 , Jae-Young Lim
, Jae-Young Lim

 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim

 , Jihyun Ahn
, Jihyun Ahn
 , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang

Citations

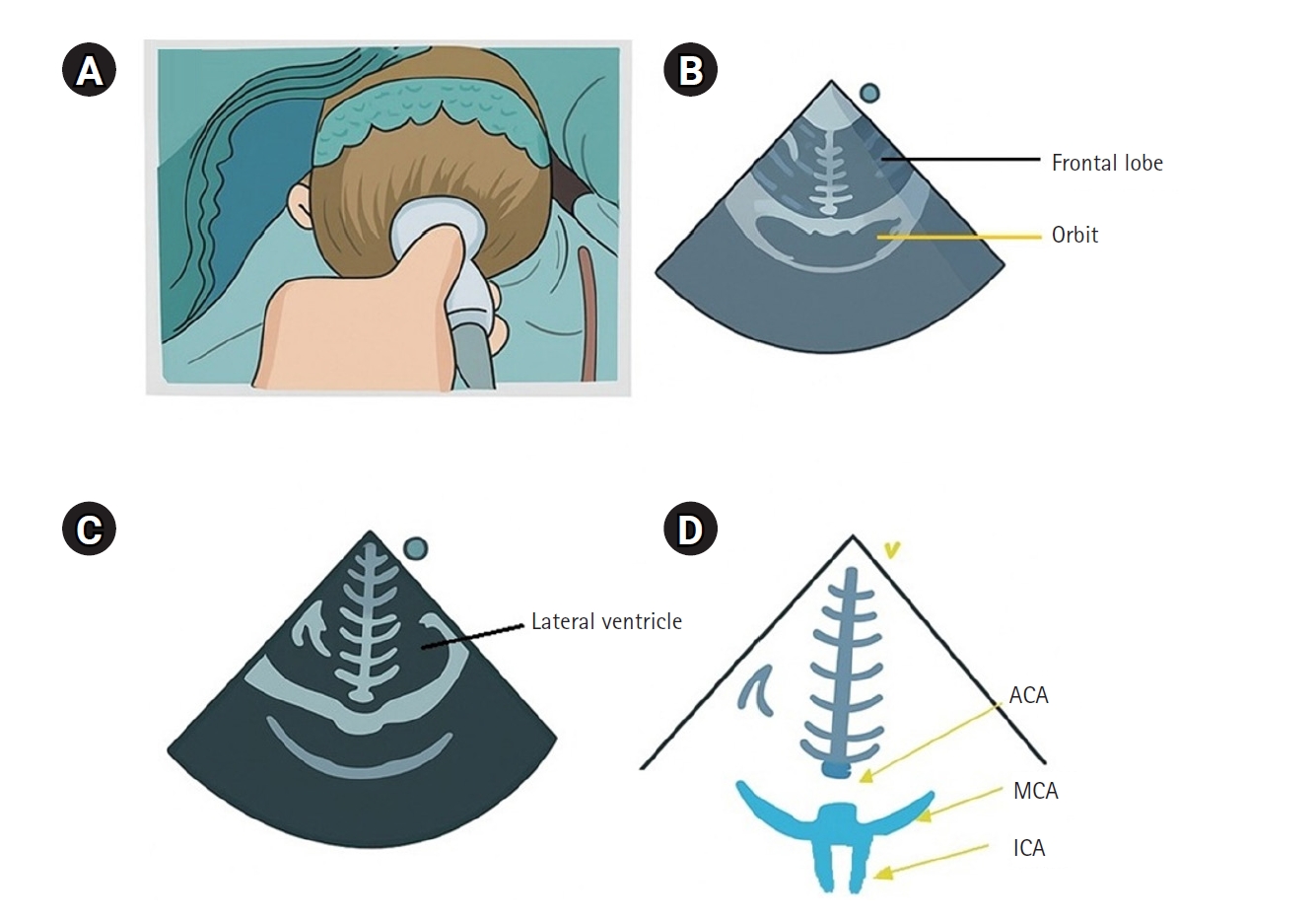
Shoulder pain is a common complaint in primary care settings. The prevalence of shoulder pain is on the rise, especially in societies with aging populations. Like other joint-related conditions, shoulder pain is predominantly caused by degenerative diseases. These degenerative changes typically affect bones, tendons, and cartilage, with common conditions including degenerative rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Diagnosing these degenerative diseases in older adults requires a thorough understanding of basic anatomy, general physical examination techniques, and specific diagnostic tests. This review aims to outline the fundamental physical examination methods for diagnosing shoulder pain in older adult patients in primary care. The shoulder's complex anatomy and its broad range of motion underscore the need for a systematic approach to evaluation. Routine inspection and palpation can identify signs such as muscle atrophy, bony protrusions, or indications of degenerative changes. Assessing range of motion, and distinguishing between active and passive deficits, is crucial for differentiating conditions like frozen shoulder from rotator cuff tears. Targeted strength tests, such as the empty can, external rotation lag, liftoff, and belly press tests, are instrumental in isolating specific rotator cuff muscles. Additionally, impingement tests, including Neer’s and Hawkins’ signs, are useful for detecting subacromial impingement. A comprehensive understanding of shoulder anatomy and a systematic physical examination are vital for accurately diagnosing shoulder pain in older adults. When properly executed and interpreted in the clinical context, these maneuvers help differentiate between various conditions, ranging from degenerative changes to rotator cuff pathology.
Health and safety issues in micro and small enterprises (MSEs) are recognized as a global challenge. This study aimed to examine Workers' Health Centers (WHCs) as a representative public organization providing occupational health services to MSEs in Korea. WHCs were established in 2011 after a trial period aimed at addressing occupational diseases in MSEs with limited resources. As of 2024, there are 24 WHCs, 22 branch offices, and 23 trauma counseling centers for workers. These health centers are managed by the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency, with their actual operation delegated to private organizations. Each WHC employs an average of 13 staff members and is organized into four specialized teams: cardiovascular disease prevention, workplace environment improvement, musculoskeletal disease prevention, and occupational stress management. These centers also offer common basic programs along with region-specific specialized initiatives. In 2023, the total cumulative number of users reached 203,877, with employees from MSEs comprising approximately 88.5% of the total. WHCs can thus be seen as playing a pivotal role as case managers of health requirements in the workplace by fostering strong relationships with MSEs and linking them to other relevant programs through a problem-solving-oriented approach. Given the limited resources of these enterprises, proactive policies and the equitable application of safety and health regulations are essential. A balanced strategy that combines regulatory enforcement with practical assistance is critical to ensure the success of WHCs in improving health and safety conditions in MSEs.
Shoulder diseases pose a significant health challenge for older adults, often causing pain, functional decline, and decreased independence. This narrative review explores how deep learning (DL) can address diagnostic challenges by automating tasks such as image segmentation, disease detection, and motion analysis. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of DL-based convolutional neural networks and machine learning frameworks in diagnosing various shoulder pathologies. Automated image analysis facilitates the accurate assessment of rotator cuff tear size, muscle degeneration, and fatty infiltration in MRI or CT scans, frequently matching or surpassing the accuracy of human experts. Convolutional neural network-based systems are also adept at classifying fractures and joint conditions, enabling the rapid identification of common causes of shoulder pain from plain radiographs. Furthermore, advanced techniques like pose estimation provide precise measurements of the shoulder joint's range of motion and support personalized rehabilitation plans. These automated approaches have also been successful in quantifying local osteoporosis, utilizing machine learning-derived indices to classify bone density status. DL has demonstrated significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in the management of shoulder diseases in older patients. Machine learning-based assessments of imaging data and motion parameters can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, to ensure their generalizability, reproducibility, and effective integration into routine clinical workflows, large-scale, prospective validation studies are necessary. As data availability and computational resources increase, the ongoing development of DL-driven applications is expected to further advance and personalize musculoskeletal care, benefiting both healthcare providers and the aging population.
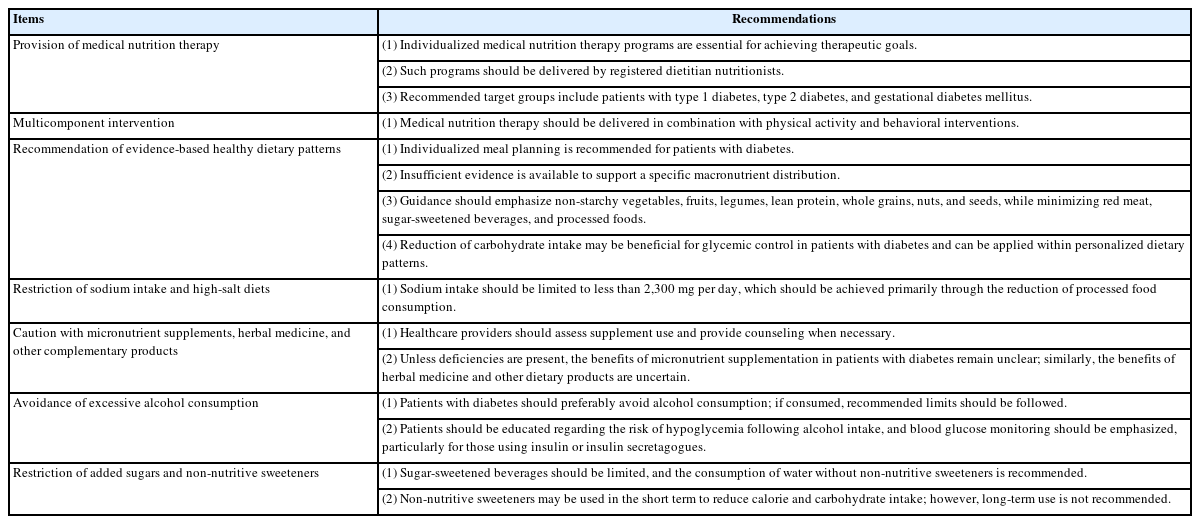
The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive guide for managing older adult patients with shoulder diseases, specifically rotator cuff tears and osteoarthritis, and to explore effective nonsurgical treatment options. Chronic rotator cuff tears are typically degenerative, whereas acute tears result from trauma. A key feature of these tears is tendon degeneration accompanied by type III collagen predominance, predisposing tears to progression. Osteoarthritis in the glenohumeral joint arises from wear-and-tear changes that compromise cartilage integrity, leading to pain and restricted motion. Accurate clinical assessment and imaging, including plain radiographs, ultrasonography, and MRI, facilitate diagnosis and guide treatment. The physic-al examination emphasizes range of motion, rotator cuff strength, and scapular stability. Management strategies prioritize pain relief, function preservation, and improving mobility. Nonsurgical modalities, including exercise, manual therapy, and activity modification, constitute first-line treatments, especially for older adults. Pharmacological approaches involve NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, and neuropathic pain medications. Steroid injections have short-term benefits, but repeated treatments may compromise tissue integrity. Platelet-rich plasma is a regenerative option that may improve tendon healing, but mixed findings highlight the need for further investigation. A structured physical therapy program focusing on range of motion and strengthening is essential, with alternative interventions used judiciously. Patients should be counseled regarding the potential progression of tears and the possible need for future surgical intervention if nonsurgical methods are unsuccessful. Multimodal approaches, including joint mobilization and personalized exercise regimens, hold potential for optimizing functional outcomes and supporting independence in older adults.
Citations

