes. Prevention focuses on lifestyle modifications. Surveillance in patients with MASH cirrhosis is crucial but is hindered by poor ultrasound sensitivity in obese patients, necessitating alternative methods. Treatment mirrors that of other HCC types, but comorbidities and potentially reduced efficacy of immunotherapy necessitate tailored approaches. MASH is becoming the leading cause of HCC, necessitating lifestyle interventions for prevention. Improved surveillance and early detection are critical but challenging due to obesity-related factors. Treatments align with those for other HCC types, but comorbidities and potential differences in immunotherapy efficacy due to T-cell dysfunction require careful consideration. Key needs include identifying molecular drivers in non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, developing preventive therapies, refining surveillance methods, and tailoring treatments. Trials should specifically report MASH-HCC outcomes to enable personalized therapies. Further research is needed to understand T-cell dysfunction, optimize immunotherapies, and identify predictive biomarkers.
 , Haeryoung Kim
, Haeryoung Kim
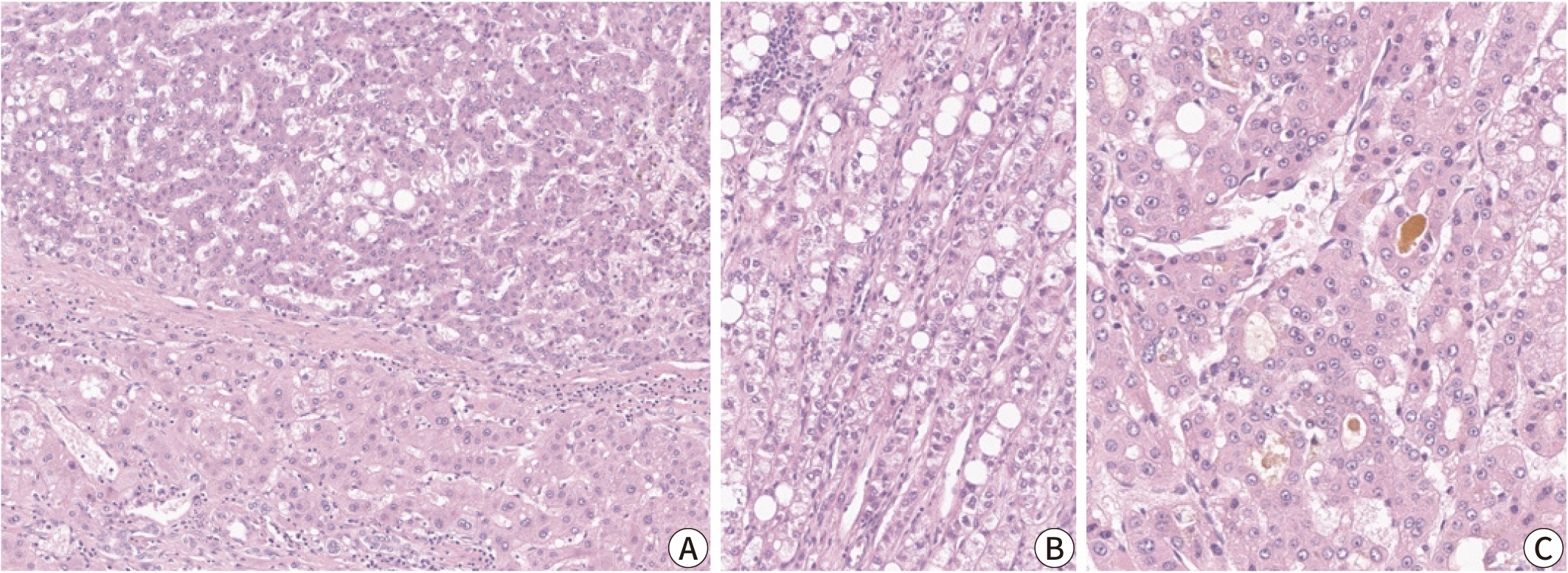
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths
worldwide, with poor clinical outcomes due to challenges in early detection and
limited efficacy of current treatments such as receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors and immunotherapy. HCC exhibits significant heterogeneity at both
histopathological and molecular levels, complicating its management but offering
potential for personalized therapeutic approaches. This review outlines the
morpho-molecular heterogeneity of HCC and summarizes various histological
subtypes, including steatohepatitic, clear cell, macrotrabecular-massive,
scirrhous, lymphocyte-rich, and fibrolamellar HCCs. Each subtype possesses
distinct clinical, histological, and molecular features; for instance,
steatohepatitic HCC is associated with metabolic dysfunction and shows
IL-6/JAK/STAT activation, while clear cell HCCs often have
Citations

