 , Jitendra Singh Nigam
, Jitendra Singh Nigam , Immanuel Pradeep
, Immanuel Pradeep , Ashutosh Rath
, Ashutosh Rath , Seetu Palo
, Seetu Palo , Naina Kumar
, Naina Kumar
 , Seungpil Jeong
, Seungpil Jeong , Eunhee Ha
, Eunhee Ha
Shoulder pain is a common complaint in primary care settings. The prevalence of shoulder pain is on the rise, especially in societies with aging populations. Like other joint-related conditions, shoulder pain is predominantly caused by degenerative diseases. These degenerative changes typically affect bones, tendons, and cartilage, with common conditions including degenerative rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Diagnosing these degenerative diseases in older adults requires a thorough understanding of basic anatomy, general physical examination techniques, and specific diagnostic tests. This review aims to outline the fundamental physical examination methods for diagnosing shoulder pain in older adult patients in primary care. The shoulder's complex anatomy and its broad range of motion underscore the need for a systematic approach to evaluation. Routine inspection and palpation can identify signs such as muscle atrophy, bony protrusions, or indications of degenerative changes. Assessing range of motion, and distinguishing between active and passive deficits, is crucial for differentiating conditions like frozen shoulder from rotator cuff tears. Targeted strength tests, such as the empty can, external rotation lag, liftoff, and belly press tests, are instrumental in isolating specific rotator cuff muscles. Additionally, impingement tests, including Neer’s and Hawkins’ signs, are useful for detecting subacromial impingement. A comprehensive understanding of shoulder anatomy and a systematic physical examination are vital for accurately diagnosing shoulder pain in older adults. When properly executed and interpreted in the clinical context, these maneuvers help differentiate between various conditions, ranging from degenerative changes to rotator cuff pathology.
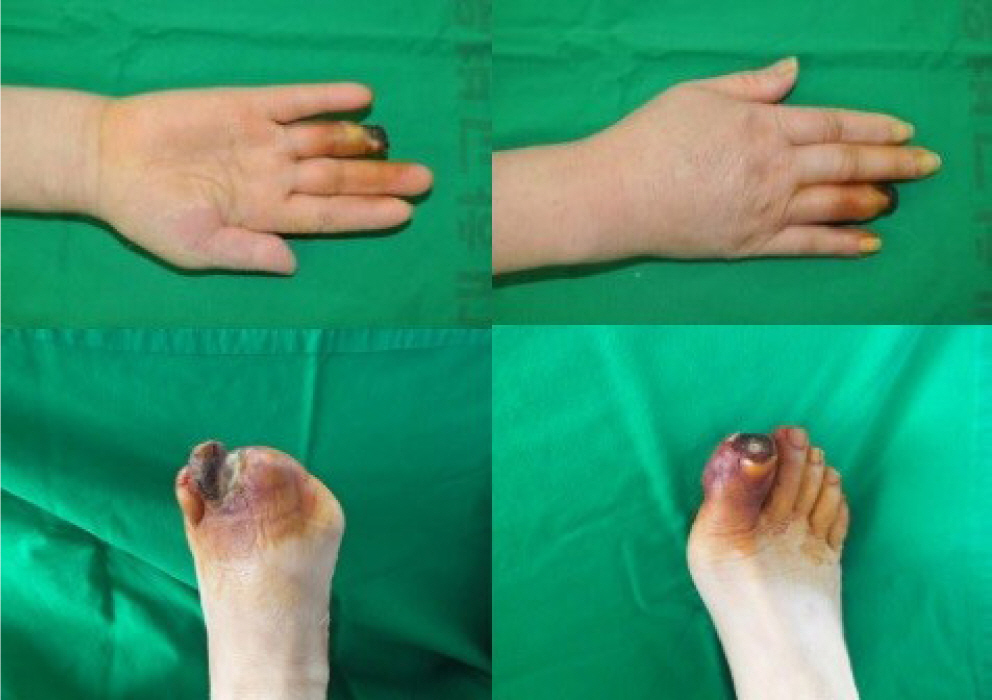
Symmetrical peripheral gangrene is a severe condition marked by symmetric acral necrosis without obstruction of the major blood vessels. This case report examines the critical decisions involved in choosing between early and delayed amputation, as well as determining the extent of the necessary amputation. We present three cases: one involving antiphospholipid syndrome, another with disseminated intravascular coagulation, and a third associated with diabetes mellitus. All three cases ultimately required amputation due to symmetrical peripheral gangrene. In the first two cases, amputation was delayed, which is typically advantageous as it allows for the clear demarcation of necrotic tissue. However, in the third case, where infection was evident, immediate amputation was necessary despite the patient's overall poor health.
 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the parasite
Citations