 , Hee-June Kim
, Hee-June Kim , Sung Hun Kim
, Sung Hun Kim , Suk-Joong Lee
, Suk-Joong Lee
Citations


Influenza presents a considerable disease burden, particularly among adults over 65 years old. In this population, the disease is associated with high rates of infection, hospitalization, and mortality. The objective of this study was to assess the impact of influenza on older adults and to evaluate the effectiveness of influenza vaccines within this demographic. A literature search was conducted using PubMed to identify relevant English-language studies published from January 2000 to January 2024. The analysis indicated that influenza-related hospitalization rates (ranging from 10.1 to 308.3 per 100,000 persons) and all-cause excess mortality rates (1.1 to 228.2 per 100,000 persons) were notably high in older adults, although these rates varied over time and by location. Hospitalization rates due to influenza increased considerably after the age of 50 years, with the highest rates observed in individuals aged 85 years and older. Excess mortality attributable to influenza also rose with age, with rates between 17.9 and 223.5 per 100,000 persons in those over 75 years old. The effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing severe infections requiring hospitalization was found to be only 37% in individuals aged 65 years and older. The unadjuvanted, standard-dose influenza vaccine had an estimated effectiveness of just 25% against laboratory-confirmed influenza and between 37% and 43.7% in preventing hospitalizations. Therefore, considering the substantial burden of influenza and the limited efficacy of standard vaccines, the use of highly immunogenic influenza vaccines should be prioritized for older adults.
Citations