 , Jeong-Ju Yoo
, Jeong-Ju Yoo , Sang Gyune Kim
, Sang Gyune Kim , Young Seok Kim
, Young Seok Kim
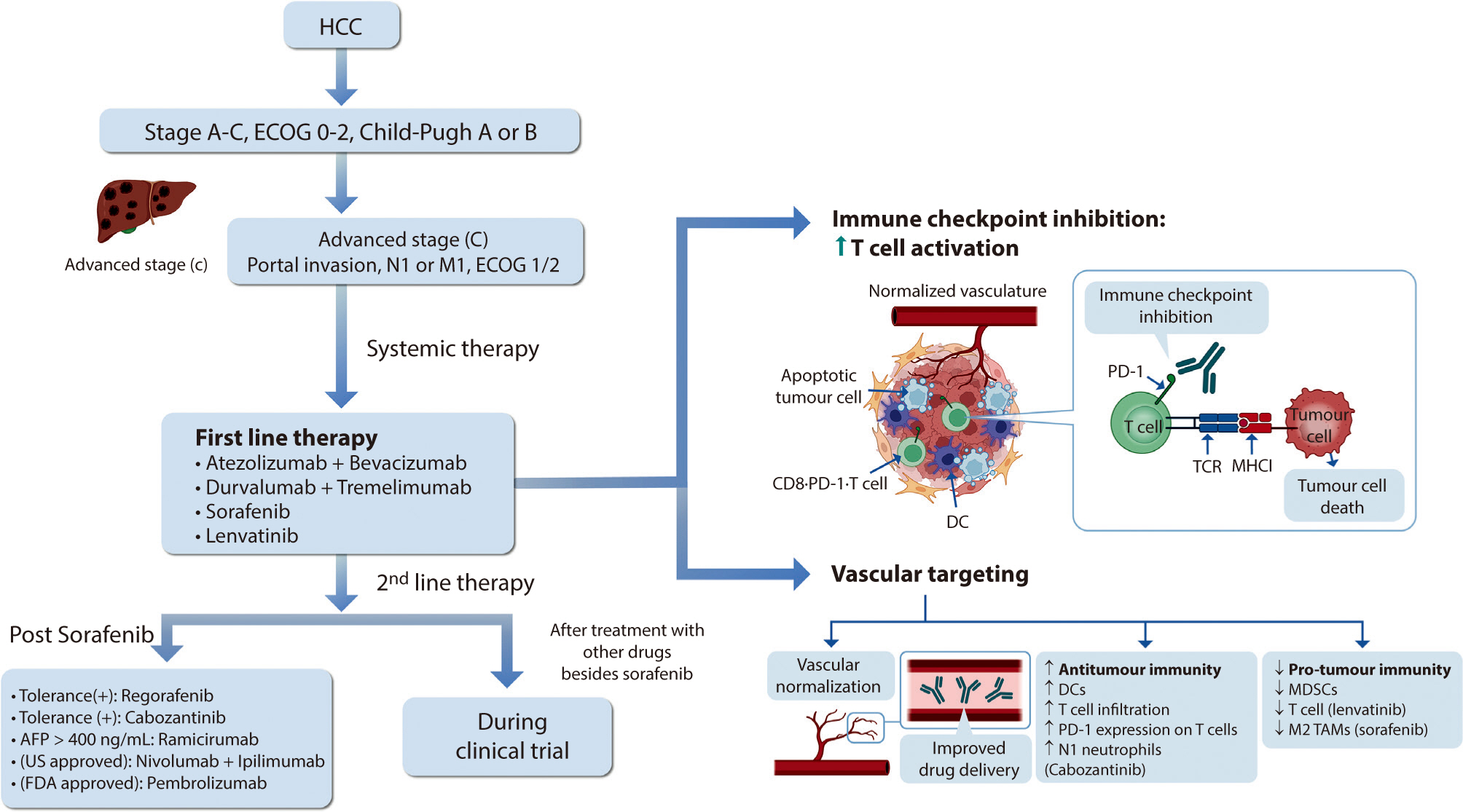
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a critical health concern in Korea, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer mortality and imposing substantial economic burdens, particularly among the working-age population. This review examines recent advancements in treating advanced HCC, referencing the updated 2022 HCC guidelines and the Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer system. Historically, first-line systemic therapies included sorafenib and lenvatinib, with regorafenib, cabozantinib, or ramucirumab serving as second-line options. Since 2020, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown superior overall survival than sorafenib, leading to the adoption of combination therapies such as atezolizumab with bevacizumab and durvalumab with tremelimumab as first-line treatments. The IMbrave150 study demonstrated that atezolizumab–bevacizumab significantly extended median overall survival and progression-free survival, with the longest survival reported in any phase 3 trial for advanced HCC. Similarly, the HIMALAYA study indicated that durvalumab combined with tremelimumab significantly improved survival rates. Second-line therapies now include regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab, nivolumab with ipilimumab, and pembrolizumab, each offering benefits for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, these therapies are associated with side effects that require careful management. Traditional targeted therapies can lead to hypertension, cardiovascular events, and hand-foot skin reactions, whereas immune checkpoint inhibitors may cause immune-related adverse events affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. Clinicians must be well-versed in these treatments and their potential side effects to provide optimal patient care. The emergence of combination therapies targeting complex biological pathways signifies a new paradigm in HCC treatment, emphasizing the importance of continuous education and vigilant monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Citations

 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Dong Chan Joo
, Dong Chan Joo , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Kyung Bin Kim
, Kyung Bin Kim
We report a rare case of gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation (GAED) that was treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection followed by additional distal gastrectomy with lymph node dissection. A 67-year-old man underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection for a gastric lesion, which was diagnosed as GAED with submucosal and lymphatic invasion. Histologically, GAED is characterized by a tubulopapillary growth pattern and clear cells that resemble those of the primitive fetal gut. Immunohistochemically, GAED variably expresses oncofetal proteins such as glypican-3, alpha-fetoprotein, and spalt-like transcription factor 4. Despite negative margins, additional gastrectomy with lymph node dissection was performed due to submucosal and lymphatic invasion. No residual tumor or metastasis was detected, and the patient remained disease-free for 2 years before dying from causes unrelated to GAED. Given its aggressive nature, frequent lymphovascular invasion, and high metastatic potential, clinicians should recognize the histopathological diagnosis of this rare tumor and its propensity for aggressiveness.
 , Won Kim
, Won Kim
Understanding the effects of sex and sex differences on liver health and disease is crucial for individualized healthcare and informed decision-making for patients with liver disease. The impact of sex on liver disease varies according to its etiology. Women have a lower prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) than men. However, postmenopausal women face a higher risk of advanced liver fibrosis due to hormonal influences. Sex differences affect the pathogenesis of MASLD, which involves a complex process involving several factors such as hormones, obesity, and the gut microbiome. Furthermore, sex-related differences in the development of MASLDrelated hepatocellular carcinoma have been observed. The sex-specific characteristics of MASLD necessitate an individualized management approach based on scientific evidence. However, research in this area has been lacking. This article reviews the current understanding of sex differences in MASLD.
Citations

 , Jong Kil Nam
, Jong Kil Nam , Bon Jin Koo
, Bon Jin Koo , Hyun Jung Lee
, Hyun Jung Lee , Tae Un Kim
, Tae Un Kim , Hwaseong Ryu
, Hwaseong Ryu , Yun Jeong Hong
, Yun Jeong Hong , Seungsoo Lee
, Seungsoo Lee , Dong Hoon Lee
, Dong Hoon Lee , Sung Woo Park
, Sung Woo Park
The aim of this study was to examine the clinical presentation, treatment delivery, and cisplatin eligibility of Korean patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC) in a real-world setting.
We performed a retrospective cohort study of patients initially diagnosed with UC from March 2013 to June 2018. Creatinine clearance >60 mL/min and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (0-1) were adopted as cisplatin eligibility criteria.
This study included 557 eligible patients. Median age was 71.0 years (range, 33-94 years), and males were dominant (80%). Primary tumor sites were: upper genitourinary tract, 18%; bladder, 81%; and urethra, 0.4%. Initial disease status was non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (313, 56%), diffuse infiltrating non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (19, 3%), cTanyN0 upper tract UC (75, 13%), cT2-4N0 bladder UC (82, 15%), TanyN1-3 UC (36, 7%), or initially metastatic UC (32, 6%). At the time of analysis (June 2019), following treatments were delivered to 134 patients with localized UC: radical operation with or without perioperative treatment (89, 67%), definitive chemoradiation (7, 5%), and palliative surgery or supportive care only (36, 28%). In total, 89 patients had metastatic UC, including those with recurrent disease (n=57), and 34 (38%) of the 89 were eligible for cisplatin.
Clinical presentations in East Asian UC patients were consistent with those of previous studies in other countries, except for a relatively high incidence of upper genitourinary tract. Our results can serve as a benchmark for further advances and future research for treatments of UC in East Asian patients.
Citations