 , Kye Hwa Lee
, Kye Hwa Lee
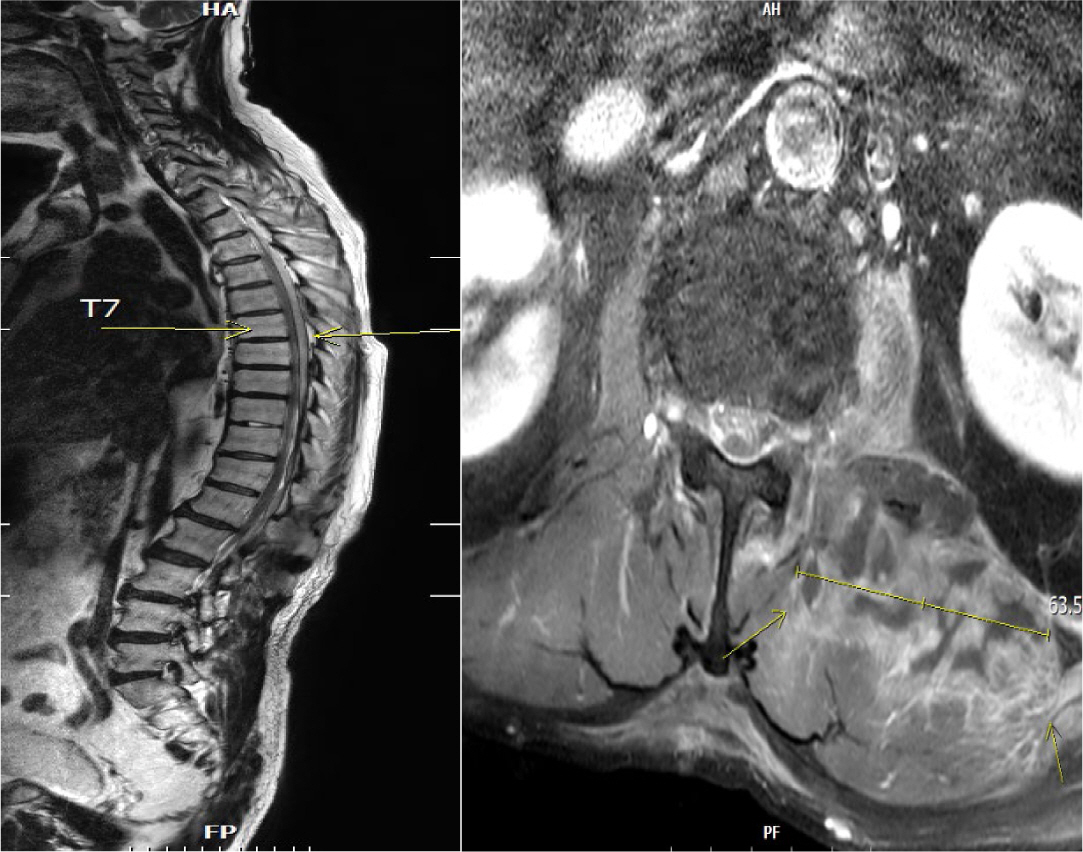

Septic embolism and stroke are serious complications in patients with sepsis and often necessitate urgent surgical intervention to control the source of infection. A 69-year-old man presented with severe pain in his back and left thigh. MRI revealed extensive posterior epidural or subdural abscesses extending from the cervical to the lumbar level, as well as an abscess in the iliopsoas muscle. The patient underwent urgent drainage of the abscesses and decompression of the lumbar spine. Postoperatively, he developed sudden-onset atrial fibrillation and altered mental status. Brain CT showed multiple embolic infarctions. His condition deteriorated due to persistent infection, leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute kidney injury, and septic shock. This case highlights the risk of cerebral embolism and hemorrhagic complications in patients with sepsis who undergo surgery. Early recognition of individuals at high risk and comprehensive perioperative management are critical to reducing the likelihood of such complications.

Infectious spondylitis, an infection of the vertebral body, intervertebral disc,
or paraspinal tissues, poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. This review
examines the clinical approach and management of infectious spondylitis in
Korea. The incidence of pyogenic spondylitis has increased, primarily due to the
aging population, more frequent use of invasive procedures, and higher
prevalence of immunocompromising conditions. Conversely, tuberculous spondylitis
has declined, reflecting shifts in population demographics and medical
practices.
Citations


Influenza presents a considerable disease burden, particularly among adults over 65 years old. In this population, the disease is associated with high rates of infection, hospitalization, and mortality. The objective of this study was to assess the impact of influenza on older adults and to evaluate the effectiveness of influenza vaccines within this demographic. A literature search was conducted using PubMed to identify relevant English-language studies published from January 2000 to January 2024. The analysis indicated that influenza-related hospitalization rates (ranging from 10.1 to 308.3 per 100,000 persons) and all-cause excess mortality rates (1.1 to 228.2 per 100,000 persons) were notably high in older adults, although these rates varied over time and by location. Hospitalization rates due to influenza increased considerably after the age of 50 years, with the highest rates observed in individuals aged 85 years and older. Excess mortality attributable to influenza also rose with age, with rates between 17.9 and 223.5 per 100,000 persons in those over 75 years old. The effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing severe infections requiring hospitalization was found to be only 37% in individuals aged 65 years and older. The unadjuvanted, standard-dose influenza vaccine had an estimated effectiveness of just 25% against laboratory-confirmed influenza and between 37% and 43.7% in preventing hospitalizations. Therefore, considering the substantial burden of influenza and the limited efficacy of standard vaccines, the use of highly immunogenic influenza vaccines should be prioritized for older adults.
Citations

 , Sooyoung Huh
, Sooyoung Huh , Haesook Seo
, Haesook Seo
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the first seasonal influenza epidemic was declared in the 37th week of 2022 in Korea and has continued through the winter of 2023–2024. However, this finding has not been observed in the United States and Europe. The present study aimed to determine whether the prolonged influenza epidemic in Korea from 2022 to 2023 was caused by using a different influenza epidemic threshold compared to the thresholds used in the United States and Europe.
Korea, the United States, and Europe use different methods to set seasonal influenza epidemic thresholds. First, we calculated the influenza epidemic thresholds for influenza seasons using the different methods of those three regions. Using these epidemic thresholds, we then compared the duration of influenza epidemics for the most recent three influenza seasons.
The epidemic thresholds estimated by the Korean method were lower than those by the other methods, and the epidemic periods defined using the Korean threshold were estimated to be longer than those defined by the other regions’ thresholds.
A low influenza epidemic threshold may have contributed to the prolonged influenza epidemic in Korea, which was declared in 2022 and has continued until late 2023. A more reliable epidemic threshold for seasonal influenza surveillance needs to be established in Korea.
Citations

 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Dong Chan Joo
, Dong Chan Joo , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Kyung Bin Kim
, Kyung Bin Kim
We report a rare case of gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation (GAED) that was treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection followed by additional distal gastrectomy with lymph node dissection. A 67-year-old man underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection for a gastric lesion, which was diagnosed as GAED with submucosal and lymphatic invasion. Histologically, GAED is characterized by a tubulopapillary growth pattern and clear cells that resemble those of the primitive fetal gut. Immunohistochemically, GAED variably expresses oncofetal proteins such as glypican-3, alpha-fetoprotein, and spalt-like transcription factor 4. Despite negative margins, additional gastrectomy with lymph node dissection was performed due to submucosal and lymphatic invasion. No residual tumor or metastasis was detected, and the patient remained disease-free for 2 years before dying from causes unrelated to GAED. Given its aggressive nature, frequent lymphovascular invasion, and high metastatic potential, clinicians should recognize the histopathological diagnosis of this rare tumor and its propensity for aggressiveness.