 , Yoon Jin Choi
, Yoon Jin Choi , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Joo Young Roh
, Joo Young Roh , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which are often acquired from environmental sources such as water and soil, exhibit a variety of cutaneous manifestations that frequently lead to misdiagnoses and delays in treatment. A 77-year-old woman presented with multiple skin lesions in a sporotricoid distribution on her right leg, which persisted despite standard antibiotic treatments. Based on the skin biopsy, revealing granulomatous inflammation with acid-fast bacilli, and PCR testing, a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection was diagnosed. Antimycobacterial drug combinations, including clarithromycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin for 4 months, complete the skin lesion's clearance. This case underscores the need for heightened suspicion and the use of appropriate diagnostic techniques, including tissue biopsies and molecular methods such as PCR.
Citations

 , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn , Rena Lee
, Rena Lee
This study aimed to develop an accurate pediatric bone age prediction model by utilizing deep learning models and contrast conversion techniques, in order to improve growth assessment and clinical decision-making in clinical practice.
The study employed a variety of deep learning models and contrast conversion techniques to predict bone age. The training dataset consisted of pediatric left-hand X-ray images, each annotated with bone age and sex information. Deep learning models, including a convolutional neural network , Residual Network 50 , Visual Geometry Group 19, Inception V3, and Xception were trained and assessed using the mean absolute error (MAE). For the test data, contrast conversion techniques including fuzzy contrast enhancement, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (HE) , and HE were implemented. The quality of the images was evaluated using peak signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), mean squared error, SNR, coefficient of variation, and contrast-to-noise ratio metrics. The bone age prediction results using the test data were evaluated based on the MAE and root mean square error, and the t-test was performed.
The Xception model showed the best performance (MAE=41.12). HE exhibited superior image quality, with higher SNR and coefficient of variation values than other methods. Additionally, HE demonstrated the highest contrast among the techniques assessed, with a contrast-to-noise ratio value of 1.29. Improvements in bone age prediction resulted in a decline in MAE from 2.11 to 0.24, along with a decrease in root mean square error from 0.21 to 0.02.
This study demonstrates that preprocessing the data before model training does not significantly affect the performance of bone age prediction when comparing contrast-converted images with original images.
Citations

 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Cheolung Kim
, Cheolung Kim
Subepithelial tumors in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract are often detected during nationwide endoscopic gastric cancer screening in Korea. Most GI lipomas are asymptomatic and do not necessitate further treatment. However, large tumors may lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, intussusception, and bleeding. These GI lipomas require endoscopic or surgical resection. On radiological examination, GI lipomas typically manifest as hypodense lesions with similar density to that of fat tissue. White-light endoscopy generally reveals a yellowish subepithelial tumor exhibiting a positive cushion sign, while endoscopic ultrasonography shows a homogeneous hypoechoic mass within the third layer of the GI tract. We present the case of an 81-year-old woman with symptomatic duodenal lipoma following endoscopic resection.
 , Yaiza Del Pozo Martín, Joan Marsh
, Yaiza Del Pozo Martín, Joan Marsh 성별(sex)과 젠더(gender)의 차이를 이해하는 것은 질병 관련 병태생리학 연구, 사회인구학적 건강결정요인, 의학적 또는 사회적 중재의
긍정적 영향 및 위해성 등을 막론하고 엄밀하고 포용적연구에 있어 필수적이다. 다양한 젠더를 포함한 연구가 활발해졌지만 성별과 젠더를 변수로
명시하는 연구는 여전히 부족하다. 2016년에 발표된 성별과 젠더 형평성(Sex and Gender Equity in Research,
SAGER) 지침은 널리 지지되고 있지만, 소수의 과학 학술지와 기관들에서만 이를 공식적인 편집 및 출판 정책에 반영하고 있다.
 , Paola De Castro, Sera Tort, Mirjam Curno
, Paola De Castro, Sera Tort, Mirjam Curno Citations


Anastomotic leakage (AL) after colorectal surgery is a significant concern, as it can lead to adverse functional and oncologic outcomes. Numerous studies have been conducted with the aim of identifying risk factors for AL and developing strategies to prevent its occurrence, thereby reducing the severe morbidity associated with AL. The intraoperative method for reducing AL includes a mechanical assessment of AL, an assessment of bowel perfusion, drain placement, and the creation of diverting stomas. The anastomosis technique is also associated with AL, and the appropriate selection and accurate application of anastomotic methods are crucial for preventing AL. Indocyanine green fluorescence imaging has recently gained popularity as a method for assessing bowel perfusion. While it is useful for detecting bowel perfusion, standardized protocols and measurement methods need to be established to ensure its reliability and effectiveness in clinical practice. The use of intraoperative drains to reduce AL has produced inconsistent results, and the routine adoption of this practice is not currently recommended. Diverting stomas can be used to help reduce the morbidity associated with AL. However, it is important to carefully consider the complications that can arise directly from the stoma itself. It should be noted that while a stoma can reduce AL, it cannot completely prevent it. This descriptive review examines various intraoperative methods aimed at reducing AL, discussing their effectiveness in reducing AL.
Citations

Over the past 3 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has posed significant challenges to the healthcare system, leading to delays in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases due to the need for social distancing measures. Colorectal cancer has not been immune to these disruptions, and research in various countries has explored the impact of COVID-19 on the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. One notable consequence has been the postponement of colorectal cancer screenings, potentially resulting in disease progression, which can adversely affect surgical and oncological outcomes. Furthermore, the treatment approach for colorectal cancer may vary depending on the extent of disease progression and the healthcare policies implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this systematic review, we examine treatment strategies, surgical outcomes, and oncological variables across multiple studies focusing on colorectal cancer treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this analysis was to assess how medical policies enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have influenced the outcomes of colorectal cancer treatment. We hope that this review will provide valuable insights and serve as a foundational resource for developing guidelines to address potential medical crises in the future.
 , Sang Yoon Kim
, Sang Yoon Kim , Heejin Bang
, Heejin Bang , Kyoung Eun Lee
, Kyoung Eun Lee
Extramammary Paget’s Disease (EMPD) is a rare intraepithelial malignancy of apocrine bearing glands, which occur usually in the perianal region, vulva, scrotum, penis and ax-illa. Most of the disease are treated by surgical resection and the prognosis is generally good. Even though recurrent disease, it is usually slowly progressed with good prognosis. Here we describe the case of a 70-year-old male who has presented with initially just as an EMPD component of squamous cell carcinoma in inguinal skin, but he showed recur-rence of EMPD. The disease has progressed rapidly, finally he died of that EMPD in 2 months of recurrence. The purpose of this study is to report the rare case of fulminant disease course of EMPD after recurrence.
Citations