 , Angela Cho
, Angela Cho , Chul Min Park
, Chul Min Park
A 66-year-old postmenopausal woman received routine gynecologic check-up. Transvaginal ultrasonography and abdominal and pelvic computed tomography showed about 5-cm cystic mass in uterus with solid component and the patient had thin endometrium and the serum level of CA 125 was normal. We performed a total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and found tumor which had brownish cystic fluid and about 2 cm sized and colored in light yellowish, polypoid protruding solid mass, located within the myometrial wall. Histopathological examination of frozen section revealed malignancy. The tumor was confined within the myometrium and its histologic type was clear cell adenocarcinoma. Finally we identified that the myometrial mass was clear cell adenocarcinoma originated from adenomyosis pathologically. The malignant transformation of adenomyosis is very rare. When we find a cystic change with solid component in adenomyosis patients, clear cell adenocarcinoma should be suspected as a differential diagnosis and magnetic resonance imaging should be considered for further evaluation.
 , Eun-Suk Cha
, Eun-Suk Cha , Jee Eun Lee
, Jee Eun Lee , Jeoung Hyun Kim
, Jeoung Hyun Kim , Bom Sahn Kim
, Bom Sahn Kim , Jin Chung
, Jin Chung
We aimed to compare the diagnostic performances of digital mammography (DM), digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), breast specific gamma imaging (BSGI) and/or positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for the detection of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
Index ILCs and multifocal/multicentric (multiple) ILCs were analyzed using various imaging modalities. The final surgical pathology was regarded as the reference standard. The detection rate for index cancers and the diagnostic performance for multiple ILCs per breast were evaluated.
Seventy-eight ILCs in 76 women were enrolled. Twenty-six breasts had multiple ILCs. DM (n=72), DBT (n=15), US (n=77), MRI (n=76), BSGI (n=50), and /or PET/CT (n=74) were performed. For index cancer, the detection rate was 100% for DBT, US, and MRI. For multiple ILCs, the sensitivity was 100% for DBT and MRI (P<0.001). The diagnostic accuracy for multiple ILCs were 73.3% for DBT and 73.0% for PET/CT (P=0.460).
DBT was the most accurate imaging modality for both index and multiple ILCs. PET/CT was also valuable for multiple ILCs, whereas DM and BSGI showed relatively low diagnostic performances. DBT and PET/CT have promising roles in the diagnosis of multiple ILCs.
Citations

 , Hyung Jun Park
, Hyung Jun Park , Kyoung-Gyu Choi
, Kyoung-Gyu Choi , Key Hwan Lim
, Key Hwan Lim , Kee Duk Park
, Kee Duk Park
Orbital metastases are rare and predominantly unilateral occurrences. Bilateral metastases affecting the extraocular muscles are extremely rare. A few case reports of bilateral metastases to extraocular muscles described binocular diplopia with conspicuous bilateral external ophthalmoplegia as an initial symptom. We report a case in which unilateral ptosis was an initial symptom and bilateral incomplete ophthalmoplegia was found on initial neurologic examination in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. The patient had hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, and so was treated by hormonal therapies and closely monitored. The presence of a secondary orbital lesion presents many difficulties of differential diagnosis and treatment. A thorough neurologic examination to detect ocular manifestations is most important for localization and broad differential diagnosis including mechanical orbital metastatic lesion.
Citations

 , Se Yong Gill
, Se Yong Gill , Haemin Jeong
, Haemin Jeong , Kyung-Chan Choi
, Kyung-Chan Choi , Junshik Hong
, Junshik Hong , Sang Min Park
, Sang Min Park
Pericardial drainage is an important diagnostic and therapeutic option in the symptomatic patient with large amount of pericardial effusion (PE). However, when the amount of PE is relatively small, physicians are often reluctant to perform the invasive drainage of the fluid due to the increased risk of causing myocardial injury during the procedure. Even in some cases of suspected pericarditis with small amount PE, an initial empirical anti-inflammatory therapy is often recommended. A 65-year-old woman presented with mild dyspnea for two weeks. The echocardiography revealed small amount of PE. A careful fluoroscopy-guided pericardiocentesis, subsequent pericardial fluid cytology, and thorough whole body check-up demonstrated adenocarcinoma with no proven primary site. After the palliative chemotherapy, she had survived for 15 months until her death due to asphyxia. Although pericardiocentesis is considered dangerous in small amount of PE, a prompt and careful drainage may provide early detection of hidden malignancy and better survival outcome.
 , Min Jeong Kim
, Min Jeong Kim , Seung Yon Baek
, Seung Yon Baek
To evaluate MRI findings of non-recurrent hepatocellular carcinomas with lipiodol uptake (LHCCs) treated with transarterial chemoembolization.
28 LHCCs were divided into two groups according to amount of lipiodol uptake and tumor size, retrospectively. According to amount of lipiodol uptake, HCCs were classified into group A with dense lipiodol uptake (more than 90%) and group B with partial lipiodol uptake (between 50% and 90%). For HCC size analysis, group I was defined by a longest diameter of less than 2 cm, and group II was defined by a longest diameter of greater than or equal to 2 cm.
In group A (n=16), eight LHCCs showed high signal intensity (SI) on T2-weighted images (T2WI), ten LHCCs showed low SI on T1-weighted imaged (T1WI), six LHCCs showed decreased SI at higher b value of diffusion-weighted images (DWI). In group B (n=12), six LHCCs revealed high SI on T2WI, six LHCCs revealed low SI on T1WI, ten LHCCs decreased SI at higher b value of DWI. As compared with tumor size and SI, six of 12 LHCCs in group I and eight of 16 LHCCs in group II showed high SI on T2WI. Six LHCCs in group I and ten LHCCs in group II showed low SI on T1WI. All LHCCs were not enhanced.
Signal intensities of LHCCs were variable, but more than half of LHCCs showed high SI on T2WI, low SI on T1WI, decreased SI at higher
Citations