This study analyzed drug-induced death statistics in Korea between 2011 and 2021.
Cause-of-death statistics data from Statistics Korea were examined based on the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision.
In 2021, there were 559 drug-induced deaths, marking a 172.7% increase compared to 2011, which recorded 205 deaths. The rate of drug-induced deaths per 100,000 people was 1.1 in 2021, up 153.6% from 0.4 in 2011. The mortality rate for men aged 25−34 years and women aged 35−44 years each increased fourfold from 2011 to 2021: from 0.3 to 1.2 for the former and 0.3 to 1.3 for the latter. Of the drug-induced deaths in 2021, 75.0% (419/559) were due to intentional self-harm, and 10.4% (58/559) were accidental. The number of deaths attributed to medical narcotics in 2021 was 169, a 5.5-fold increase from 2011. The most commonly implicated drugs in these deaths were sedative-hypnotic drugs, benzodiazepines, and opioids. Sedative-hypnotic drugs and benzodiazepines were frequently involved in cases of intentional self-harm, while opioids and psychostimulants were more often associated with accidental deaths.
The death rate from drug-induced causes is considerably lower in Korea than in the United States (1.1 vs. 29.2). However, the number of such deaths has increased recently. Since these deaths occur predominantly among younger age groups and are often the result of intentional self-harm, there is a clear need for systematic management and the implementation of targeted policies.
Citations

 , In-Young Yoon
, In-Young Yoon , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Sooyoung Cho
, Sooyoung Cho
OxyMask, a novel product, has recently been used to administer oxygen postoperatively to patients who have undergone general anesthesia. This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of hypoxia in patients under general anesthesia upon arrival to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) using arterial blood gas analysis, and to compare the effectiveness of OxyMask with a non-rebreathing oxygen mask for oxygen administration.
We retrospectively investigated anesthesia-related data from the electronic medical records of 460 patients treated from April to November 2021. We analyzed patients aged 20 years or older who had undergone general anesthesia and whose perioperative arterial blood gas analysis results were available upon arrival to the PACU. These patients were grouped into the non-rebreathing oxygen mask (n=223) and OxyMask (n=237) groups, and statistical analysis was performed utilizing their anesthesia records.
No patients exhibited hypoxia upon arrival to the recovery room. The oxygen concentration increased after oxygen administration; its concentration during the recovery room period (Δ2 PaO2) was 10.7±42.3 and 13.9±38.5 mmHg in the non-rebreathing oxygen mask and OxyMask groups, respectively. This difference was not statistically significant. Moreover, the arterial oxygen saturation between the end of surgery and upon arrival to the PACU (Δ1 SaO2) and the arterial oxygen saturation 20 minutes after oxygen administration at the PACU (Δ2 SaO2) did not significantly differ between the groups.
OxyMask was not superior to a non-rebreathing oxygen mask in terms of the effectiveness of oxygen supply.
 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Cheolung Kim
, Cheolung Kim
Subepithelial tumors in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract are often detected during nationwide endoscopic gastric cancer screening in Korea. Most GI lipomas are asymptomatic and do not necessitate further treatment. However, large tumors may lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, intussusception, and bleeding. These GI lipomas require endoscopic or surgical resection. On radiological examination, GI lipomas typically manifest as hypodense lesions with similar density to that of fat tissue. White-light endoscopy generally reveals a yellowish subepithelial tumor exhibiting a positive cushion sign, while endoscopic ultrasonography shows a homogeneous hypoechoic mass within the third layer of the GI tract. We present the case of an 81-year-old woman with symptomatic duodenal lipoma following endoscopic resection.
 , Hyeonuk Hwang
, Hyeonuk Hwang , Hyungju Kwon
, Hyungju Kwon
Conventional open thyroidectomy is a safe procedure, but it has the disadvantage of leaving noticeable scars on the neck. Bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA) robotic thyroidectomy was developed as an alternative technique to remove thyroid glands without making incisions in the neck. In traditional BABA robotic thyroidectomy, dividing the isthmus is a routine step to improve the efficiency of the dissection during thyroid surgery. However, there are safety concerns when performing this procedure on patients with thyroid cancer located in the isthmus. We report a case of BABA robotic total thyroidectomy carried out without dividing the isthmus in a patient with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma. Our experience suggests that BABA robotic surgery can be a feasible and safe option for selected patients with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma.

The primary objective in the treatment of early rectal cancer is to achieve optimal oncological control while minimizing the long-term impact of therapeutic interventions on patients' quality of life. The current standard of care for most stage I and II rectal cancers involves radical surgery, specifically total mesorectal excision. Although total mesorectal excision is generally curative for early rectal cancers, it can significantly affect patients' quality of life by potentially necessitating a permanent colostomy and causing bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction. Given the morbidity associated with radical surgery, alternative approaches to managing early rectal cancer, such as local excision through transanal excision, transanal endoscopic microsurgery, and transanal minimally invasive surgery, have been investigated. If these surgical approaches are applied cautiously to carefully selected cases of early rectal cancer, it is anticipated that these local procedures will achieve comparable oncological outcomes to the established standard of radical surgery, potentially offering superior results regarding morbidity, mortality, and overall quality of life.
 , Dong Chan Joo
, Dong Chan Joo , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Kyungbin Kim
, Kyungbin Kim
Esophageal subepithelial tumors (SETs) are commonly encountered during screening endoscopy, and leiomyomas are the most common SET of the esophagus. Almost all patients with esophageal leiomyomas are asymptomatic; however, some present with dysphagia, depending on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it encroaches on the lumen. The typical endosonographic features of esophageal leiomyomas include well-demarcated, homogeneously hypoechoic lesions with echogenicity similar to that of the surrounding proper muscle layer, but without cystic changes. Histopathologically, esophageal leiomyomas do not undergo cystic or myxoid degeneration. This report presents a case involving a 65-year-old man with a symptomatic esophageal SET and endosonographic features indicative of malignant neoplasms, who was diagnosed with esophageal leiomyoma with cystic and myxoid degeneration following surgical resection.
Citations

 , Mina Kang
, Mina Kang , Young Min Hur
, Young Min Hur , Young Ju Kim
, Young Ju Kim , Sunwha Park
, Sunwha Park
Ectopic pregnancy (EP) refers to blastocyst implantation outside the uterine endometrium. EP is major cause of maternal morbidity and mortality. Treatment options include surgery, medical therapy with methotrexate, or expectant management. Methotrexate is the primary regimen used in cases of early, unruptured ectopic pregnancies. Most side effects of methotrexate are minor, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and photosensitive skin reaction. Serious side effects, including bone marrow suppression, and pulmonary fibrosis, are invariably observed when methotrexate is administered in high doses with frequent dosing intervals, in chemotherapeutic protocols for malignancy. These side effects are uncommon with the doses used to treat ectopic pregnancies. Since cases of methotrexate-induced pancreatitis are rare, we report a case of pancreatitis in a patient with EP treated with methotrexate and expect to consider pancreatitis as a side effect of methotrexate in a patient with upper abdominal pain undergoing methotrexate chemotherapy.
Citations