 , Yongil Kim
, Yongil Kim
A bezoar, a mixture of various undigested foreign substances in the gastrointestinal tract, causes intestinal obstruction at times. We report a case of non-surgical treatment in old age patient. An 89-year-old female presented with epigastric pain, general weakness, and intermittent melena for 1 month. There were episodic attacks of vomiting. An abdominal computed tomography scan showed a 5×4 cm, firm, atypically shaped mass at the stomach body and duodenal bulb with interspersed gas. Endoscopy showed a mass of fiber impacting the antrum pylorus, and the endoscopist failed to remove the bezoar at the first attempt. We subscribed olive oil for few days to make the bezoar small, and eventually, it was fragmented and removed without surgery. A phytobezoar is not uncommon disease required surgical removal if obstructive system developed. Ingestion of olive oil would be a helpful substitute for immediate operation in case of phytobezoar.
 , Wookeun Lee
, Wookeun Lee , Tae-Dong Jeong
, Tae-Dong Jeong , Hae-Sun Chung
, Hae-Sun Chung , Ki-Sook Hong
, Ki-Sook Hong
Six sigma is a quality management system for the assessment of precision and accuracy. We aim to apply the six sigma rule to quality control (QC) of point-of-care (POC) glucose meters in a tertiary hospital.
Thirty POC glucose meters installed at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital were monitored between January 2013 and March 2014. The QC data from the POC glucose meters at low and high levels were collected. The monthly mean, standard deviation, bias, coefficient of variation, and mean sigma metrics were calculated. The correlation between accuracy and precision was assessed based on the percentage bias and coefficient of variation. Comprehensive instructions on the QC and maintenance of the devices were provided in the departments with poor sigma scores. A follow-up assessment was performed after the intervention.
The mean sigma values for the low and high controls were 3.29 and 3.71, respectively. At the low and high controls, 36.6% and 10% of the glucose meters showed a sigma value <3. The causes of low sigma values included the use of expired control materials, prolonged air exposure of the sample strip, lack of user training, and errors in device maintenance. On follow-up monitoring for 3 months following QC intervention, 23.3% (low control) and 6.6% (high control) of the glucose meters scored a sigma value <3, indicating improved QC.
Sigma metrics-based QC can successfully improve accuracy and precision of POC glucose meters in an objective and quantitative manner and can be used for follow up after QC intervention.
Citations

 , Tae-Jin Song
, Tae-Jin Song , Young-Jae Kim
, Young-Jae Kim , Ji Hoe Heo
, Ji Hoe Heo , Kyung-Yul Lee
, Kyung-Yul Lee , Young Eun Kim
, Young Eun Kim , Min Uk Jang
, Min Uk Jang , Soo-Jin Cho
, Soo-Jin Cho , Suk Yun Kang
, Suk Yun Kang
Although there have been several reports that described characteristics for young age stroke, information regarding very young age (18–30 years old) has been limited. We aimed to analyze demographic factors, stroke subtype, and 3-month outcome in acute ischemic stroke patient who have relatively very young age in multicenter stroke registry.
We evaluated all 122 (7.1%) consecutive acute ischemic stroke (within 7 days after symptom onset) patients aged 18 to 30 from 17,144 patients who registered in multicenter prospective stroke registry, 1997 to 2012. Etiology was classified by Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment criteria. Stroke severity was defined as National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) and stroke outcome was defined by modified Rankin scale (mRS) at 3 months after index stroke.
The mean age of all included patients was 25.1±3.7 years and 76 patients (62.2%) were male. The median NIHSS at admission was 4. Considering stroke subtype, 37 patients (30.3%) had stroke of other determined etiology (SOD), 37 (30.3%) had undetermined negative evaluation (UN) and 31 (25.4%) had cardioembolism (CE) were frequently noted. After adjusting age, sex and variables which had P<0.1 in univariable analysis (NIHSS and stroke subtype), CE stroke subtype (odds ratio, 4.68; 95% confidence interval, 1.42–15.48; P=0.011) were significantly associated with poor functional outcome (mRS≥3).
In very young age ischemic stroke patients, SOD and UN stroke subtype were most common and CE stroke subtype was independently associated with poor discharge outcome.

Antimicrobials were one of the great invention of modern era. However, the abuse of antimicrobial both in human and animals has led to a high rate of occurrence of antimicrobial resistant microbes. Disease treatment caused by antimicrobial resistant microbes including superbacteria has emerged as critical issue worldwide. Communication and cooperation among researchers in diverse fields are needed to solve the resistance to antimicrobials. Culture Collection of Antimicrobial Resistant Microbes (CCARM) has taken a leadership role an intermediary among various research fields by providing certified antimicrobial resistant microbes with their information since 1999. CCARM collects antimicrobial resistant microbes from clinical, agricultural animals and products, and environmental fields, and classifies and stores them according to their origins, species and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. CCARM is performing the roles (collection, deposit, preservation, distribution, service, and consulting) of Biological Resource Center designated by Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Citations

 , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Ji Sun Jeong
, Ji Sun Jeong
We analyzed retrospectively incidence, management, and predictors of difficult intubation, which have been known through practical cases.
A total of 217 cases of difficult intubation (DI) between 2010 and 2014 were investigated. Risk factors such as age, body mass index, Mallampati score, thyromental distance, degree of mouth opening and range of neck motion, Cormack-Lehane grade, intubation and airway management techniques were investigated. The cases of each department were analyzed and the airway management techniques according to simplified risk scores (SRS) were also investigated.
The average incidence of DI was 0.49%. Patients undergoing surgery in the departments of oro-maxillo-facial surgery (1.35%), ophthalmologic surgery (0.96%), urologic surgery (0.80%), and head and neck surgery of ear-nose-throat (0.62%) showed the higher incidence of DI. Difficult mask ventilation (10 of 217, 4.6%) was occurred with DI. Higher SRS were related to high rates of video laryngoscope use and fiberoptic guided intubation. There was a decrease in the use of McCoy blades after 2013, an increase in the use of video laryngoscope, and a consistent rate of fiberoptic intubation.
It is not easy to check all the predictors of DI in a preanesthetic evaluation and the predictors are not accurate. The role of clinical preparation and practical management is important, and the most important thing is to establish a planned induction strategy. Multiple factors system, such as simplified risk factors should be used to evaluate patients to prepare for appropriate airway management techniques in case of DI.
Citations