 , Joo Ho Lee
, Joo Ho Lee , Yun Bin Lee
, Yun Bin Lee , Hana Park
, Hana Park , Seong Gyu Hwang
, Seong Gyu Hwang , Kyu Sung Rim
, Kyu Sung Rim
Acute clinical deterioration in patients with chronic liver disease is called acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF). Principles of management of ACLF consist of early identifying etiology of liver disease, rapid intervention of precipitating event and discreet intensive cares. Despite medical intensive cares, if liver failure progresses, liver transplantation could be the other option. Also, liver transplantation is the only treatment that offers a chance of cure for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the underlying liver cirrhosis simultaneously. Emergent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) can be performed for patients with acute liver failure and improves survival rate, especially in circumstances which liver graft is often not available because of deceased donors are not affordable. Here, we describe a chronic hepatitis B patient who developed ACLF accompanying early HCC. Because he did not improved with medical care, he received emergent LDLT. After LDLT, he showed great improvement without critical complications.
Citations

 , Seon Bin Yoon
, Seon Bin Yoon , Mi Ju Cheon
, Mi Ju Cheon , Young Min Koh
, Young Min Koh , Hyeon Sik Oh
, Hyeon Sik Oh , Se Joong Kim
, Se Joong Kim , Seung Hyeun Lee
, Seung Hyeun Lee
Pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is a rare form of lung cancer that originates from submucosal glands of tracheobronchial tree. Unlike low-grade tumor with benign nature, high-grade case is even rarer and has aggressive clinical features with no definite treatment option. Here, we report a case of high-grade pulmonary MEC with fulminant clinical course. A 74-year-old man presented with cough, sputum and mental change. Chest imaging showed massive mediastinal lymphadenopathy with obstructive pneumonia, and multiple metastases in lung and adrenal gland. Bronchoscopy showed polypoid masses obstructing right main bronchus and bronchus intermedius. Histopathology revealed a mixture of glandular structure lined with mucussecreting cells and nests of squamoid cells with nuclear atypia and pleomorphism, which is compatible with high-grade MEC. We intensively treated the patient with combination antibiotics and ventilator care. However, the patient did not respond to the treatment and rapidly deteriorated, and finally expired a month after diagnosis.
 , Sung Sook Kim
, Sung Sook Kim
The host immune system normally functions to destroy neoplastic cells that continually develop as a result of somatic mutations. However, patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma have depressed cell-mediated immune function, which has recently been shown to be most pronounced in the local and regional environment of the primary tumor. Recent studies suggest a local modulation of the host immune response to tumor by secreted immunoregulatory factors such as cytokines, especially pro-inflammatory cytokines(interleukin-1, interleukin-6, interleukin-8, interferons, and tumor necrosis factor).
To assessthe ability of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to produce these cytokines, initially, we have performed immunohistochemical staing for interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor in 20 cases of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and 10 cases of laryngeal nodule as a control group.
We detected interleukin-6 in 11 cases of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma(55%) and tumor necrosis factor in 11 cases of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma(55%). All of 10 papillomas showed no expression of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor. There is no statistical correlation between interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor expression and clinical stage or pathologic grade.
These results suggest that laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma may secrete cytokines influencing the response of local immune cells. But future studies of the role of tumorderived cytokines in the local immune response to tumor could be investigated,since cytokines may directly or indirectly regulate tumor growth and metastasis.

To compare fast spin echo(FSE) T2WI of the body coil(BC) with FSE T2WI of the endorectal surface coil(ERC) in the evaluation of parametrial and vaginal invasion and to evaluate tue dynamic enhanced images on the aspect of parametrial invasion.
Twenty consecutive patients of uterine cervical carcinomas confirmed by biopsy were included in this study and staging was determined by the surgery (2 cases) and the radiologic and clinical studies(18 cases). 1.5T Signa(GE,USA) was used and FSE T2-weighted axial and sagittal images were obtained by the body coil and endorectal surface coil respectively. Then dynamic enhanced axial images with FMPSPGR were performed at 2-3 slices of cervical cancer level. Parametrial and vaginal invasion on the body coil images were compared with those on the endorectal coil images retrospectively. Parametrial enhancement was evaluated on the dynamic enhanced images.
The accuracy of parametrial invasion was 100% of BC and 60% of ERC in 5 cases below stage Ib, 64% of BC and 73% of ERG in 11 cases of stage IIb and IIIa, 100% of BC and ERC in 4 cases above stage IVa. Overall accuracy of parametrial invasion was 80% of Bc and 75% of ERC without significant difference between two images. The accuracy of vagianl invasion was 80% of BC and 100% of ERC below stage Ib, 100% of BC and ERC above stage IIb. Overall accuracy of vaginal invasion was 95% of BC and 100% of ERC without difference between two images. On the dynamic enhanced images, parametrial enhancement was seen in all 20 cases and vascular enhancement in the parametrium was noted in 9 pf 20(45%) cases regardless of parametrial invasion.
There was no difference between BC and ERC images to evaluate the accuracy of parametrial and vaginal invasion. Therefore, ERC should be used in the cases which revealed suspicious invasion on BC images. Dynamic-enhanced images were not useful in the evaluation of parametrial invasion.