 , Ji Su Chung
, Ji Su Chung , Yeo-Jin Lee
, Yeo-Jin Lee , Seonwoo Lee
, Seonwoo Lee , Juhyun Jeong
, Juhyun Jeong , Min-Kyung So
, Min-Kyung So , Miae Lee
, Miae Lee
The Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device (Panbio COVID-19 Ag, Abbott Rapid Diagnostics) is a lateral flow immunochromatographic assay targeting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleoprotein in nasopharyngeal specimens for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to verify the performance of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag for implementation in clinical laboratories.
Sixty nasopharyngeal swab specimens (30 positive and 30 negative) dipped in transport medium, and COVID-19 was confirmed using real-time RT-PCR using Allplex SARS-CoV-2 assay (Seegene), were tested using the Panbio COVID-19 Ag. Reproducibility was evaluated using positive and negative control materials. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated based on the results of real-time RT-PCR as the standard test method.
Reproducibility was confirmed by the consistent results of repeated tests of the quality control materials. The overall sensitivity and specificity of Panbio COVID-19 Ag were 50.0% and 100.0%, respectively. Panbio COVID-19 Ag demonstrated high sensitivity (88.2%) in analyzing the detection limit cycle threshold (Ct) value of 26.67 provided by the manufacturer as a positive criterion, and the sensitivity was 100.0% for the positive criterion of Ct values <25, although it was less sensitive for Ct ≥25.
Considering the high sensitivity for positive samples with Ct values <25 and the rapid turnaround of results, Panbio COVID-19 Ag can be used in clinical laboratories to diagnose COVID-19 in limited settings.
 , Ji-Eun Ban
, Ji-Eun Ban
Cardiac rhabdomyomas are typically presented in the tuberous sclerosis. Although benign and often associated with spontaneous regression, in rare circumstances huge mass size and critical location can lead to heart failure, ventricular outflow tract obstruction and refractory tachyarrhythmias. An 1-day-old girl was diagnosed as cardiac tumor during perinatal period. At birth, transthoracic echocardiography revealed huge cardiac mass located in septal area of both ventricle measuring 34×30 mm. It protruded into the left ventricular (LV) outflow tract, potentially obstructing it. A surface ECG revealed atrial tachycardia with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia with heart rate of 217 beats per min. The tachyarrhythmias were controlled with intravenous amiodarone. Reduction of the giant cardiac mass was treated with mammalian target of rapamycin pathway inhibitor sirolimus. However, she unfortunately died at 10 days-old because of sudden cardiac arrest maybe due to LV outflow tract obstruction during therapy. Gene analysis revealed TSC2 mutation after death. (Ewha Med J 2022;45(3):e5)
Citations

 , Il Tae Hwang
, Il Tae Hwang
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the most common cause of death worldwide, and dyslipidemia is a major risk factor. Atherosclerosis can begin in childhood and continue into adulthood, thereby contributing to CVD development. Obesity is the most common cause of dyslipidemia, and the prevalence of childhood obesity and dyslipidemia is increasing worldwide, making it a public health concern. As clinical evidence has accumulated, guidelines for dyslipidemia in children have been continuously revised since 1992. The limitations of screening tests for individuals with a family history of dyslipidemia emphasize the necessity of universal screening, and non-HDL cholesterol assessment is recommended as a screening test for dyslipidemia in children. The guidelines for dyslipidemia in Korean children and adolescents published in 2017 recommend that non-HDL cholesterol screening tests be performed in non-fasting conditions at 9–11 years and 17–21 years of age. The main purpose of this article is to describe the history and rationale of lipid screening recommendations in children and adolescents and to review the currently recommended screening methods and treatments for dyslipidemia. (Ewha Med J 2022;45(3):e4)
Citations


Small-for-size syndrome (SFSS) is a critical complication of partial liver
transplantation, particularly in adult-to-adult living donor liver
transplantation (ALDLT) using a small graft. Minimally required liver graft size
for a successful ALDLT is classically 40% of a standard recipient’s liver
volume or 0.8% of recipient body weight. Recent progress in perioperative care
and technical improvement push the lower limit of safe graft size to 25% of the
recipient’s standard liver volume or 0.6% of the graft versus recipient
weight ratio although this is an ongoing debate. The clinical manifestations of
SFSS include various symptoms and signs related to graft dysfunction and portal
hypertension in patients with small grafts. The risk factors for SFSS include
poor preoperative patient condition, including portal pressure, surgical
techniques to reduce portal pressure, and graft quality and size. Hence, various
approaches have been explored to modulate inflow and pressure to a small graft
and to decrease the outflow block to alleviate this SFSS as well as the
selection of a patient and graft. Additionally, recent research and efforts to
prevent and treat SFSS are reviewed.
A notable secular trend in early puberty onset has been described over the past few decades. Also, the prevalence and incidence of precocious puberty is increasing not only in Korea, but also around the world. The manifestation of secondary sex characteristics before 8 years in girls and 9 years in boys is defined as precious puberty. The causes of precocious puberty can be classified as gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)-dependent, also known as central precocious puberty (CPP), or GnRH-independent. Evaluation of patient with precocity requires detailed examination of the clinical manifestation, GnRH stimulation test, and imaging of the central nervous system if indicated. The standard treatment for CPP is GnRH agonist, which is beneficial for adequate pubertal development and preservation of final adult height. In this paper, we investigate the diagnosis and adequate treatment of CPP.
 , Na Yun Bang
, Na Yun Bang , Da In Baik
, Da In Baik , Koo Young Jung
, Koo Young Jung , Junbeom Park
, Junbeom Park
: This study aimed to characteristic the systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic pressure, pulse pressure, glucose, creatine, and lipid profile. This study also aimed to investigate the prevalence of hypertension and the relationship between hypertension and the lipid profile in Uzbekistan.
The subjects consisted of 58 Uzbekistan subjects recruited from Ewha Medical Care patients. Blood samples were collected from the patients for the lipid profile and random glucose and creatinine levels. Paired t tests were used for the group means and a chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. A multiple logistic regression analysis was performed.
Among the 58 patients constituting the baseline population, hypertension developed in 42 patients. Among them, the triglyceride (TG) level was significantly higher in the hypertension group than normal group (173.19 vs. 127.06 mg/dL, P=0.014). The SBP had a positive correlation with the TG (r=0.979, P<0.01) and creatinine (r=0.002, P<0.05) levels and also, the pulse pressure had a positive correlation with the cholesterol level (r=0.539, P<0.05). A multivariate analysis (adjusted for age and sex) indicated that there was a positive correlation between the SBP and TG level (r=0.941, P<0.05).
There was a positive correlation between the SBP and TG level in the Uzbekistan population according to this study.
 , Ji Hyen Lee
, Ji Hyen Lee , Hyun-Hae Cho
, Hyun-Hae Cho , Hae Soon Kim
, Hae Soon Kim
To investigate brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings in patients with central precocious puberty (CPP) by age at onset and sex.
We included 130 CPP patients with brain MRI findings of the pituitary gland treated at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between February 2007 and October 2013 and divided them by age and sex: boys, girls aged ≤6 years, and girls aged >6 years. The control group comprised 224 patients who underwent brain MRIs, and we compared their incidental brain findings with those of the CPP group.
In the CPP subgroups who underwent pituitary MRIs, the frequency of incidental brain lesions was 31.6% in boys, 47.1% in girls ≤6 years and 29.8% in girls >6 years. The incidence of pituitary abnormalities was 42.1% in boys, 64.7% in girls ≤6 years and 47.9% in girls >6 years. Among pituitary abnormalities, pituitary hypoplasia had a significantly higher incidence rate in girls ≤6 years (41.2%) than in boys (15.8%) or girls >6 years (13.8%, P=0.027). Hypothalamic hamartomas were detected in one girl aged ≤6 years and in one boy, but not in girls aged 6 years (P=0.075). The incidence of pineal cysts was higher in the CPP groups and significantly higher in girls ≤6 years (47.1%) than in the control group (11.2%, P=0.001).
There was a higher incidence of brain abnormalities on pituitary MRIs and a higher incidence of pineal cysts, possibly associated with CPP pathogenesis, in younger CPP patients than in other patients.
Citations