 , Joo Kyoung Cha
, Joo Kyoung Cha , Hyun Jung Lee
, Hyun Jung Lee , Seok Lae Chae
, Seok Lae Chae , Hee Jin Huh
, Hee Jin Huh , Jae-Woo Chung
, Jae-Woo Chung , Do Yeun Kim
, Do Yeun Kim
To assess the current state of anemia evaluation in the elderly over 80 years of age.
Patients who were more than 80 years old and visited Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital from April 2005 to February 2014 were included. Statistical analysis were assessed using the logistic regression model.
Total 548 patients, who had anemia according to WHO criteria, were identified. The median age was 85 years old (range, 82 to 99 years) and median hemoglobin level was 11.0 g/dL (range, 2.7 to 12.9 g/dL). Twenty-eight, 468, and 52 patients were classified as microcytic anemia, normocytic anemia, and macrocytic anemia, respectively. Among them, 397 patients (72.4%) did not undergo proper evaluation for the cause anemia i.e., 8 cases (28.5%) of microcytic anemia, 361 cases (77.1%) of normocytic anemia, and the 28 cases (53.84%) of 52 macrocytic anemia patients. The remaining 151 patients (27.6%) had completed the evaluation, and 24 patients (15.9%) were diagnosed as solid malignancies. In the assessment of iron deficiency anemia, hemoglobin levels, and age had no effect on whether or not to perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
This finding showed that physicians often neglected anemia in individuals over 80 years of age. Though these patients have limited life expectancy, physicians should carefully discriminate the sub-population who will be benefit from adequate evaluation and treatment.
Citations



It is well known that changes in end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure (PETCO2) can reflect changes in cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The present study was performed to evaluate quantitative relationship between the changes in PETCO2 and cardiac output in the acute hemorrahagic dogs.
Six anesthetized(isoflurane 1.0%), paralyzed, and mechanically constant ventilated dogs submitted to hemorrhage were studied. The dogs were hemorrhaged by progressive withdrawal of 50% of blood volume. After withdrawal of each 10% of blood volume, PETCO2, arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure(PaCO2), mean arterial pressure and cardiac output were measured.
After 40% blood loss, the percent decrease in PETCO2 decreased significantly. The percent decrease in PETCO2 correlated with the percent decrease in cardiac output(slope=0.33, r=0.7, P<0.001). The percent decrease in PETCO2 correlated with the percent decrease in cardiac output(slope=0.35, r=0.55, P<0.05).
There is a linear correlation between the percent decrease in PETCO2 and cardiac outpit with the ratio approximately 1:3 during acute hemorrhage in the constant tidal volume ventilation. The cause of PETCO2 change induced by cardiac output might be change in PaCO2. This finding suggests that PETCO2 monitoring can easily detect a critical reduction in cardiac output when ventilationis constant.

The multifactorial character of cervical spondylotic myelopathy indicates a probable onset and progression of this disease as well as a diversity of clinical manifestations.
Patients admitted with the clinical symptomatology of a progressive myelopathy associated with radiologic findings compatible with spondylotic degeneration of the cervical spine and who manifest appropriate neurophysiological abnormalities should be considered as candidates for surgical treatment. For several decades, both anterior and posterior spinal decompressive procedures have been performed who are generally being informed before the operation that the aim of surgery is to stabilize their neurologic condition and that actual improvement often cannot be expected.
A retrospective analysis of 42 patients admitted to the Dongdaemoon hospital utilizing MRI, CT in small amount to make diagnosis and surgical indication of degenerative cervical spine lesions was undertaken. Almost all patents were taken T1 Weighted Image(T1W1),T2 Weighted Image(T2W1) and gradient echo image on 1.5 Tesla unit. All patients could be evaluated the extent and degrees of disc hemiation, osteophytes and cord compression.
A focal area of High-Signal-Intensity(HSI) was observed on T2W1 in 15 patients with myelopathy predominantly. HSI was diminished postoperatively in the patients who improved clinically , remained and unchanged who didn't improve.
In this study, MRI with high resolution images I the initial procedure of choice of degenerative cervical spine lesion was important on the decision making of the patients, Furthermore hight signal of the spinal cord by the compressive lesions appear to be an important indicator for predicting prognosis of patients with myelopathy.
 , Sung Hak Kim
, Sung Hak Kim
Improvements in microsurgical and neuroanesthesiological have resulted in an increasing number of operation for aneurysm clipping in elderly patients. It is the purpose of this article to evaluate surgical outcome of elderly patients(stand point of three groups), considering neurologic grade on admission, amount of subarachnoid hemorrhage(SAH) on computerized tomography(CT) findings and timing of surgery.
The subjects of the present study are 34 patients who were admitted to department of neurosurgery and treated surgically between 1991 and 1997 in Mok-Dong and Tongdaemun hospital. All the patients in this study were verified as having aneurysmal SAH on CT scanning followed b cerebral argiography. The patients were classified by age into three groups : 65 to 70 years(24 cases), 76 years(7 cases) and 76 years or older(3 cases). On admission, the clinical condition of patients was graded according to the scals of Hunt and Hess and the amounts of SAH was graded according to grading system of Fisher. The day 7 SAH was defined as Day O. the timing of operation was divided into three. 1-3 days ; 3-7 days; 8-days.
The surgical mortality according to the different age groups, Hunt-hess grade, grading system of Fisher and timing of operation was analised.
Overall, 11 of the 34 patients died, for a mortality rate 32%. The mortality rate by age groups was 21% for 65 to 70 years, 57% for 71 to 75 years and 20% for 76 years of older. The mortality rate by Hunt-Hess grade was 35%, in I-II, 33% in III and 20% in IV-V, and the mortality rate as related to grading system of Fisher was 0% in 1, 36% in 2, 36% in 3 and 25% in IV. The mortality rate according to timing of operation was 31% in 1-3 days, 25% in 3-7 days and 25% in over days.
In recent years, with improvement in surgical technique and neuroanesthesia, the number of operation for ruptured aneurysm have increased in elderly patient. A more aggressive treatment in elderly patients is justified.