Various mechanisms are involved in drug resistance of tumor cells. Among them one such mechanism is the overexpression of the multidrug resistance(mdr1) gene product P-glycoprotein(Pgp) that functions as an energy - dependent drug efflux pump.
The expression of P-glycoprotein by immunohistochemistry was examined in 20 cases of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and vocal nodules as a control pump using a newly developed monoclonal antibody(MDR/JSB-1) which is specipic to human mdr1 gene product and recognizes an external epitope of the protein. Mdr1 gene product expression was compared with clinical response to chemotherapy in six patients who received mdr1 dependent drugs.
The results are summerized as follows.
1) Among 20 laryngeal cancer tissues, P-glycoprotein was detected in 8 patients and none of 20 vocal nodules showed expression of P-glycoprotein.
2) There is a correlation in between positive P-glycoprotein staining and tumor differentiation.
3) No correlation in between positive P-glycoprotein standing and tumor stage of tumor site is observed.
4) 2 patients with negative clinical response to chemotherapy among 6 patients who received inductive chemotherapy with cisplatin, vincristine and p pepleomycin revealed positive P-glycoprotein staining.
Therefore, analyzing the expression of P-glycoprotein may play a role when planning chemotherapeutic regimens for patients with head and neck cancer and may be an additional prognostic and diagnostic tools in these patients.
 , Soon Nam Lee
, Soon Nam Lee , Young Yo Park
, Young Yo Park , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Woon Sup Han
, Woon Sup Han
Choriocarcinonla is very rare malignancy, accounting for less than 1% of all testicular germcell tumor. However, it is an important disease in the field of oncology, as it represents ahighly curable malignancy. and one in which the incidence is focused on young patients attheir peak of productivity. In nonserninomatous germ cell testis tumor, assessment of prognosticfactors is related to develop a basis for more rational therapy for each individual patient.Along with prognostic staging, appropriate treatment shoud be applied to each patient to improve disease-free survival. And. surgical resection of residual masses after cisplatin-based chemotherapy is an established adjuvant to chemotherapy, because complete remission can be improvedabout 10% with appropriately timed complete resection of residual diseases. So, we reporta case of a 27-year old male patient with testicular choriocarcinoma who presented with multiplelung metastases after radical orchiectomy. He recieved lung wedge resection after 8 cycles ofcisplatin, etoposide, ifosfamide combination chemotherapy. and complete remission was confirmed and maintained.
 , Seung Ki Ryu
, Seung Ki Ryu , Seung Jung Kim
, Seung Jung Kim , Jun-Hyuk Choi
, Jun-Hyuk Choi , Soon Nam Lee
, Soon Nam Lee , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Woo Sup Han
, Woo Sup Han
Although the role of surgical management of metastatic disease from primary carcinoma of the coln and recutm is still controversial, resection of hepatic metastasis improves survival rate of patients with primary colorectal carcinoma treated locally. The lung is the most common site of extra-abdominal metastasis following resection of a prymary colorectal tumor and not amenable to curative therapy.
It is possible to resect the pulmonary metastasis in selected patients following resection of colorectal cancers, but the 5-year survival rates are ranged from 9% to 57%. Authors report a case of resection of pulmonary metastasis occured 3 years after resection of primary colon carcinoma.

Estrogen receptor-related protein was examined on gastrectomy specime from 16 cases of advaced gastric adenocarcinoma and 7 cases of early gastric carcinoma(EGC) by using peroxidase-anti-peroxidase method on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections. Positive reaction was seen in 7 out of 16 cases of advanced carcinoma and in 4 out of 8 cases of EGC(50%). Among advanced carcinoma, 3 cases of mucinous carcinoma were negative and 2 cases of signet ring cell carcinoma(SRC) showed focal positive reaction only in combined poorly differentiated(PD) area(10% of tumor cells). PD advanced carcinoma consisted of 4 cases of medullary type and 3 cases of individual cell type. Two out of 4 medullary type showed positive reaction in 20 and 80% of tumor cells and 2 out of 3 individual cell type showed positive reaction in 50 and 70% of tumor cells. Gland-forming type of advanced carcinoma consisted of 1 each case of intestinal and cardiac type and 1 mixed intestinal and cardiac type. Only 1 case of intestinal type showed positive reaction in 50% of tumor cells Among EGC, 2 cases of SRC were negative and 2 cases of PD carcinoma showed 5 and 10% positivity in PD area and 20 and 40% positivity in admixed gland-forming area. Gland-forming EGC consisted of 3 cased of intestinal type and 1 case of cardiac type. One case from each group showed positive reaction in 50 and 20% of tumor cells, respectively. In summary, positive reaction to antibody to estrogen receptor-related protein(P29) was expressed in PD(66.7%), gland-forming(50%), SRC, and mucinous type in order in both early and advanced carcinoma. The difference between age, sex, and other factors was not clear due to limitation of specimen.
 , Chung Nam Kang
, Chung Nam Kang , Jin Man Wang
, Jin Man Wang , Kwon Jae Roh
, Kwon Jae Roh , Chul Shin Kim
, Chul Shin Kim
Metastatic tumors of the spine often cause severe pain and paralysis because of deformity and neural encroachment. As oncology now extends the life expectancies of these patients, spinal decompression and stabilization are necessary.
2 patients who had vertebral metastases of hepatocarcinoma were operated on by decompressive corporectomy and firm stabilization. They had significant neural recovery and pain relief immediately.
Now, 2 cases are presented with a brief review of literatures.
 , Jeong Hee Hahm
, Jeong Hee Hahm , Hong Il Kook
, Hong Il Kook
We present herein a case of squamous cell carcinoma arising from leukoplakia developed in 1 51-year-old male. He has had a walnut sized whitish plaque with a central ulceration for one year. Histopathologic findings grade II of squamous cell carcinoma. Ten months after irradiation, he died.
 , Sun Seob Park
, Sun Seob Park , Eun Jeong Ko
, Eun Jeong Ko , Si Won Lee
, Si Won Lee , Mihong Choi
, Mihong Choi , Kiwon Kim
, Kiwon Kim
Small cell lung cancer is primarily treated with chemotherapy. For patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), systemic chemotherapy is often challenging since renal excretion of chemotherapeutic agents might be decreased due to impaired renal function, leading to increased toxicity. No consensus is made so far regarding appropriate dosage and combination of chemotherapeutic agents for patients on hemodialysis. We report two cases of chemotherapy without significant toxicity in small cell lung cancer patients who were on hemodialysis for ESRD.
 , Tae Yeob Kim
, Tae Yeob Kim , Joo Hyun Sohn
, Joo Hyun Sohn , Jae Keun Park
, Jae Keun Park , Seung Lee
, Seung Lee , Han Joon Kim
, Han Joon Kim , JuYeon Pyo
, JuYeon Pyo , Young-Ha Oh
, Young-Ha Oh
The major risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma include hepatitis B or C virus infection and alcohol consumption in Korea which lead to liver cirrhosis development and progression. However, prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related hepatocellular carcinoma is rising worldwide and hepatocellular carcinoma cases in patients with non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis are increasing. A hypoechoic nodule was incidentally detected in a 52-year-old woman, with no evidence of liver cirrhosis or specific hepatocellular carcinoma findings on radiological examination. Non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma was diagnosed based on clinical, laboratory, and histopathological findings of liver biopsy. To our knowledge, this is the first such case report in Korea.
 , Yehyun Park
, Yehyun Park , Hye Jung Park
, Hye Jung Park , Ah-young Ji
, Ah-young Ji , Changho Song
, Changho Song , Moo-Nyun Jin
, Moo-Nyun Jin , Young Ju Kim
, Young Ju Kim , Sun Wook Kim
, Sun Wook Kim , Jung-Hee Lee
, Jung-Hee Lee , In-Soo Kim
, In-Soo Kim , Hye Ryun Kim
, Hye Ryun Kim , Joohang Kim
, Joohang Kim , Byoung Chul Cho
, Byoung Chul Cho
The rearrangement of c-ros oncogene 1 (
 , Jae Y. Ro
, Jae Y. Ro
The incidence of renal cell neoplasms has been increased in worldwide as well as in Korea. Even though the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of renal tumors (2004) is currently used, new entities require to be added in the updated classification because of recent modification with our understanding of the molecular biology and different clinical behavior of new renal tumors. In this review, recently described tumors and candidate entities will be discussed. It is of importance to know these new entities for the proper diagnosis, treatment, and their prognosis.
 , Jeong-Mi Lee
, Jeong-Mi Lee , Ja Yoon Choi
, Ja Yoon Choi , Dong-Hoon Lew
, Dong-Hoon Lew , Ra Ri Cha
, Ra Ri Cha , Hye Won Oh
, Hye Won Oh , Hong-Jun Kim
, Hong-Jun Kim , Hyun Ju Min
, Hyun Ju Min , Hyun Jin Kim
, Hyun Jin Kim , Woon-Tae Jung
, Woon-Tae Jung , Ok-Jae Lee
, Ok-Jae Lee , Chang Yoon Ha
, Chang Yoon Ha , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) has become an effective alternative treatment strategy for patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Although TACE is relatively safe, acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pulmonary lipiodol embolism is a rare and potentially fatal complication. We report a rare case of acute respiratory distress syndrome after TACE for inoperable HCC. A 75-year-old man, with huge HCC in right lobe, was treated by TACE for the first time. Seven hours after uneventful TACE procedure, he felt dyspneic and his oxygen saturation recorded by pulse oximetry (SpO2) fell to 80% despite of applying non-rebreathing mask. He underwent mechanical ventilation with a protective ventilatory strategy. We experienced a case of acute respiratory distress syndrome after TACE for HCC.
 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Min-Sun Cho
, Min-Sun Cho , Min-Jin Lee
, Min-Jin Lee , Myung-Eun Song
, Myung-Eun Song , Da-Yeon Oh
, Da-Yeon Oh , Ha Eung Song
, Ha Eung Song
Sunitinib an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, is highly effective against renal cell carcinoma and is now widely used in patients with metastatic disease. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is rarely reported as a side effect of sunitinib. We report two cases of GERD with upper gastrointestinal bleeding related to sunitinib administration. Both cases responded well to conservative management. Microscopic findings in both cases showed cellular atypia such as hyperchromasia, increases in nuclear size, and multinucleation. The cellular atypia of the squamous mucosa appears to be associated with reparative processes.
Citations