 , Geon Woo Lee
, Geon Woo Lee , Jae-Joon Kim
, Jae-Joon Kim , Sang-Bo Oh
, Sang-Bo Oh , So Yeon Oh
, So Yeon Oh , Eun-Ju Park
, Eun-Ju Park , Jin Hyeok Kim
, Jin Hyeok Kim , Joo Yeon Jang
, Joo Yeon Jang , Ung-Bae Jeon
, Ung-Bae Jeon
Terminally ill cancer patients in hospice palliative care unit are reluctant to undergo repetitive invasive procedures due to coagulopathies and poor performance or condition, while catheter management such as regular irrigation during hospitalization is easy. The purpose of this study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of indwelling intraperitoneal (IP) catheter in hospitalized terminally ill cancer patients with recurrent ascites.
A retrospective review was conducted in patients who underwent IP catheter at the hospice palliative care unit of Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital between August 2016 and June 2018. All catheters were inserted by interventional radiologists with radiological guidance. The primary end-points were functional IP catheter maintenance rate, which is catheter maintained with patency for drainage until the intended time.
A total of 25 terminally ill cancer patients underwent IP catheters placements during the study period. All catheters were successfully inserted without major complications, but one patient had trivial bleeding and one other patient had temporary pain. The median time from admission to catheter insertion was 5 days (range, 1 to 49 days). Twenty-one catheters were maintained with function until the intended time, three cases were maintained without function, and the last one was removed early due to obstruction and pain. Finally, the functional IP maintenance rate was 84% (21/25) and the median functional catheter life span was 15 days (95% confidence interval, 10.8 to 17.2).
Our study showed relatively favorable results for IP catheter maintenance and safety in hospitalized terminally ill cancer patients with malignant ascites.
With advances in medicine and technology, treatment modalities for diseases have evolved. Consequently, physicians’ roles have also changed. Because of advances in endovascular treatment, neurosurgeons specializing in cerebrovascular surgery are increasingly using endovascular techniques. Accordingly, the number of so-called “hybrid neurosurgeons” who perform both traditional craniotomy cerebrovascular surgeries and endovascular treatments is on the rise. This phenomenon is also occurring in department of neurology, traditionally a non-surgical specialty, and the number of neurologists using endovascular treatments is also increasing. Nowadays endovascular treatments become more common across medical specialties such as neurointerveional radiology, neurosurgery, and neurology. In this time, what should be the role of neurosurgeons? Standardized hybrid surgeons should contribute to society by treating hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke, maintaining a proper number of hybrid-neurosurgeons to ensure demand for such treatments is met. Further, more neurosurgeons should be trained to perform sophisticated traditional surgeries, as these surgeries cannot be performed by anyone else. Finally, neurosurgery patients often require a combination of surgical and medical treatment. In these situations, primary and secondary prevention are also crucial. And, many neurosurgery patients also have psychoneurotic symptoms. Within neurosurgery backgrounds, we, neurosurgeons, need to be intensivists for critical care medicine, hospitalization experts, epidemiologists, neuropsychiatry experts, and basic researchers. Because we have to be in charge of neurosurgical patients with various problems in our healthcare environment. Therefore, advancing beyond hybrid neurosurgeons and beginning an era of convergence neurosurgeons should be our role in the future.
 , Seon-Yi Lee
, Seon-Yi Lee , Daeun Ko
, Daeun Ko , Junbeom Park
, Junbeom Park , Sowoon Ahn
, Sowoon Ahn , Chunghyun Park
, Chunghyun Park
Brugada syndrome is an arrhythmic syndrome characterized by right bundle branch block, ST segment elevation in the precordial lead (V1-V3), and sudden death caused by ventricular fibrillation, which is not effectively prevented by anti-arrhythmic drug therapy. We are reporting a 30-year-old male patient with Brugada syndrome who got an exploratory laparotomy and a tenorrhaphy due to stab wound which was managed with general anesthesia and brachial plexus block without any complications.
 , Rack Kyung Chung
, Rack Kyung Chung , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Geun Hong
, Geun Hong
Liver transplantation (LT) is the only treatment for end stage of liver failure. In Korea, annually it has been performed 1,300 cases. Most of LTs are performed in large volumes centers. More than half of centers performing LT in Korea are low volume hospital and started a LT program recently. We present our four-year experiences and outcomes of anesthesia for LT since 2013.
Anesthetic and surgical outcomes of 49 consecutive patients who received LT (living donor LT, 21 cases; deceased donor LT, 28 cases) between April 2013 and April 2017 were analyzed retrospectively.
All patients were adult, with the mean age of 53.5±9.2 years. The most common cause of original liver diseases was hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis (40.8%). The mean MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score was 18.8±10.7. Postreperfusion syndrome was observed in 34.7%, which were all controlled by calcium, norepinephrine, ephedrine and epinephrine. The mean postoperative intensive care unit stay of deceased donor LT recipients (13.6±9.0 days) was significantly longer than that of living donor LT recipients (8.0±3.3 days). There was no intraoperative mortality in patients receiving LT. Thirty-day post-transplant survival rate was 93.8% and 3-year survival rate was 88.6 %. The most common postoperative complication was pneumonia.
We have started LT successfully with multidisciplinary team's steady effort. Adaptation and setting up LT protocol, adequate equipment, proper training at established transplant centers are essential to begin a successful LT program.
 , Hee Won Kang
, Hee Won Kang , Young Min Youn
, Young Min Youn , So-Yeon Shim
, So-Yeon Shim , Eun Ae Park
, Eun Ae Park , Su Jin Cho
, Su Jin Cho
To compare the epidemiology, clinical presentation, laboratory findings, seasonality and hospital course of enteroviral meningitis (EM) and non-enteroviral meningitis (NEM) cases in infants under 3 months of age.
A retrospective chart review was performed of infants under 3 months of age or less with viral meningitis admitted to Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between January 2010 and December 2016.
EM patients were more likely to have siblings compared with NEM. Most of EM was diagnosed during the summer season. Almost 80% of EM was diagnosed between July and September. Fever lasted longer in EM patients compared to NEM. White blood cell count (WBC) from the cerebrospinal fluid was higher in EM patients compared with NEM patients. WBC in blood were lower in EM patients compared with NEM patients. C-reactive protein was lower in EM patients compared with NEM patients. Most of the patients were initially started on antibiotics therapy to rule out bacterial meningitis. EM patients received shorter duration of antibiotic treatment compared with NEM patients.
This study was conducted to augment the understanding of the incidence, epidemiology, transmission in infants, clinical presentation, laboratory findings, seasonality and hospital courses of enteroviral meningitis compared to NEM. Early recognition, rapid diagnosis and proper clinical management can reduce duration of antibiotic treatment.
Citations