The aim of this study was to investigate whether or not endothelin-1 content of bronchoalveolar lavage was elevated in allografted lungs during acute rejection.
After single lung allotransplantation, dogs were immunosuppressed with triple standard therapy and divided into 2 groups. Group 1(Immunosupression ; n=4) was maintained on immunosuppression as controls. In group 2(Rejectin ; n=13), triple therapy was discontinued to induce acute rejection from postoperative day 5.
At postoperative day 9, broncholaveolar lavage was done through bronchoscopy in native unoperated lung and transplanted lung in group 1. Bronchoalveolar lavage was repeated in group 2 in the same way. Endothelin-1 content of bronchoalveolar lavage was measured by radiommunoassay.
Endothelin-1 content in transplanted lung of group 2 was compared to that of transplanted lung of group 1 and to that of native unoperated lung of group 2.
Endothelin-1 content of bronchoalveolar lavage in transplanted lung of group 2 was comparable to that of group 1(42.18±26.39 vs 3.08±3.08pg/ml ; p=0.08). Endothelin-1 content of bronchoalveolar lavage in transplanted lung of group 2 was comparable to that of native unoperated lung of group 2(42.18±26.39 vs 3.74±2.62pg/ml ; p=0.07).
Endothelin-1 content of bronchoalveolar lavage in transplanted lung was altered during acute rejection, but without statistical significance.

Experiment was designed to compare cellular profile of bronchoalveolar lavage following induced bacterial infection, acute rejection and acute rejection plus bacterial infection after lung allotranplantation.
After single lung allotransplantation, dogs were immunosuppressed with standard triple therapy and divided into 4 groups. Group I(n=4) was maintained on immunosuppression as controls. In group II(n= 6), infection was induced by bronchoscopic inoculation of
At postoperative day 9, bronchoalveolar lavage was obtained in the native and transplanted lung resprctively through bronchoscopy. Total cell count and differential cell count of bronchoalveolar lavage were compared in four groups.
In the native lung, there was no significant difffrence in total cell count and differential cell count in four groups. In the transplanted lung, total cell count of group II(Infection) was increased, compared to group III(Rejection) (p <0.05). In the transplanted lung, differential neutrophil count of group II(Infection) and group III(Rejection) were increased, compared to group I(Immunosuppression) (p <0.05). In the transplanted lung, differential macrophage count of group II(Infection), III(Rejection) and IV(Rejecion plus Infection) were decreased, compared to group I(Immunosuppuression) (p<0.05).
Cellular profile of bronchoalveolar lavage reflected the pathological process ofinfection or acute rejection following lung allotransplantation in the transplanted lung. But conventional total and differential cell counts had limitation to differentiate either process.
 , Na-Young Lee
, Na-Young Lee , Hyo-Jin Lee
, Hyo-Jin Lee , Sun-Young Lee
, Sun-Young Lee , Jin-Hyuk Choi
, Jin-Hyuk Choi , Soon-Nam Lee
, Soon-Nam Lee , Kang Sup Shim
, Kang Sup Shim , Sun-Hee Sung
, Sun-Hee Sung , Woon-Sup Han
, Woon-Sup Han
Multiple primary cancer means that more that two cancers occur independently in an individual. Recently, the incidence of multiple primary cancer has increased with lengthened survival, of cancer patients, development of new diagnostic technique and increased clinical evaluation. We report a patient who had adenocarcinoma of stomach combined with squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus simultaneously.

To compare fast spin echo(FSE) T2WI of the body coil(BC) with FSE T2WI of the endorectal surface coil(ERC) in the evaluation of parametrial and vaginal invasion and to evaluate tue dynamic enhanced images on the aspect of parametrial invasion.
Twenty consecutive patients of uterine cervical carcinomas confirmed by biopsy were included in this study and staging was determined by the surgery (2 cases) and the radiologic and clinical studies(18 cases). 1.5T Signa(GE,USA) was used and FSE T2-weighted axial and sagittal images were obtained by the body coil and endorectal surface coil respectively. Then dynamic enhanced axial images with FMPSPGR were performed at 2-3 slices of cervical cancer level. Parametrial and vaginal invasion on the body coil images were compared with those on the endorectal coil images retrospectively. Parametrial enhancement was evaluated on the dynamic enhanced images.
The accuracy of parametrial invasion was 100% of BC and 60% of ERC in 5 cases below stage Ib, 64% of BC and 73% of ERG in 11 cases of stage IIb and IIIa, 100% of BC and ERC in 4 cases above stage IVa. Overall accuracy of parametrial invasion was 80% of Bc and 75% of ERC without significant difference between two images. The accuracy of vagianl invasion was 80% of BC and 100% of ERC below stage Ib, 100% of BC and ERC above stage IIb. Overall accuracy of vaginal invasion was 95% of BC and 100% of ERC without difference between two images. On the dynamic enhanced images, parametrial enhancement was seen in all 20 cases and vascular enhancement in the parametrium was noted in 9 pf 20(45%) cases regardless of parametrial invasion.
There was no difference between BC and ERC images to evaluate the accuracy of parametrial and vaginal invasion. Therefore, ERC should be used in the cases which revealed suspicious invasion on BC images. Dynamic-enhanced images were not useful in the evaluation of parametrial invasion.
 , Dong Been Park
, Dong Been Park

Recently Computers are more and more widely used in many aspects of medicine, including education, and using computers to assist in traditional learning has many advantages. This study was carried out to provide modeling of computer learning program in health statistics.
The author analysed the present program and then surveyed the student's need by self administrated questionnaires. By one student modeling, the computer learning program has been developed and then the program was remodeled into the whole(80-90) students program.
The students thought that the current health statistical experiment was useful but laborius. And they wanted to try to new program with computer statistical package. In the aspect of trial on new educational method, the model of computer learning program in Health Statistics has been developed.
The computer learning program will be implemented in this second semester(1996) but the teacher and the students will be devoted to the program. And then it will be succeeded.

Intraperitoneal hemorrhage during reproductive age usually result from ruture of ectopicpregnancy, corpus luteum, and endometrioma.
The symptom and sign of the corpus luteum hemorrhage is lower abdominal pain and tenderness so differential diagnosis with ectopic pregnancy is needed.
The sonographic findings of corpus luteum hemorrhage is free blood in cul de sac and adnexal mass. In the case of hemorrhagic corpus luteum of the considerable size with evidence ofintraperitoneal hemorrhage, operative intervention may be necessary. But operation is complicated and have some hazard.
So we reported these cases of hemorrhagic corpus luteum with intraperitoneal hemorrhagetreated by transvaginal sonogrphy successfuly.