 , Dae Ho Kim
, Dae Ho Kim , Hyun A Yun
, Hyun A Yun , Hwa Young Seok
, Hwa Young Seok , Seong Hun Hong
, Seong Hun Hong , Sang Wan Jung
, Sang Wan Jung , Jae Myung Cha
, Jae Myung Cha , Joung Il Lee
, Joung Il Lee , Kwang Ro Joo
, Kwang Ro Joo , Hyun Phil Shin
, Hyun Phil Shin , Jae Jun Park
, Jae Jun Park , Jung Won Jeoun
, Jung Won Jeoun
Surgery is the primary treatment for adenocarcinoma originating from the esophagogastric junction. However, many physicians attempt various endoscopic treatments for the cases of early adenocarcinoma and high-grade dysplasia of esophagogastric junction in order to avoid the high risk of complications associated with surgical resection. Recently, there is an increasing tendency to use endoscopic mucosal resection for the management of early esophageal cancer due to low morbidity and mortality rates. We report here on a case of early adenocarcinoma at esophagogastric junction successfully treated with endoscopic mucosal resection.
 , Yoo-Ri Kim
, Yoo-Ri Kim , Hyun-Mi Heo
, Hyun-Mi Heo , Suh-Eun Bae
, Suh-Eun Bae , Myung-Won Lee
, Myung-Won Lee , Yun-Jung Choi
, Yun-Jung Choi , Go-Heun Kim
, Go-Heun Kim , Tae-Hun Kim
, Tae-Hun Kim , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo , Il-Hwan Moon
, Il-Hwan Moon
Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)is one of common causes of cancer-related death in Korea where the majority of HCC patients were Hepaitc B virus(HBV)carriers and have cirrhosis. Transarterial chemoembolization(TACE)is commonly applied to the treatment of multinodular HCC in Korea and careful selection of candidate is important for the risk of various side effects. Besides common side effects as fever, nausea, abdominal pain and elevation of liver enzyme, TACE may predispose to hepatic failure, ischemic cholecystitis, pulmonary embolism, cerebral embolism and pneumonitis. In previous studies, some cases of pulmonary and cerebral embolism cases were reported but lipiodol pneumonitis after TACE was rarely reported. A 65-year-old woman with a multinodular HCC associated with HBV infection, was treated with TACE. Seven days after the procedure, nonspecific respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea and dry cough developed. Chest X-ray and chest computed tomography showed diffuse ground glass opacities in whole lung fields, suggestive of lipiodol pneumonitis. After several days of supportive care with steroid administration, radiologic abnormalities and subjective symptoms were much improved, considered that the disease was compatible with lipiodol pneumonitis.
Citations

 , Jae Jung Park
, Jae Jung Park , Il Hwan Moon
, Il Hwan Moon , Seo Woo Kim
, Seo Woo Kim , Hyun Kyung Kim
, Hyun Kyung Kim , Hyun Jung Oh
, Hyun Jung Oh , Go Heun Kim
, Go Heun Kim , Yoon Jung Choi
, Yoon Jung Choi , Hyun Mi Huh
, Hyun Mi Huh , Young Wook Roh
, Young Wook Roh , Tae Hun Kim
, Tae Hun Kim , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo , Ji Yoon Bae
, Ji Yoon Bae , Dong Eun Song
, Dong Eun Song
Mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma accounts for about 1% of all hepatocellular carcinoma. In many cases, mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma has been misdiagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma because of the indistinctive clinical course and radiologic findings. The clinical course and the pathologic characters are not known well, but it resembles the characteristics of hepatocellularcarcinoma rather than cholangiocarcinoma. So mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma was classified as a kind of hepatocellular carcinoma. But the growth and dissemination rate is faster than that of hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognosis more poor. So the exact diagnosis is important. Authors experienced a patient who has the mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma diagnosed by liver and neck node biopsy in patient who complain-ed abdominal discomfort and palpable mass, so we report the case.
Citations