 , Yoon Suk Lee
, Yoon Suk Lee , Sang Won Lee
, Sang Won Lee , Sejung Sohn
, Sejung Sohn , Young Mi Hong
, Young Mi Hong
Kawasaki disease (KD) is the self-limited and multisystem vasculitis which accompanies many complications. Ophthalmic findings in KD are bilateral conjunctival injection, iridocyclitis, superficial keratitis, vitreous opacities and subconjunctival hemorrhage. Optic disc swelling is a rare ophthalmic complication in KD. We describe a 3-year-old boy who presented with 7 days of fever, both conjunctival injection without discharge, and right cervical lymph node enlargement of more than 1.5 cm. He was diagnosed as incomplete KD. He had no ocular symptom except bilateral conjunctival injection. On ophthalmic examination, he was diagnosed by anterior uveitis with optic disc swelling. The brain magnetic resonance imaging was performed and revealed no evidence of increased intracranial pressure. Echocardiography revealed the dilated right coronary artery up to 3.4 mm. Fever subsided and optic disc swelling was completely improved after intravenous immunoglobulin (2 g/kg) treatment. Optic disc swelling is a rare ophthalmic complication in KD.
Citations

 , Min Jeong Kim
, Min Jeong Kim , Seung Yon Baek
, Seung Yon Baek
To evaluate MRI findings of non-recurrent hepatocellular carcinomas with lipiodol uptake (LHCCs) treated with transarterial chemoembolization.
28 LHCCs were divided into two groups according to amount of lipiodol uptake and tumor size, retrospectively. According to amount of lipiodol uptake, HCCs were classified into group A with dense lipiodol uptake (more than 90%) and group B with partial lipiodol uptake (between 50% and 90%). For HCC size analysis, group I was defined by a longest diameter of less than 2 cm, and group II was defined by a longest diameter of greater than or equal to 2 cm.
In group A (n=16), eight LHCCs showed high signal intensity (SI) on T2-weighted images (T2WI), ten LHCCs showed low SI on T1-weighted imaged (T1WI), six LHCCs showed decreased SI at higher b value of diffusion-weighted images (DWI). In group B (n=12), six LHCCs revealed high SI on T2WI, six LHCCs revealed low SI on T1WI, ten LHCCs decreased SI at higher b value of DWI. As compared with tumor size and SI, six of 12 LHCCs in group I and eight of 16 LHCCs in group II showed high SI on T2WI. Six LHCCs in group I and ten LHCCs in group II showed low SI on T1WI. All LHCCs were not enhanced.
Signal intensities of LHCCs were variable, but more than half of LHCCs showed high SI on T2WI, low SI on T1WI, decreased SI at higher
Citations

 , In Je Kim
, In Je Kim , Young Sun Hong
, Young Sun Hong , Soo Mee Lim
, Soo Mee Lim , Min Sun Cho
, Min Sun Cho , Jisoo Lee
, Jisoo Lee
Localized granulomatosis with polyangiitis (loc-GPA) is a milder disease state of GPA restricted to the respiratory tract. Transition from localized form to systemic/generalized disease is predicted to occur in approximately 10% of the patients. We report an unusual case of loc-GPA involving multiple cranial nerves, which in 3 years progressed into systemic disease involving pituitary gland. Initially antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) was negative, but as symptoms of diabetes insipidus started, ANCA became positive. Clinical course of ANCA negative loc-GPA should be carefully monitored for development of systemic disease. ANCA may be a useful marker for detecting transition from localized to systemic disease.

Despite recent advances in the development of diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines, the ease of international travel and increasing global interdependence have brought about particular challenges for the control of infectious diseases, highlighting concerns for the worldwide spread of emerging and reemerging infectious diseases. Korea is also facing public health challenges for controlling imported cases of infectious diseases; dengue virus, which is the most commonly reported case of imported infectious diseases; the largest outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infections outside the Arabian Peninsula in 2015; and the Zika virus infection, which was declared by the WHO as a "Public Health Emergency of International Concern." Although national and global partnerships are critical to controlling imported infectious disease threats, the role of local hospitals, public health sectors, and laboratory capacity remains the cornerstone for initial disease recognition and response. The current status of laboratory diagnosis for imported infectious diseases is reviewed.
Citations