This paper reports a study on 246 cases of upper gastrointestinal(UGT) hemorrhage thatwere treated in the Department of Internal Medicine of the Ewha Womans University(Mokdong Hospital) over a period of 18 months from September of 1993 to May of 1995.
The results were as follows.
1) The causes of UGI hemorrhage were 156 peptic ulcer cases(63.4%) including 71 gastriculcer,82 duodenal ucler, and 3 marginal ulcer ; 44 esophageal varix cases(17.9%) ; 18 MalloryWeiss syndrome cases(7.3%) : 15 stomach cancer cases(6,1%) ; 7 acute gastric mucosal lesioncases(2.8%) ; 2 unknown causes ; and 4 other causes.
2) There were 204 males and 42 females(4.8 : 1). The age distribution was 51 in fifties(20.7%),49 in forties(19.9%), 44 in thirties(17.9%), 40 in sixties(16.2%), 24 in twenties(9.5%), and 24 in seventies(9.8%) resulting in 58.5% of the total cases from the thirties to fifties. Agedistribution of duodenal ulcer and Mallory-Weiss tear was younger than stomach cancer andgastric ucler(P<0.05).
3) The seasonal distribution showed spring 78 cases(31.7%), summer aS cases(10.1%), autum67 cases(27.2%), and winter 74 cases(30.1%) with peak incidence in spring.
4) The severity of UGI hemorrhage according to Palumbo's criteria was mild bleeding in 71 cases(28.8%), moderate bleeding in 115 cases(46.7%), and massive bleeding in 60 cases(24.4%)
5) The mean amount of transfusion for treatment was 4.2±2.4 unit for peptic ulcer, 3.2±1.8unit for varix, 5.9±3.1 unit for stomach cancer, and 0.3±0.2 unit for Mallory-Weiss tear.
6) Ninety one peptic ulcer was received endoscopic treatment(58.4%). Among them, therewere 13 rebleeding cases(14.3%) and 9 cases required surgical opertaion(9.8%). Thirly fivevarix cases received endoscopic treatment(79.5%) and there were 3 rebleeding cases(8.6%).
7) The motality was 4.1%(10 cases). The main causes of deaths were 1 sepsis case, 3 hepaticcoma cases, and 6 hepatoma intraperitoneal rupture cases.
 , Jin Young Choi
, Jin Young Choi , Ho Jun Kang
, Ho Jun Kang , Ji Hee Sung
, Ji Hee Sung , Sang Jong Park
, Sang Jong Park , Sun Hong Yoo
, Sun Hong Yoo , Young Min Park
, Young Min Park
Vitamin A deficiency can occur as a result of malnutrition, malabsorption, or poor vitamin metabolism due to liver disease and night blindness might develop as the first symptom. Although there have been foreign reports about night blindness due to vitamin A deficiency which was derived from liver cirrhosis, primary biliary cirrhosis, intestinal bypass surgery or bariatric operation, it is hard to find reports about night blindness after percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage for external bile drainage. We report a case of night blindness derived from fat-soluble vitamin A deficiency developed after long-term (18 months) external bile drainage for benign biliary stricture occurred after left hepatic lobectomy and hepaticojejunostomy due to the Klatskin tumor (IIIb). Her night blindness and low serum retinol level (0.02 mg/L) was dramatically improved after vitamin A supplementation. We recommend lipid-soluble vitamin supplementation on the case of long-term external bile drainage.

Organ transplantation has become the standard of care for treatment of end stage organ failure patients medically suitable for transplantation. Unfortunately, the availability of transplantable organs has not been able to meet the high demand. The organ shortage of transplantation has become worldwide and a national crisis. Despite various attempts to expand the donor pool, the difference between organ supply and organ demand continues. This article reviews methods to increase the number of potential deceased organ donor and the number of organs per donor by aggressive donor management protocol.
Citations

 , Woosung Lim
, Woosung Lim
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in Korean women and its mortality rate has increased steadily. Although breast cancer is heterogeneous tumor, hormone receptor-positive tumors comprise about 75 percent of all breast cancers. Therefore endocrine therapy that works by targeting estrogen receptor is a pivotal treatment for breast cancers. There are selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as tamoxifen and raloxifene, aromatase inhibitors, such as anastrozole, letrozole and exemestane, fulvestrant and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists used in endocrine therapy. Endocrine therapy is effective in treating early breast cancer as an adjuvant therapy and metastatic breast cancer as a palliative therapy. Also in women who are at high risk for breast cancer, tamoxifen or raloxifene can prevent breast cancer. Studies for neoadjuvant endocrine therapy are emerging. Considering side effects of each drug and overcoming drug resistance are needed to maximize effectiveness of treatment and advance endocrine therapy.
Citations


Moyamoya disease is a cerebrovascular disease of unknown etiology, which is characterized by bilateral stenosis or occlusion at terminal portion of internal carotid artery and at proximal portion of anterior cerebral artery and/or middle cerebral artery and abnormal vascular network in the vicinity of the arterial occlusions. It occurs frequently in Asian countries, particularly in Korea and Japan, but is rare in Western countries. To establish the etiology of moyamoya disease, much about the pathology from autopsies, factors involved in its pathogenesis, and its genetics have been studied. It may occur at any age from childhood to adulthood and in general, initial manifestation is cerebral ischemic symptoms in children and intracranial hemorrhage symptoms in adults. Because it progress and cause recurrent stroke, early diagnosis and proper management has been recognized. Cerebral angiography is essential for definitive diagnosis and treatment plan. Magnetic resonance imaging/magnetic resonance angiography is useful for diagnosis and follow-up tools after revascularization. Evaluation of the cerebral hemodynamics by single photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography is useful for diagnosis and assessment of the severity of cerebral ischemia in moyamoya patients. Surgical revascularization is effective for moyamoya disease manifesting as ischemic symptoms, to prevent further ischemia and infarction. In hemorrhagic type moyamoya disease, revascularization can be considered. Direct bypass, indirect synangiosis and combined methods are used. Outcomes of revascularization are excellent in preventing transient ischemic attacks in most patients.
Citations

 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Min-Sun Cho
, Min-Sun Cho , Min-Jin Lee
, Min-Jin Lee , Myung-Eun Song
, Myung-Eun Song , Da-Yeon Oh
, Da-Yeon Oh , Ha Eung Song
, Ha Eung Song
Sunitinib an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, is highly effective against renal cell carcinoma and is now widely used in patients with metastatic disease. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is rarely reported as a side effect of sunitinib. We report two cases of GERD with upper gastrointestinal bleeding related to sunitinib administration. Both cases responded well to conservative management. Microscopic findings in both cases showed cellular atypia such as hyperchromasia, increases in nuclear size, and multinucleation. The cellular atypia of the squamous mucosa appears to be associated with reparative processes.
Citations