 , So Ra Kang
, So Ra Kang
Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma of the eyelid is an adenocarcinoma of the eccrine glands. These tumor is a rare ocular adnexal neoplasm that has a predilection for the periorbital and scalp region. It is more common in men and occur primarily in 50-70 year-old age range. We present the occurrence, clinical and histological features, and management of this tumour in a old male, who could exclude the presence of primary mucinous carcinoma elsewhere by extensive systemic evaluation.
A 67-year-old male presented with a small nodular erythematous nontender left lower lid lesion, which had increased in size and pigmentation over four years. Pneumoconiosis was noted on preoperative chest CT, but it was correlated with his occupational history. Lymphatic involvement was not noted on physical examination. So he underwent wide local excision with frozen section control of the margins. Clear margin were achieved and the defect was repaired with a local rotation flap.
Histologic examination showed mucinous carcinoma of the eccrine glands. A whole body screening test(PET) was performed to excluded the presence of primary mucinous carcinoma elsewhere metastating to the eyelid, or any distant spread from the eyelid lesion. PET demonstrated mildly increased hypermetabolism in both lungs and hypermetabolic lymph nodes at both supraclavicular areas and mediastinum. But extensive systemic workup, including abdominal ultrasonography, upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscope, neck CT, and lung biopsyrevealed no other abnormal lesion. Immunohistochemical markers including CEA, S-100, CK-PAN, CK7, CK-20, TTF-l were also helpful in establishing the diagnosis of the primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma of the skin. There has been no recurrence of tumor 2 months following excision.
 , Tae Hun Kim
, Tae Hun Kim , Kum Hei Ryu
, Kum Hei Ryu , So Yeon Lim
, So Yeon Lim , Ju Ho Lee
, Ju Ho Lee , Shi Nae Lee
, Shi Nae Lee
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma was described by Ishikura in 1985 for the first time. It is a very rare variant of adenocarcinoma characterized by morphological and functional features of hepatocyte differentiation. It is most commonly presented as gastric adenocarcinoma with otherwise unexplained elevation of serum alpha-fetoprotein level. Most of the patients with gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma were diagnosed in advanced stages having vascular invasion and/or extensive metastasis in liver or lymph nodes. Accordingly, the prognosis of hepatoid adenocarcinoma is dismal. We experienced a typical case of gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma and described the clinical features.
The role of Helicobacter pylori(HP) in benign and malignant pancreatico-biliary tract disease is concerned in recent papers. The urease gene of Hp were found in human bile, and bacteria morphologically resembling Hp were found in resected gallbladder mucosa from patients with gallbladder disease. It was hypothesized that there is an association between the presence of Hp in bile and pancreatico-biliary disease. The aims of this study are to examine if Hp exist in the bile juice and to investigate whether Hp plays a role in the pancreatico-biliary disease.
Thirty-eight patients (18 males and 20 females, mean age 71 ?27yr ; range 45-92yr) with gallstone and malignant pancreatico-biliary disease were enrolled in this study ; 23 cases were gallstone diseases, 10 cases were cholangiocarcinomas, and 5 cases were pancreatic cancers. Thirty-eight controls were age- and sex-matched and enrolled from subject attending routine medical check-up. The presence of Hp in stomach was confirmed by ?4C-breath test. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay was used to detect the Hp in bile.
The Hp-positive rate in stomach was much higher in control (26/38,68.4%) than the patients with pancreatico-biliary disease(l1/38, 28.9%) (p<0.01). The Hp-positive rate in bile of pancreatico-biliary disease was 18.4% but, there is no relation between of the presence of Hp in the stomach and in the bile (p=0.33). Also there was no significant difference of the presence of Hp in bile (p>0.05) and stomach (p=0.28) between benign and malignant disease.
The Hp-positive rate in bile was similar in benign and malignant pancreatico-biliary disease. But Hp may not be important risk factor in pancreatico-biliary disease in Hp-prevatent country like south Korea.
 , Jae Hun Kim
, Jae Hun Kim , Sung Jae Park
, Sung Jae Park , Dong Won Byun
, Dong Won Byun , Duk Hee Kang
, Duk Hee Kang , Bong Suk Shim
, Bong Suk Shim
Renal cell carcinoma can presents wide range of signs and symptoms, and commonly associated with paraneoplastic syndrome. Paraneoplastic manifestations are present in up to 20% of patients with renal cell carcinoma. There is convincing evidence that renal cell carcinoma tumor cells elaborate proteins that serve as mediators of endocrine (ex ; ectopic production of parathyroid hormone-related protein or erythropoietin) as well as nonendocrine paraneoplastic syndromes. A paraneoplastic syndrome may be the various clinical presentation of renal cell carcinoma in a significant number of patients, therefore mimicked other general disease. We report a case of renal cell carcinoma associated with paraneoplastic syndrome mimicking pyelonephritis.
 , Doe-Young Kim
, Doe-Young Kim , Hye-Kyoung Jung
, Hye-Kyoung Jung , Seung-Hyun Nam
, Seung-Hyun Nam , Il-Hwan Moon
, Il-Hwan Moon , Hea-Soo Koo
, Hea-Soo Koo
Nowadays increasing use of abdominal ultrasound in routine check-up may increase the detection rate asymtomatic cystic lesions of pancreas. Even through the majority of the cystic lesions of pancreas is pseudocyst, about 10-15% of those lesions are caused by pancreatic cystic tumor. In the pancreatic cystic tumor, especially, mucinous cystic tumor should be exicised due to its malignant potential, while the pancreatic pseudocyst or serous cystic tumon can be observed for a period or treated medically. Several clinical, radiological, biochemical and pathologic guidelines have been developed in order to distinguish among them. Among pancreatic cystic tumors, mucinous cystic adenocarcinoma is very rare and accounts for only 1% of all pancreatic neoplasms. Unlike extremely poor prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, mucinous cystic adenocarcinoma has an indolent course and shows a good prognosis after its curative resection. Recently we experienced a 69-year-old woman who had a mucinous cystic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. We report this case with a review of literature.
 , Chun Dong Kim
, Chun Dong Kim
To establish new
Four SCCHN cell lines were used for MTS and raft culture.
All cell lines formed MTS, but only Tu-138 showed a good stratification at the airliquid interface in the raft culture system.
MTS and raft culture system were established successfully from the SCCHN cell lines.
 , Byung Chul Kang
, Byung Chul Kang , Jung Soo Suh
, Jung Soo Suh , Eung Bum Park
, Eung Bum Park , Kang Sup Shim
, Kang Sup Shim
We studied to determine the usefulness of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) in the preoperative evaluation of invasion of colorectal cancer and to compare its usefulness with the conventional CT. To observe the enhancement pattern of colorectal wall after iv administration of Gd-DTPA between normal and cancerous wall.
Twenty patients with colon cancer and 8 patients with rectosigmoid cancer, who were diagnosed between October 1997 and June 1998 by barium enema, colonoscopic biopsy were evaluated. The patients population consisted of 16 men and 12 women, with ages ranging from 46 to 68 years(mean 61years). Preoperative staging was done by conventional CT and dynamic MRI. All MR images were performed with 1.5T superconducting magneting unit(Vision, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). 2D-FLASH(Fast Low-Angle Shot) sequence was used for the dynamic and delayed images(TR/TE/NEX/FA=72.5-117.3/4.1/1/80°), and acquisition time of 13-15sec.
For the dynamic images, five MR images were obtained with a single breath hold. Precontrast images(axial, or sagittal or coronal) was obtained first, and then dynamic MR images were obtained at 30, 60, 90, 120sec after intravenous injection of 0.1mmol/kg Gd-DTPA. Ten to fifteen delayed images were also obtained with the interval of 4-5 minutes with a single breath hold. Preoperative staging of CT and MRI were decided with a consensus by two radiologists. Pathologic staging were done by TNM classification.
The dynamic MR image-determined stage of colorectal cancer correlated with histopathologic findings in 2 of 3 pT2 tumor(67%), 19 of 21 pT3(90%), and 4 of 4 pT4 tumors(100%). MRI correctily diagnosed tumor deposits of involved lymph nodes in 16 patients, overall accuracy was 57%(16/28%). And the signal intensities after IV Gd-DTPA administration between the cancerous wall and normal wall ws not significantly different at the 30, 60, and 90 seconds MR images with the indifferent Student
Dynamic MRI has a role for the preoperative assesment of colorectal carcinoma.
 , Sun Hee Sung
, Sun Hee Sung , Hea Soo Koo
, Hea Soo Koo , Woon Sup Han
, Woon Sup Han , Ok Kyong Kim
, Ok Kyong Kim
Gastric polyp is histologically very diverse and its classification is still unsettled. The purpose of the article is to classify the endoscopically diagnosed polypoid lesions and to evaluate their malignant potential.
A retrospective study was done on 142 cases of endoscopically diagnosed gastric polypoid lesions from September 1993 to May 1996. We investigated their clinical findings, histopathology, and nuclear gradings of PCNA by immunohistochemistry.
1) The mean age is 57.9 and sex ratio os 0.8:1
2) The most prevalent location is antrum(57.7%).
3) Morphologically, Yamada type II is the most frequent(35.9%).
4) Histologically, lesions are classified as true polyps and reactive lesions. True polyps are subclassified as hyperplastic polyp(61.2%), adenomatous polyp(19.4%), mixed adenomatous and hyperplastic polyp(10.2%), fundic gland polyp(2.0%), and adenocarcinoma(7.1%). Reactive lesions are subclassified as chronic superficial gastritis(68.2%), mucosal hyperplasia(15.9%), edema of lamina propria(9.1%), xanthoma(4.5%), and ectopic pancreas(2.3%).
5) Atypical changes is accompanied in 12 cases(20%) of hyperplastic polyps.
6) Adenocarcinoma arising from adenomatous polyp is noted in 6 cases. In hyperplastic polyp one case is combined with adenocarcinoma.
7) Among the true polyps single lesions are 127 cases(89.4%), and multiple lesions, 15 cases(10.6%)
8) Immunohistochemical staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen(PCNA) reveals that hyperplastic polyps show focal positive rection in the area of pit and fundus, and adenomatous polyps show diffuse positive reaction. Dysplastic foci in both adenomatous and hyperplastic polyps shows diffuse positive reaction of PCNA.
Endoscopically diagnosed polypoid lesions show variable histologic findings ranging from chronic superficial gastritis to adenocarcinoma. They are mainly subclassified as histologically true polyps and reactive lesions. Some of true polyps have atypical changes of varing dgree in not only adenomatous polyps but also hyperplastic polyps.