 , Dong Il Kim
, Dong Il Kim , Hyo Jin Yun
, Hyo Jin Yun , Se Hee Yoon
, Se Hee Yoon , Sung Ro Yun
, Sung Ro Yun , Won Min Hwang
, Won Min Hwang
Prostatic abscess is not a common entity which is characterized by non-specific clinical presentations. This poses a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Clinicians routinely consider antibiotic treatments concomitantly with drainage for the treatment of prostatic abscess. But there are no established guidelines for its optimal timing, methods and indications. Surgical drainage procedures include transurethral resection of the prostate and perineal incision and drainage. But there is variability in the prognosis of patients between the procedures. We have treated a 48-year-old diabetes patient with prostatic abscess accompanied by MRSA bacteremia using a percutaneous fine-needle aspiration under the computed tomography (CT) guidance. The patient achieved improvement of the symptoms and in follow up CT findings. A percutaneous drainage under the CT guidance is advantageous in that it causes fewer complications. However, Further studies are warranted to establish the optimal timing, methods and indications in patients with prostate abscess.
 , Hyun-Jung Kim
, Hyun-Jung Kim , Tae-Hee Han
, Tae-Hee Han , Min Kwan Kwon
, Min Kwan Kwon , Soo Ya Bae
, Soo Ya Bae , Young Jin Yuh
, Young Jin Yuh
Myeloid sarcoma is a rare tumor mass consisting of immature granulocytic cells occurring in an extramedullary site or in a bone. It has often been observed during the course of an acute leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome or myeloproliferative neoplasms, and it can involve any site of the body. However, it rarely present in the absence of bone marrow infiltration, especially for the isolated spinal myeloid sarcoma. In this report, we describe a case of isolated myeloid sarcoma that showed spinal compression. A 66-year-old male, with no underlying disease or medication history, presented with a progressive back pain and numbness in bilateral lower extremities that had begun two weeks before. He was diagnosed with myeloid sarcoma with no evidence of bone marrow involvement. Tumor cells were positive for CD34, c-KIT, and Bcl-2 on the immunohistochemical stain. He was treated with systemic chemotherapy with daunorubicin plus cytosine arabinoside and achieved a partial response.
 , Hyun Soo Park
, Hyun Soo Park , Myung Hwa Lee
, Myung Hwa Lee , Sung Hee Kim
, Sung Hee Kim , Jung Hwan Shin
, Jung Hwan Shin
Ectopic pregnancy is an implantation of the fertilized ovum outside the uterine cavity. Most of ectopic pregnancies are located within the fallopian tube. We describe a rare case of 34-year-old woman complaining of lower abdominal pain and positive urinary pregnancy test. Pelvic ultrasound exam suggested tubal pregnancy with hemoperitoneum. However, pelviscopy revealed the bleeding point was subserosal myoma located just next to the right ovary. Uterus and both fallopian tubes were grossly free. Laparoscopic myomectomy with ectopic mass excision was performed and we observed the serial decrease of β-hCG level. Patient was well recovered and postoperative finding was not remarkable. Hereby, we report a rare case of ectopic pregnancy on uterine myoma with subserosal type with a brief review of literatures.
 , Seon Bin Yoon
, Seon Bin Yoon , Mi Ju Cheon
, Mi Ju Cheon , Young Min Koh
, Young Min Koh , Hyeon Sik Oh
, Hyeon Sik Oh , Se Joong Kim
, Se Joong Kim , Seung Hyeun Lee
, Seung Hyeun Lee
Pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is a rare form of lung cancer that originates from submucosal glands of tracheobronchial tree. Unlike low-grade tumor with benign nature, high-grade case is even rarer and has aggressive clinical features with no definite treatment option. Here, we report a case of high-grade pulmonary MEC with fulminant clinical course. A 74-year-old man presented with cough, sputum and mental change. Chest imaging showed massive mediastinal lymphadenopathy with obstructive pneumonia, and multiple metastases in lung and adrenal gland. Bronchoscopy showed polypoid masses obstructing right main bronchus and bronchus intermedius. Histopathology revealed a mixture of glandular structure lined with mucussecreting cells and nests of squamoid cells with nuclear atypia and pleomorphism, which is compatible with high-grade MEC. We intensively treated the patient with combination antibiotics and ventilator care. However, the patient did not respond to the treatment and rapidly deteriorated, and finally expired a month after diagnosis.
 , Sung Min Chung
, Sung Min Chung , Myoung Sil Ju
, Myoung Sil Ju
The surgical modalities for treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis have changed in recent years. The radical Caldwell-Luc operation has been replaced by the more conservative endoscopic sinus surgery(ESS). Good clinical results for the ESS technique have been reported(Wigand, 1978 ; Stammberger, 1991 ; Kennedy, 1992), but only a few papers give detailed data on the symptoms(Kamel, 1989 ; Levin, 1990 ; Lund, 1991). From April 1992 to January 1996, a total of 118 patients(primary ESS 62 patients and ESS after previous nasal surgery 56 patients) who underwent ESS at the department of otolaryngology, Ewha womans university Hospital, were evaluated.
Preoperative nasal symptoms, except for nasal discharge were higher in revision cases. The previous most common nasal surgery was polypectomy accounting for 25(44.6%) of the 56 revision cases. All had preoperative CT scans of the ostiomeatal unit area(OMU CT) and severity of inflammatory disease had been graded by CT. In revision cases, 30(53.6%)cases had complete opacification of one or more major sinuses. But in primary ESS cases, 19(30.6%) had findings limited to the osteomeatal complex. Overall, 43(76.8%) patients benefited from ESS in revieion cases, and 58(93.5%) in primary ESS cases. Synechia was the most common complication in revision and primary FESS cases. The difference of outcomes between primary ESS and ESS after previous nasal surgery is explained by the difference of preoperative state of the sinus mucosa.
The author's review of 118 patients showed that there was significant difference in the postoperartive success rate between the primary ESS and ESS after previous nasal surgery.
 , Chong-Nahm Kim
, Chong-Nahm Kim , Soon-Kwan Hong
, Soon-Kwan Hong , Ji-Ae Lee
, Ji-Ae Lee , Ok-Kyung Chung
, Ok-Kyung Chung , Moon-Jung Kim
, Moon-Jung Kim
Rhinocerebral mucormycosis is a well-described fulminant fungal infection that typically presents in a rapidly fulminant manner. This condition is more likely to occur among patient with diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, who have long-term steroid treatment, or who suffer from some debilitating diseases.
We report 3 cases of rhinoorbitocerebral mucormycosis, all suffered from diabetes mellitus. In all 3 cases, endoscopic sinus surgery was done and the antifungal agent(amphotericin B) was administered intravenously, and two patients died. One survivor who had focal extension of paranasal sinus and orbit, required one surgical intervention without orbital exenteration and he is alive without recurrence disease.
The severity of the disease is probably dependent upon the gost resistance to the invasion of phycomycetes. Early diagnosis and immediate, effective treatment are the key for cure of the disease.
 , Kyu-Man Shin
, Kyu-Man Shin , Jun-Hyeok Song
, Jun-Hyeok Song
 , Jung Sun Kim
, Jung Sun Kim , Young Sook Park
, Young Sook Park
This study attempts to explore the adapting behaviors of medical professions in information society, focusing on nurses' responses to the changes driven by the implementation of information system in four general hospitals. In addition to the general status of the information in the hospitals, we analyze four dimensions of the adapting behaviors of nursed in the implementation process of the hospital work. These are 1) changes in the jobs and functions of the nurses ; 2) changes in their autonomy and status; 3)changes in human relations ; and 4) the quality of medical services.
Both quantitative and qualitative data were collected from two university-affiliated hospitals and two private general hospitals in Seoul. The quantitative data contain the responses of 92 nurses from four hospitals and we performed an in-depth-interview with 12 nurse to complement the quantitative data.
1) The implementation of information system in the sample hospitals are limited to the computerization of the administrative part of the medical care.
2) This limited computerization of the hospital works does not seem to increase the efficiency of nursing itself, but rather put mote burden on nurses doing double jobs of handwriting and computerization.
3) The autonomy of nurses and their relate status has not been noticeably changed in the process. Nurses, however, reported to have conflicts with other professions over the job distributions.
4) The computerization of the hospital works tend to reduce an unnecessary face-to-face interaction, which is expected to facilitate communications in the hospital. But there are still conflicts among medical professions over the boundary of their duties and responsibilities.
5) Nurse pointed out that the positive effects of the computerization on the quality of service are limited to shorten the time of care.
The results of this study confirms our hypothesis that the information system would change jobs and functions, autonomy and status, human relations, and quality of sevices in nursing. Some of the changes are positive although the implementation of information system is expected to put more burden on nursing for a while. Most nurses, however, expected the computerization will provide better services to the patients in the long run.