 , Yong-Hyun Kim
, Yong-Hyun Kim , Jong Soo Lee
, Jong Soo Lee , Young Jae Hwang
, Young Jae Hwang , Jae Min Lee
, Jae Min Lee , Keunhee Kang
, Keunhee Kang , Woo-Hyuk Song
, Woo-Hyuk Song , Jeong-Cheon Ahn
, Jeong-Cheon Ahn
A 30-year-old man visited the emergency room for chest pain, dyspnea and fever. Despite increased serum cardiac enzymes, ST segment elevation and inferior wall akinesis in electrocardiography and echocardiography, no atherosclerosis was evident in the coronary angiography. However, radionuclide myocardial perfusion image at day 2 showed a persistent perfusion defect in the left ventricular (LV) inferior wall. At day 3, prominent myocardial edema and severe LV systolic dysfunction developed with signs of heart failure. In this case, fulminant myocarditis seemed to originate from the right coronary artery territory and simulated a ST segment elevation myocardial infarction without coronary artery obstruction. The pathogenesis of the localized perfusion defect was unlcear.
 , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Sun-Kyung Na
, Sun-Kyung Na , Do-Kyeong Song
, Do-Kyeong Song , Jung-Wha Chung
, Jung-Wha Chung , Ka-Young Jung
, Ka-Young Jung
Double primary cancers are two independently developed cancers in an individual. There have been some reports on double primary cancer since Billroth reported it for the first time in 1879. Double primary cancer of the stomach and esophagus has been revealed a very low incidence worldwide. The incidence of an esophageal cancer with another primary cancer is reported to be 9.5~27%, but double primary cancers in the esophagus and stomach have been rarely reported to our knowledge. In this study, we present here a case of double primary esophageal and stomach cancer in a 66-year-old man because of progressive dysphagia.
 , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Hyoung Won Cho
, Hyoung Won Cho , Ju Young Choi
, Ju Young Choi , Shin A Lee
, Shin A Lee , Min Jin Lee
, Min Jin Lee , Da Yeon Oh
, Da Yeon Oh , Sun Hee Roh
, Sun Hee Roh , Chung Hyun Tae
, Chung Hyun Tae , Seong-Eun Kim
, Seong-Eun Kim , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Tae Hun Kim
, Tae Hun Kim , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo , Il Hwan Moon
, Il Hwan Moon
Ingestion of corrosive substances can produce severe injury to the gastrointestinal tract and can even result in death in the acute phase. The extent and degree of damage depends on the type and amount of substances. There are occasional reports of severe contiguous injury to the esophagus and stomach caused by strong alkali ingestion in the acute phase. Usually the deaths occur within a couple of days due to multi-organ failure after ingestion of relatively much amount of agent for a suicidal attempt. But death due to late progression is very rare.
We have reported a case of 60-year-old female patient who was diagnosed as corrosive esophagitis after accidental ingestion of strong alkali. Initial endoscopic findings were compatible with IIa-IIa-0(according to Zargar's classification) in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, respectively. After several weeks of supportive care, her subjective symptoms were much improved during she had been wating for the operation of colon interposition due to esophageal stricture. Metabolic acidosis and thrombocytopenia developed abruptly probably due to upper gastrointestinal tract necrosis and she died when 60 days had passed after the occurrence of initial esophageal injury.
Citations

 , Eun Mi Song
, Eun Mi Song , Doo Hyun Beak
, Doo Hyun Beak , Hyun Jung Oh
, Hyun Jung Oh , Hyun Kyung Kim
, Hyun Kyung Kim , Min Young Choi
, Min Young Choi , Kyung Joo Kwon
, Kyung Joo Kwon , Hye Won Kang
, Hye Won Kang , Seo Woo Kim
, Seo Woo Kim , Unjin Shim
, Unjin Shim , Yeon Ah Sung
, Yeon Ah Sung , Young Sun Hong
, Young Sun Hong
Propylthiouracil(PTU) is a commonly used antithyroid drug in the management of hyperthyroidism. However, it is associated with a variety of side effects. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody( ANCA)-positive vasculitis is an extremely rare side effect of PTU. We report a case of a patient with diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage while being treated with PTU. A 28-year-old woman was admitted due to fever and abdominal pain. She was diagnosed as Graves' disease 4 years before the admission, and was taking PTU intermittently. Thyroid storm was suspected and we treated her with PTU, hydrocortisone, lugol solution and propranolol. However, coughing was aggravated, with chest X-ray and computed tomography revealing diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Perinuclear-ANCA was positive. After discontinuation of PTU, all symptoms resolved. In conclusion, ANCA-positive diffuse alveolar hemorrhage is a rare but a potential side-effect of PTU. Therefore, early awareness of this complication is important.

 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Joo Hee Hong
, Joo Hee Hong , Hye Sook Park
, Hye Sook Park
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease(GERD) is increasing in Asian countries, but the majority of patients does not present with endoscopic abnormalities, the assessment of the symptom severity and quality of life, and their response to treatment, have become increasingly important. Our objectives were to develop and evaluate a questionnaire about Health-related quality of lif (HRQOL) related with gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with GERD.
Eighty eight, consecutive patients with GERD and 174 healthy subjects were enrolled in the study. GERD was defined by the presence of reflux symptom that are heartburn and acid reflux with occurring more than once per week with/without endoscopic reflux esophagitis. All subjects were examined with endoscopy and performed self-reported questionnaires that were modified Korean form of gastrointestinal symptom rating scale(KGSRS), newly developed instrument, and KSF-36(Korean version of Medical Outcomes Study Short Form), a conventional one. We compared the score of KGSRS between response group and non-response group after 2-weeks omeprazole trial for evaluation of discriminative validity of KGSRS.
Internal consistency for the KGSRS scales range from 0.58-0.84. The repeatability was confirmed by test-retest results(Pearson's correlation coefficients=0.62-0.80, p<0.01). The KGSRS scale scores were significantly correlated with those of KSF-36. It revealed construct validity. The total score of KGSRS in patients with GERD was significantly lower than control(376.1±51.3 vs. 433.5±42.0, p=0.000). There were significant differences for 4 symptom complex except diarrhea between response group and non-response group.
The KGSRS has good reliability and construct validity and discriminates symptom severity and frequency of patients with GERD.
Citations