Endometrial hyperplasia(EH) and endometrial carcinoma(EC) very in their biologic potential, which may be correlated with the histologic grade. Evaluation of cellular kinetics, which may prove to be another measure of predicting biologic behavior. Accessments of AgNORs and PCNA(proliferative cell nuclear antigen) indeces in 33 cases of EH including 16 cases of simple hyperplasia(SH), 8 of complex hyperplasia(CH), and 9 of atypical hyperplasia(AH), and 28 of EC including 7 of grade I, 12 of grade II, and 6 of grade III were performed. The results were as follows :I, 12 of grade II, and 6 of grade III were performed. The results were as follows : 1. AgNOR counts per glandular cells(Mean SD) were 2.7±0.2 in normal proliferative and 2.3±0.2 in secretory endometrium, and increased to 3.2±0.3 in SH, 3.5±0.3 in CH, to 5.4±0.4 in AH, and finally 6.9±0.5 in endometrioid carcinoma(grade I: 5.8±0.7, grade II: 6.7±0.6, grade III: 8.4±0.9). 2. PCNA indeces(percentages of nuclear positive cells of total cells of glands) were 16±14.2 in normal proliferative endometrium and 12±8.1 in secretory endometrium, and increased to 18.4±14.7 in SH, 21.6±17.8 in CH, 36.4±27.4 in AH, and finally 42.1±31.3 in EC(grade I: 38.3±23.2,grade II: 39.4±25.4, and grade III: 58.4±35.3). 3. DNA aneuploidy was detected in 4 cases of EC(40%), and tended to be more frequently found in poorer histologic grade. This data suggest that cell kinetic evaluation of EH and EC using AgNORs and PCNA is well correlated with histologic grade. And with the aspect of biologic potential, AH could be regarded as well differentiated EC.