The intervertebral disc has an important role in the spinal biomechanics. The influence of lumbar discectomy on the disc space height is still uncleared. This study was performed to evaluate the long term influence of lumbar discectomy on intervertebral disc space height.
The author analysed the disc space height in 25 patients who had performed open discectomy for the disc herniation at least two years age. The height was compared with that of unoperated disc and evaluated the role of discectomy in the change of disc space height.
The decrease of disc space height was 3.3mm in average. The loss of anterior height was 4.1mm and that of posterior height was 2.5mm. This discrepancy was statistically significant(p<0.05). Although the difference of disc height loss in each disc space was not significant. the loss in L4-5 disc space was greater than that of other disc space.
These data suggest that lumbar discectomy accelerate the loss of disc height and influence the process of vertebral degeneration by change of spinal biomechanics in long term period.
 , Hong Kun Cho
, Hong Kun Cho , Gil Ja Shin
, Gil Ja Shin
Ticlopidine, a platelet aggregation inhibitor, is widely used in the secondary prevention of stroke and previous manifestation of peripheral arterial occlusive disease, Ticlopidine is also used to prevent myocardial infarction and post-stenting occlusion after intracoronary stent implantation. The exact mechanism of action of ticlopidine is unclear, but likely involves the inhibition of platelet activity by the suppression of adenosine diphosphate-induced patelet aggregation. The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal problems, skin reactions, and hematologist changes. The adverse hepatic effects are not frequent(4% in different series).
We experienced a case of ticlopidine-induced cholastatic jaundice, and report with review of literatures.

Cervical spine injury is a commonly encountered entity in most neurosurgical practice and is increasing with social environment. Universally accepted treatment modality for acute cervical spine injuries do not exist and several areas of controversy surround the issue of surgical intervention in the management of trauma to the cervical spine.
A retrospective study of 86 injured cervical spine patients who admitted and carried out a surgical treatment at Dong Dae Moon Hospital between Sep.92 and Aug.96 for the past four-year-period.
The author analyzed 86 patients with traumatic cervical spine injuries for the past 4 years. The incidence was highest in middle aged men(ratio : 6.8) and the traffic accident was the most common exclusive cause(68%). In 9 cases of C1-2 spine injury, they underwent posterior approach. In 74 cases of mid-lower(C3-7) cervical injury, the anterior approach was used in 57 patients, the posterior approach was used in 13 patients and the combined approach was used in 4 patients. The surgical complication rate was 15%(13 cases).
Internal fixation with variety of devices has become a popular procedure for cervical spine injuries.
In this study, the rate of re-operation and complications following initial surgical procedures were found to be higher than previous report of other authors. It could be concluded that choosing the most proper surgical approach for cervical spine injuries with minimal risks and adhering to stringent criteria are much important than simply selecting new fancy devices over the traditional one.


The present study investgated if constitutive nitric oxide synthase(cNOS), especially neuronal type, is expressed in gastrointestinal epithelial cells of rat. Expression of cNOS was immunohistochemically determined. Some gastric epithelial cells were found to express cNOS. Although less than that by the gastric epithelial cells, cNOS was also found to be expressed by the intestinal epithelial cells. Thus it is possible that constitutive type of nitric oxide synbthase in gastrointestinal epithelial cells may play a role in normal gastrointestinal function.

This study was performed to assess the factor affecting the distance from skinto epidural space.
The distance from the skin to epidural space(DSES) was measured in 105 patients who received lumbar epidural anesthesia. The relationship between patient factors [age, weight, height, body mass index(BMI : weight/height2), pregnancy] and technical factor(posture) versus DSES was investigated using multiple regression analysis.
The mean DSES was 4.5±0.7cm. DSES correlated positively with weight and BMI in non-obstetrics(including male), and BMI in obstetrics. But, DSES did not correlated with posture.
The patient's weight and BMI in non-obstetrics and BMI in obstetrics but posture during epidural needle placement are important factors influencing DSES.
 , Mi Chung Kim
, Mi Chung Kim , Moon Hee Chang
, Moon Hee Chang
Osteoma of the paranasal sinuses is found in approximately 0.25% of routine roentgenographic sinus examinations and are most commonly found in the frontal sinus(ethmoid sinus and maxillary following in that order).
Osteomas are classified as compact, cancellous, or mixed, Compact osteoma is an ivory-hard tumor, probably formed by periosteal osteoblasts. To assess growth, a radiographic follow up within 1 to 2 years is necessary. The most frequent site of origin would seem to be the space between the frontal and ethmoid bones.
Nasal stuffiness may be a complaint if the upper lateral nasal wall is displaced medially.
Traditionally, the external ethmoidectomy approache is the route of choice for removal of osteoma of the ethmoids.
In this study, authors present a case of ethmoid osteoma hat was removed successfully through an endoscopic approach.

